We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1122
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
==HUMAN BCL-2, ISOFORM1== | ==HUMAN BCL-2, ISOFORM1== | ||
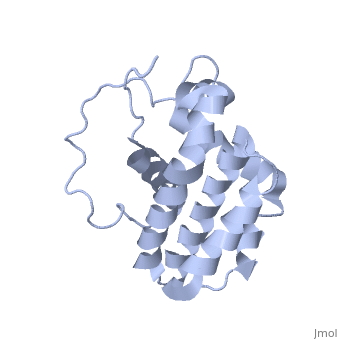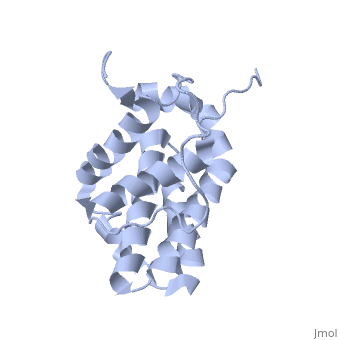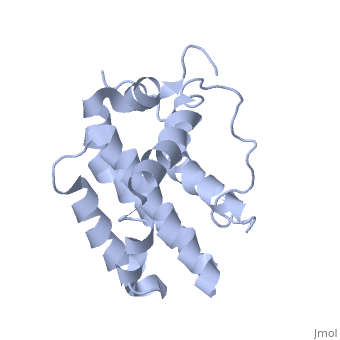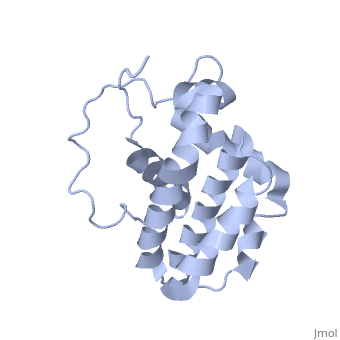
<StructureSection load='1g5m' size='400' side='right' caption='3D STRUCTURE OF HUMAN BCL-2, ISOFORM1 (from residue 3 to 207) BASED ON NMR SPECTROSCOPY' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='1g5m' size='400' side='right' caption='3D STRUCTURE OF HUMAN BCL-2, ISOFORM1 (from residue 3 to 207) BASED ON NMR SPECTROSCOPY' scene=''> | ||
| - | Human | + | Human Bcl-2 (B-Cell Lymphoma 2), isoform 1 is an oncoprotein of 239 residues regulating cell death (apoptosis), notably acting as an anti-apoptotic. It is encoded by the ''BCL-2'' gene located on the 18th chromosome (63.12-63.32 Mb). There are 2 isoforms of this protein (𝛼 and 𝛽), produced by alternative splicing, and which differ by 2 aminoacids (residues 96 (A→T) and 110 (R→G))<ref>[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC30598/ Solution structure of the antiapoptotic protein bcl-2]</ref>. Alteration of this protein is a caused of many cancers, and is also likely to be involved in schyzophrenia and autoimmunity. |
== Structure == | == Structure == | ||
| - | Human | + | Human Bcl-2, isoform 1 is a 26kDa protein of 239 residues which is negatively charged at pH 7. The linear structure highlights 5 domains: <scene name='71/719863/Scenelucas/1'>BH4</scene> (10-30), |
<scene name='71/719863/Scenebh3/2'>BH3</scene> (93-107), <scene name='71/719863/Scenebh1/1'>BH1</scene> (136-155), <scene name='71/719863/Scenebh2/1'>BH2</scene> (187-202) and a | <scene name='71/719863/Scenebh3/2'>BH3</scene> (93-107), <scene name='71/719863/Scenebh1/1'>BH1</scene> (136-155), <scene name='71/719863/Scenebh2/1'>BH2</scene> (187-202) and a | ||
| - | transmembrane domain (212-233) (due to its poor behavior in solution, it has been replaced by a segment of Bcl-xl in the presented 3D structure). It organizes as eight alpha-helices: from 11 to 25 (1) , from 93 to 107 (2), from 109 to 118 (3), from 126 to 137 (4), from 144-163 (5), from 169 to 184 (6), from 186 to 191 (7) and from 194 to 202(8). Helices 5 and 6 are mostly hydrophobic and they are surrounded by four other helices characterized by their amphipathic properties. There are also 3 turns (32-34, 123-125, 138-140). The <scene name='71/719863/Bcl2helix/1'>3rd alpha-helix</scene> is a 3(10) helix, whereas | + | transmembrane domain (212-233) (due to its poor behavior in solution, it has been replaced by a segment of Bcl-xl in the presented 3D structure). It organizes as eight alpha-helices: from 11 to 25 (1) , from 93 to 107 (2), from 109 to 118 (3), from 126 to 137 (4), from 144-163 (5), from 169 to 184 (6), from 186 to 191 (7) and from 194 to 202(8). Helices 5 and 6 are mostly hydrophobic and they are surrounded by four other helices characterized by their amphipathic properties. There are also 3 turns (32-34, 123-125, 138-140). The <scene name='71/719863/Bcl2helix/1'>3rd alpha-helix</scene> is a 3(10) helix, whereas Bcl-Xl 3rd helix is a normal alpha-helix. |
The transmembrane domain of Bcl-2 is made of 21 aminoacids and is located at the carboxy-terminal tail of the protein. It allows the docking of Bcl-2 in the mitochondrial outer membrane where the protein interacts with other effectors.<ref>[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24905660 Peptides derived from the transmembrane domain of Bcl-2 proteins as potential mitochondrial priming tools.]</ref> | The transmembrane domain of Bcl-2 is made of 21 aminoacids and is located at the carboxy-terminal tail of the protein. It allows the docking of Bcl-2 in the mitochondrial outer membrane where the protein interacts with other effectors.<ref>[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24905660 Peptides derived from the transmembrane domain of Bcl-2 proteins as potential mitochondrial priming tools.]</ref> | ||
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
=== Cancer === | === Cancer === | ||
| - | + | Bcl-2 is involved in many cancers such as breast, melanoma, prostate, chronic lymphocytic leukemia and lung cancers. In fact, its overexpression combined with an overexpression of c-Myc (another oncoprotein) produce aggressive B-lymphocytes. <ref>[http://www.bloodjournal.org/content/125/4/658 BCL2 mutations are associated with increased risk of transformation and shortened survival in follicular lymphoma]</ref>. It has also be shown that Bcl-2 overpexpression supresses DNA repair by enhancing Myc transcriptional activity. | |
| - | <ref>[http://www.jbc.org/content/281/20/14446.full | + | <ref>[http://www.jbc.org/content/281/20/14446.full Bcl-2 Suppresses DNA Repair by Enhancing c-Myc Transcriptional Activity]</ref> In fact, Bcl-2 is encoded by the ''BCL-2'' gene (0,20 Mb) located on the 18th chromosome. Nevertheless, translocation between chromosome 14 and 18 juxtaposes the ''BCL-2'' gene and the immunoglobulin locus. This brings the ''BCL-2'' gene under the regulation of the immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer, diregulating ''BCL-2'' expression level (involved in non-Hodgkin's lymphomas). <ref>[http://www.nature.com/onc/journal/v27/n50/full/onc2008307a.html Bcl-2 family proteins and cancer]</ref> |
| - | Other mechanisms appear to regulate and enhance the level of expression of BCL-2 : loss of endogenous microRNAs which normally repress | + | Other mechanisms appear to regulate and enhance the level of expression of BCL-2 : loss of endogenous microRNAs which normally repress Bcl-2 expression, and also hypomethylation.<ref>[http://www.nature.com/onc/journal/v27/n50/full/onc2008307a.html Bcl-2 family proteins and cancer]</ref> |
| - | + | Bcl-2 <scene name='71/719863/Scenelucas/1'>BH4</scene> domain mediates the interaction with MBII domain of Myc. This interaction enhance c-Myc half-life, resulting in an enhancing of its total activity. c-Myc is a well known oncoprotein (transcription factor) involved in many cancers as it regulates a lot of genes of the cell cycle. | |
Revision as of 17:31, 28 January 2016
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 15/12/2015, through 15/06/2016 for use in the course "Structural Biology" taught by Bruno Kieffer at the University of Strasbourg, ESBS. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1120 through Sandbox Reserved 1159. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
HUMAN BCL-2, ISOFORM1
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Solution structure of the antiapoptotic protein bcl-2
- ↑ Peptides derived from the transmembrane domain of Bcl-2 proteins as potential mitochondrial priming tools.
- ↑ Solution structure of the antiapoptotic protein bcl-2
- ↑ Alpha-Helical Destabilization of the Bcl-2-BH4-Domain Peptide Abolishes Its Ability to Inhibit the IP3 Receptor
- ↑ BH1 and BH2 domains of Bcl-2 are required for inhibition of apoptosis and heterodimerization with Bax
- ↑ Control of mitochondrial apoptosis by the Bcl-2 family
- ↑ Differential Targeting of Prosurvival Bcl-2 Proteins by Their BH3-Only Ligands Allows Complementary Apoptotic Function
- ↑ Distinct BH3 domains either sensitize or activate mitochondrial apoptosis, serving as prototype cancer therapeutics
- ↑ The Release of Cytochrome c from Mitochondria: A Primary Site for Bcl-2 Regulation of Apoptosis
- ↑ Prevention of Apoptosis by Bcl-2: Release of Cytochrome c from Mitochondria Blocked
- ↑ Bcl-2 and Bcl-XL Regulate Proinflammatory Caspase-1 Activation by Interaction with NALP1
- ↑ BCL2 mutations are associated with increased risk of transformation and shortened survival in follicular lymphoma
- ↑ Bcl-2 Suppresses DNA Repair by Enhancing c-Myc Transcriptional Activity
- ↑ Bcl-2 family proteins and cancer
- ↑ Bcl-2 family proteins and cancer