This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
End-binding protein
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
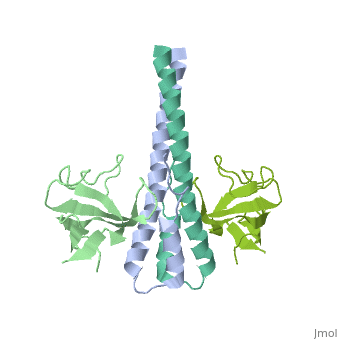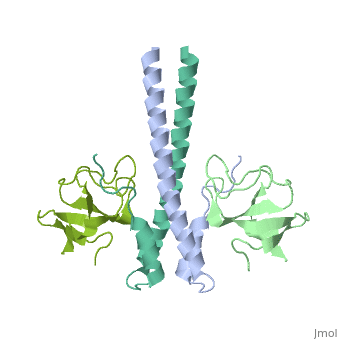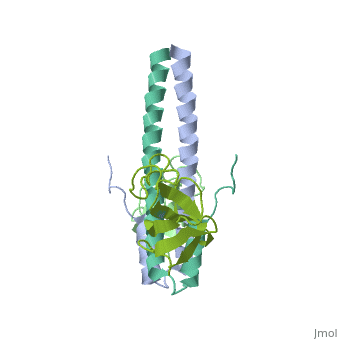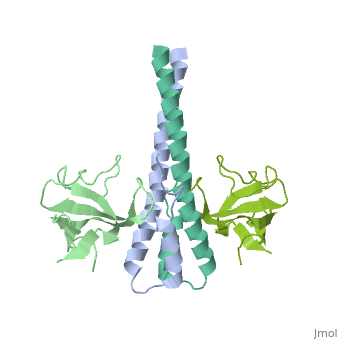
<StructureSection load='2hkq' size='340' side='right' caption='Human end-binding protein 1 C terminal (grey) complex with dynactin-1 CAP-GLY domain (green) (PDB code [[2hkq]])' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='2hkq' size='340' side='right' caption='Human end-binding protein 1 C terminal (grey) complex with dynactin-1 CAP-GLY domain (green) (PDB code [[2hkq]])' scene=''> | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
'''End-binding protein''' (EB) regulates microtubules dynamics, promotes colony formation and enhances tumor growth. EB is part of the proteins which accumulate at the growing microtubule plus end. During mitosis the EB associates with centrosome and spindle microtubules. EB is involved in the regulation of chromosome stability and microtubule structure. The C terminal domains of EB1 and EB3 are involved in dimer formation. The CH (Calponin Homology) domain is an actin-binding domain. | '''End-binding protein''' (EB) regulates microtubules dynamics, promotes colony formation and enhances tumor growth. EB is part of the proteins which accumulate at the growing microtubule plus end. During mitosis the EB associates with centrosome and spindle microtubules. EB is involved in the regulation of chromosome stability and microtubule structure. The C terminal domains of EB1 and EB3 are involved in dimer formation. The CH (Calponin Homology) domain is an actin-binding domain. | ||
Revision as of 13:45, 10 January 2016
| |||||||||||
3D Structures of end-binding protein
Updated on 10-January-2016