Calcium uptake protein 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
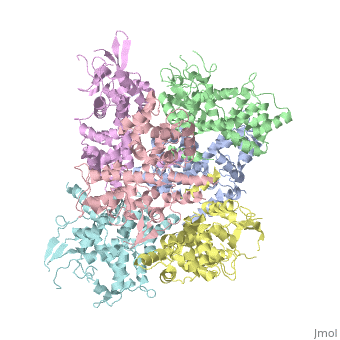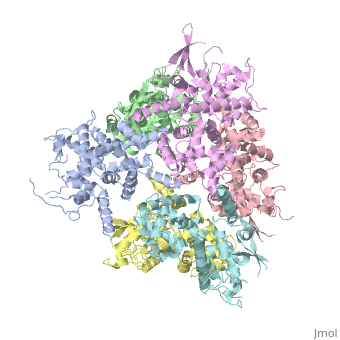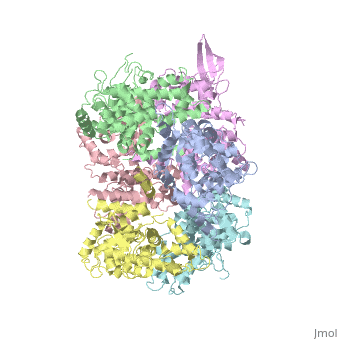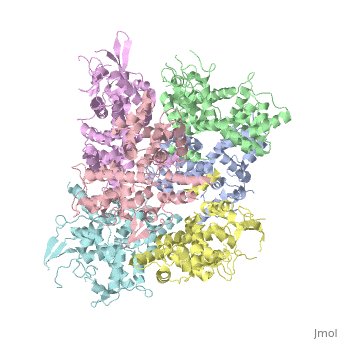
In absence of Ca2+, MICU1 is an homohexamer with a <scene name='72/723172/Secondary_structure_of_micu_1/1'>secondary structure</scene> composed by several alpha helix, beta sheets and loops. When it <scene name='72/723172/Protein_dimer_when_ca_is_bound/3'>links to this ion</scene> , it becomes a homooligomer. | In absence of Ca2+, MICU1 is an homohexamer with a <scene name='72/723172/Secondary_structure_of_micu_1/1'>secondary structure</scene> composed by several alpha helix, beta sheets and loops. When it <scene name='72/723172/Protein_dimer_when_ca_is_bound/3'>links to this ion</scene> , it becomes a homooligomer. | ||
MICU 1 is composed by differents domains : | MICU 1 is composed by differents domains : | ||
| - | :- C helix region (or Coiled-coil domain) : this domain permits different interactions with other proteins (MCU/MICU2) and is required to assemble free Ca2+ with homohexamer. | + | :- <scene name='72/723172/C-helix_region/3'>C-helix region</scene> (or Coiled-coil domain) : this domain permits different interactions with other proteins (MCU/MICU2) and is required to assemble free Ca2+ with homohexamer. |
:- <scene name='72/723172/Polybasic_region/1'>Polybasic region</scene> : it’s a domain which permits protein-protein interactions | :- <scene name='72/723172/Polybasic_region/1'>Polybasic region</scene> : it’s a domain which permits protein-protein interactions | ||
:- <scene name='72/723172/Ef_domains/1'>EF-hand domains</scene> There are 2 of them. They are the most important domains in MICU1 protein because they contain the Ca2+ binding region and detect the concentration of calcium in the cell for activation of signalling. An EF-hand domain is a calcium sensor. An EF-hand domain is a helix loop helix structural domain that means that it is 2 alpha helices linked by a short loop region. Ca2+ ions are coordinated in this space thanks to ligands within the loop : in EF-1 residues concerning are Asp231, Asn233, Asp235, Glu237 and Glu242 and in EF-2 they are Asp421, Asp423, Asn425, Glu427 and Glu432. When Ca2+ binds itself to this domain, the protein changes its conformation to expose a domain that can interact with other proteins. | :- <scene name='72/723172/Ef_domains/1'>EF-hand domains</scene> There are 2 of them. They are the most important domains in MICU1 protein because they contain the Ca2+ binding region and detect the concentration of calcium in the cell for activation of signalling. An EF-hand domain is a calcium sensor. An EF-hand domain is a helix loop helix structural domain that means that it is 2 alpha helices linked by a short loop region. Ca2+ ions are coordinated in this space thanks to ligands within the loop : in EF-1 residues concerning are Asp231, Asn233, Asp235, Glu237 and Glu242 and in EF-2 they are Asp421, Asp423, Asn425, Glu427 and Glu432. When Ca2+ binds itself to this domain, the protein changes its conformation to expose a domain that can interact with other proteins. | ||
Revision as of 13:02, 29 January 2016
Structure of MICU1
| |||||||||||