Flagellar motors are locomotive organelles located in bacterial cell envelopes and push the cell in its environment. These motors are composed of a variety of proteins and consist of a rotary motor, a universal joint, and a helical filament [2]. They are driven by the flow of ions down their concentration gradient with respect to the cytoplasmic membrane through a stator, and are regulated by the chemotaxis pathway. The stator complex serves as a channel to couple the proton flow with a torque generation that occurs at the interface between the stator(s) and a rotor. The torque generation and stator assembly around the rotor require highly conserved charged residues to be present [1,3].
Function
Bacterial flagellar motors power bacterial locomotion driven by the rotation of one or more long flagellar filaments. In turn, these serve to propel the cell in liquid environments whenever it wants to move towards more favorable conditions, where there may be food and light, and escape from undesirable ones for their survival by sensing temporal changes in the environment, such as fluctuations in temperature and pH, or the presence of chemical attractants and repellents. Bacterial flagellar motors are also in charge of driving fundamental processes involving pathogenesis and biofilm formation [1-3].
Structure
More than 40 genes are involved in flagellar motor assembly and function, but the final structure consists of about 13 different proteins of numerous copies [1].
Flagellar motors are composed of a long helical semi-rigid filament linked to the motor by the hook. The filament works as a helical screw and propels the bacterial cell through its environment.
The basal body makes up the core of the motor. It is composed of a set of rings spanning the cell envelope and acts as a reversible rotary motor. The rings that make up the core structure include the L-, P-, MS-, and C-rings. . The L-ring is located in the outer lipopolysaccharide layer and is made of the protein FlgH. The P-ring, on the other hand, is placed in the outer peptidoglycan layer and is composed of FlgI. These two rings act as a bushing for the rod of the motor, which connects the hook to the MS-ring. The MS-ring is situated within the inner membrane at the lower end of the rod and is formed by many copies of FliF [1]. It acts as the assembly platform, and its rotation, along with that of the C-ring is thought to be transmitted to the universal propeller by the rod. The C-ring is named because it is located on the cytoplasmic face of the MS-ring and extends about 15 nm into the cytoplasm. It is composed of FliG, FliM, and FliN and is referred to as the switch complex as the rotary motor undergoes a reversal of its rotational direction. FliG is of central importance because it is directly involved in the torque generation and switch mechanism [1]. However, mutations in all three proteins affect the switching between the clockwise and counter-clockwise rotations, which means that they are all responsible for the switching mechanism to occur [2].
The flagellar motor consists of one or more stators. The two protein subunits that make up the stator, MotA and MotB, form two ion-conducting channels to couple the proton flow with the torque generation in order to get a locomotive flagellar motor. Thus, a deletion of any of the genes encoding these proteins would result in a non-motile, but normally assembled, mutant rotary motor [1]. In addition, a highly conserved Asp32 residue is located in the MotB subunit and is important for the proton translocation through the channel [2].
The transport apparatus is located in the central pore of the motor and is in charge of translocating the rod, hook, and filament components through the central channel to the farthest end of the flagellum.
Energetics
Whereas most biological motors use ATP as their energy source, the bacterial cell motor is one of the only two known protein motors that are driven by the transmembrane flow of ions. The stator unit’s two integral membrane proteins, MotA and MotB, form ion-conducting channels that determine the ion specificity [1,3]. There are two types of flagellar motors: H+-driven (e.g. E. coli), and Na+-driven (e.g. marine Vibrio) [2]. The ion-motive force (IMF) that drives the unfolding and translocation of the protein exported from the bacterial flagellar motor is maintained by metabolic mechanisms that use chemical energy to pump the ions out of the cell, which permits them to flow back in again and power systems such as this one [1].
It is assumed that each revolution takes 26 elementary steps, which according to some models would require the passing of at least 52 protons for a complete revolution [3].
Although the physics involved in the energy conversion remains poorly understood, there are indications that suggest that the MotB subunits form channels where the ions flow to associate and dissociate at the conserved aspartate residue to then trigger the conformational change of the stator complex, thereby generating the torque [1-3]. In addition to providing energy to generate the torque, the IMF serves to recruit the stators. They leave the motors when the IMF is disrupted but return after its restoration [1].
Structural highlights
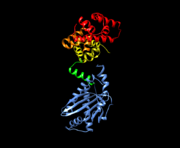
This is an image of the components of FliG and FliM (PDB files 3AJC and 3SOH, respectively)
This is a sample scene created with SAT to by Group, and another to make of the protein. You can make your own scenes on SAT starting from scratch or loading and editing one of these sample scenes.

