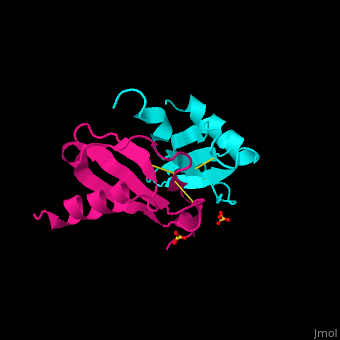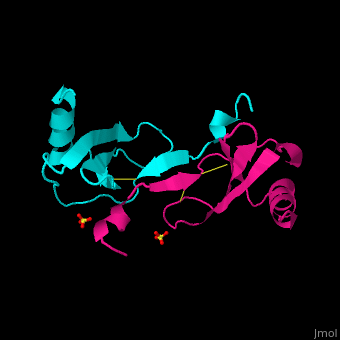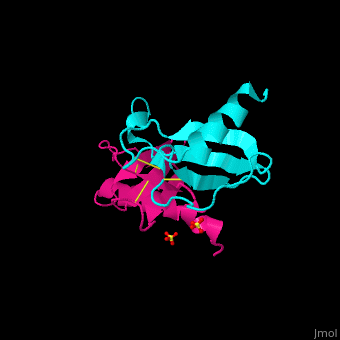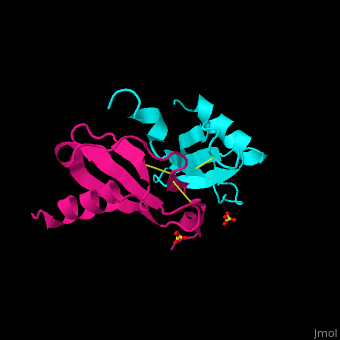Monocyte chemoattractant protein
From Proteopedia
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
Post translational modifications at the N-terminus can regulate receptor and target cell selectivity. Deletion of the N-terminal residue converts it from an activator of basophil to an eosinophil chemoattractant. | Post translational modifications at the N-terminus can regulate receptor and target cell selectivity. Deletion of the N-terminal residue converts it from an activator of basophil to an eosinophil chemoattractant. | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Synthesis == | ||
| + | |||
| + | The protein human CC chemokine ligand 2 (CCL2, also known as monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 or MCP-1) has been synthesized using a combination of solid phase peptide synthesis (SPPS) and native chemical ligation (NCL). The thioester-peptide segment was synthesized using the sulfonamide safety-catch linker and 9-fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl (Fmoc) SPPS, and pseudoproline dipeptides were used to facilitate the synthesis of both CCL2 fragments. After assembly of the full-length peptide chain by NCL, a glutathione redox buffer was used to fold and oxidize the CCL2 protein. Synthetic human CCL2 binds to and activates the CCR2 receptor on THP-1 cells, as expected. CCL2 was crystallized and the structure was determined by X-ray diffraction at 1.9-A resolution. The structure of the synthetic protein is very similar to that of a previously reported structure of recombinant human CCL2, although the crystal form is different. The functional CCL2 dimer for the crystal structure reported here is formed around a crystallographic twofold axis. The dimer interface involves residues Val9-Thr10-Cys11, which form an intersubunit antiparallel beta-sheet. Comparison of the CCL2 dimers in different crystal forms indicates a significant flexibility of the quaternary structure. To our knowledge, this is one of the first crystal structures of a protein prepared using the sulfonamide safety-catch linker and NCL. | ||
==3D structures of Monocyte chemoattractant protein== | ==3D structures of Monocyte chemoattractant protein== | ||
Revision as of 13:13, 26 January 2016
| |||||||||||
Synthesis
The protein human CC chemokine ligand 2 (CCL2, also known as monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 or MCP-1) has been synthesized using a combination of solid phase peptide synthesis (SPPS) and native chemical ligation (NCL). The thioester-peptide segment was synthesized using the sulfonamide safety-catch linker and 9-fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl (Fmoc) SPPS, and pseudoproline dipeptides were used to facilitate the synthesis of both CCL2 fragments. After assembly of the full-length peptide chain by NCL, a glutathione redox buffer was used to fold and oxidize the CCL2 protein. Synthetic human CCL2 binds to and activates the CCR2 receptor on THP-1 cells, as expected. CCL2 was crystallized and the structure was determined by X-ray diffraction at 1.9-A resolution. The structure of the synthetic protein is very similar to that of a previously reported structure of recombinant human CCL2, although the crystal form is different. The functional CCL2 dimer for the crystal structure reported here is formed around a crystallographic twofold axis. The dimer interface involves residues Val9-Thr10-Cys11, which form an intersubunit antiparallel beta-sheet. Comparison of the CCL2 dimers in different crystal forms indicates a significant flexibility of the quaternary structure. To our knowledge, this is one of the first crystal structures of a protein prepared using the sulfonamide safety-catch linker and NCL.
3D structures of Monocyte chemoattractant protein
Updated on 26-January-2016
References
https://fr.wikipedia.org/wiki/CCL2 http://www.ebi.ac.uk/thornton-srv/databases/cgi-bin/pdbsum/GetPage.pl?pdbcode=1DOK http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P13500#interaction http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore/explore.do?structureId=3IFD
- ↑ Carr MW, Roth SJ, Luther E, Rose SS, Springer TA. Monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 acts as a T-lymphocyte chemoattractant. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 26;91(9):3652-6. PMID:8170963
- ↑ Lubkowski J, Bujacz G, Boque L, Domaille PJ, Handel TM, Wlodawer A. The structure of MCP-1 in two crystal forms provides a rare example of variable quaternary interactions. Nat Struct Biol. 1997 Jan;4(1):64-9. PMID:8989326
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Coline Perrin, Alexane Caignard, Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, Joel L. Sussman