User:Elisha Lacey/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
<scene name='71/719804/Brdt_bromo_domains/1'>BRDT dimers</scene> | <scene name='71/719804/Brdt_bromo_domains/1'>BRDT dimers</scene> | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| - | Bromodomain testis specific is a monomer that is only fully functional as a dimer. BRDT is a transcriptional regulator for gene expression during spermatogenesis. BRDT is important to healthy progeny, without it sperm is unable to correctly compact genome. BRDT gives rise to the shape of sperm cells, without it the sperm cells are misshapen. | + | Bromodomain testis specific is a monomer that is only fully functional as a dimer. BRDT is a transcriptional regulator,located in the nucleus, for gene expression during spermatogenesis. BRDT is important to healthy progeny, without it sperm is unable to correctly compact genome. BRDT gives rise to the shape of sperm cells, without it the sperm cells are misshapen. |
== BRDT and fertility == | == BRDT and fertility == | ||
Loss of one of the bromodomains or even single point mutations leads to decrease spermatogenesis and defective sperm. If both bromodomains are knocked out it leads to loss of fertility. | Loss of one of the bromodomains or even single point mutations leads to decrease spermatogenesis and defective sperm. If both bromodomains are knocked out it leads to loss of fertility. | ||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
[[Image:JQ1 strucutre.jpg]] | [[Image:JQ1 strucutre.jpg]] | ||
==Analysis of Structure == | ==Analysis of Structure == | ||
| - | The functional unit for BRDT is two bromodomain motifs, each monomer is composed of 4 anti-parallel alpha helixes. At the end of the helix bundles is the acetylated-lysine binding site binding site. BRDT belongs to the histone acetyltransferase superfamily. BRDT is tissue restricted to the testis. BRDT activates the histones by hyper acetylation at the promoter of genes leading to condensed acetylated chromatin of a haploid spermatid. Running an alignment gives 200 sequence similarities which shows that this sequence is highly conserved among organism in the phylogenic tree. | + | The functional unit for BRDT is two bromodomain motifs, each monomer is composed of 4 anti-parallel alpha helixes. The 2 monomers are not unique to one another. At the end of the helix bundles is the acetylated-lysine binding site binding site. BRDT belongs to the histone acetyltransferase superfamily. BRDT is tissue restricted to the testis. BRDT activates the histones by hyper acetylation at the promoter of genes leading to condensed acetylated chromatin of a haploid spermatid. Running an alignment gives 200 sequence similarities which shows that this sequence is highly conserved among organism in the phylogenic tree. This was also seen when running multiple alignments and the sequence was similar among several different organisms. |
==Analysis of related Sequences== | ==Analysis of related Sequences== | ||
| - | Bromodomain testis specific in humans shares 97% sequence identity with bromodomain testis specific in Sumatran Orangutans. These genes are close orthologs with such similar sequence identity and they both serve a function in fertility. | + | Bromodomain testis specific in humans shares 97% sequence identity with bromodomain testis specific in Sumatran Orangutans. It also shows 99% sequence similarity. These genes are close orthologs with such similar sequence identity and they both serve a function in fertility. The most distant sequence alignment is a black flying fox with and identity of 89% and still is an ortholog to BRDT in humans. |
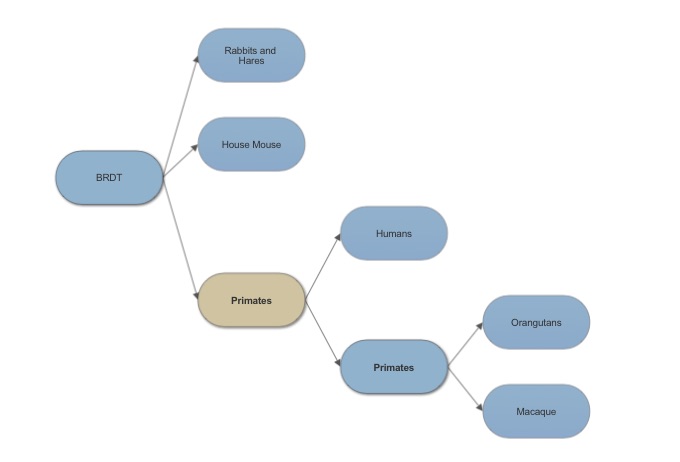
==Evolution of BRDT== | ==Evolution of BRDT== | ||
[[Image:BRDT tree.jpg]] | [[Image:BRDT tree.jpg]] | ||
Revision as of 11:35, 10 December 2015
Bromodomain testis specific
| |||||||||||
References
Berkovits B, Wolgemuth D. The first bromodomain of the testis-specific double bromodomain protein Brdt is required for chromocenter organization that is modulated by genetic background. PMC. 2011 Dec 15: 360 (2):358-368.
Barda S, Yogev L, Paz G, et al. BRDT gene sequence in human testicular pathologies and the implication of its single nucleotide polymorphism (rs3088232) on fertility. Andrology. 2014 May 28; 2(4): 641-647.
Zdrojewicz Z, Konieczyn R, Papier P, Szten F.Brdt Bromodomains Inhibitors and Other Modern Means of Male Contraception. ACEM. 2015 Feb 23; 24(4):705-714.