We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1126
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 56: | Line 56: | ||
- hydrophobic interactions between residues I537, L540, A544 of the CBS1 domain of the Bateman module of one monomer with residues I166, V189, V206, L210, I214 of the catalytic core of the other monomer <br/> | - hydrophobic interactions between residues I537, L540, A544 of the CBS1 domain of the Bateman module of one monomer with residues I166, V189, V206, L210, I214 of the catalytic core of the other monomer <br/> | ||
- hydrogen bounds between residues T460, N463, S466, Y484 of the CBS2 domain of the Bateman module of one monomer with residues E201, N194, R196, D198 of the loop 191-202 of the catalytic core of the other monomer <br/><br/> | - hydrogen bounds between residues T460, N463, S466, Y484 of the CBS2 domain of the Bateman module of one monomer with residues E201, N194, R196, D198 of the loop 191-202 of the catalytic core of the other monomer <br/><br/> | ||
| - | These hydrophobic interactions combined with the hydrogen bounds network anchor the Bateman module of one monomer | + | These hydrophobic interactions combined with the hydrogen bounds network anchor the Bateman module of one monomer to the entrance of the catalytic core of the other monomer, thus making it impossible for any substrate to access it. |
*Activation by SAM | *Activation by SAM | ||
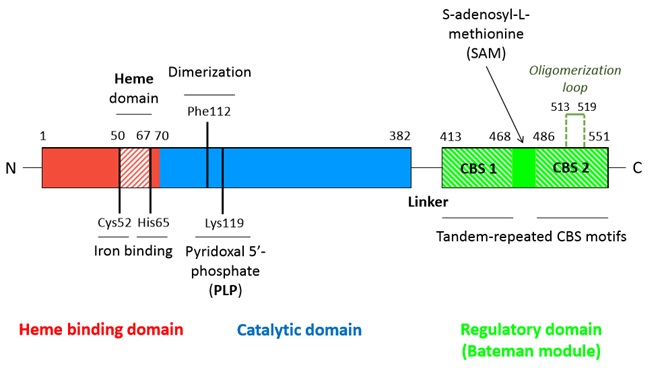
| - | S-adenosyl-methionine | + | S-adenosyl-methionine binds in a region located between the CBS1 and CBS2 domains of the Bateman module which is solvent-exposed and has less hefty hydrophobic residues. Moreover, this region shapes a hydrophobic cage able to host the adenine ring. Moreover threonine (T535) and aspartate (D538) help stabilizing the ribose through hydrogen bounds and polar interactions. |
| - | S-adenosyl-methionine (SAM) is the allosteric regulator factor of the CBS. Its binding to | + | S-adenosyl-methionine (SAM) is the allosteric regulator factor of the CBS. Its binding to the Bateman module destabilizes the interactions which sustain the tetramer structure and thus triggers the dissocciation of the tetrameric structure into two dimers. |
SAM fixation on the C-terminal regulatory domain entails the small rotation (or at least displacement) of the Bateman module (C-terminal regulatory domain), thus allowing the access to the catalytic channel. | SAM fixation on the C-terminal regulatory domain entails the small rotation (or at least displacement) of the Bateman module (C-terminal regulatory domain), thus allowing the access to the catalytic channel. | ||
Revision as of 20:15, 29 January 2016
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 15/12/2015, through 15/06/2016 for use in the course "Structural Biology" taught by Bruno Kieffer at the University of Strasbourg, ESBS. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1120 through Sandbox Reserved 1159. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Human cystathionine β-synthase (hCBS)
| |||||||||||