Sandbox Reserved 1137
From Proteopedia
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
=== Molecular effects === | === Molecular effects === | ||
---- | ---- | ||
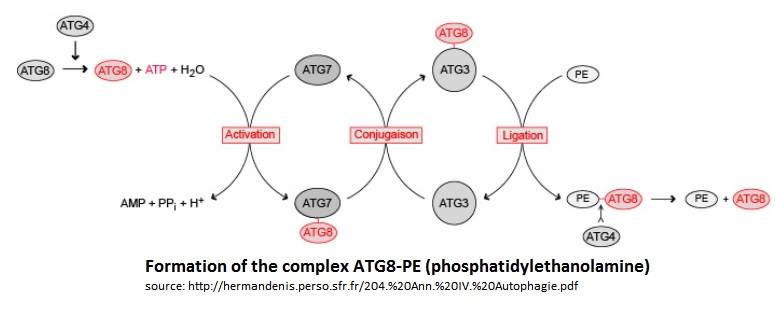
| - | In the Atg8 system, there are several steps until Atg8 is activated. Firstly, the cysteine protease Atg4 cleaves the last residue of the C-terminal domain of Atg8 by consuming 1 molecule of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adenosine_triphosphate ATP] and H20. Then, the Atg7 (E1-like enzyme) activates the C-terminal glycine exposed and therefore forms an intermediate Atg8-Atg7 by creating a thioester bond. Atg3 (E2-like enzyme) then replaces Atg7 in the complex to form an Atg8-Atg3 thioester intermediate. [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phosphatidylethanolamine Phosphatidylethanolamine] (PE) then links to the N-terminal domain of Atg8. This final complex (Atg8-Atg3-PE) serves as an intermediate for membrane tethering and hemifusion of the autophagosome. This complex is primordial for the elongation of the autophagosome. Notice that Atg8-Atg3-PE is the active complex, but Atg8-PE can also be sufficient to do this task (like this is showed on the scheme below). | + | In the Atg8 system, there are several steps until Atg8 is activated. Firstly, the cysteine protease Atg4 cleaves the last residue of the C-terminal domain of Atg8 by consuming 1 molecule of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adenosine_triphosphate ATP] and H20. Then, the Atg7 (E1-like enzyme) activates the C-terminal glycine exposed and therefore forms an intermediate Atg8-Atg7 by creating a thioester bond. Atg3 (E2-like enzyme) then replaces Atg7 in the complex to form an Atg8-Atg3 thioester intermediate. [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phosphatidylethanolamine Phosphatidylethanolamine] (PE) then links to the N-terminal domain of Atg8. This final complex (Atg8-Atg3-PE) serves as an intermediate for membrane [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tether_(cell_biology) tethering] and hemifusion of the autophagosome. This complex is primordial for the elongation of the autophagosome. Notice that Atg8-Atg3-PE is the active complex, but Atg8-PE can also be sufficient to do this task (like this is showed on the scheme below). |
[[Image:atg8f.jpg]] | [[Image:atg8f.jpg]] | ||
Revision as of 20:51, 29 January 2016
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 15/12/2015, through 15/06/2016 for use in the course "Structural Biology" taught by Bruno Kieffer at the University of Strasbourg, ESBS. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1120 through Sandbox Reserved 1159. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Plasmodium falciparum Atg8 in complex with Plasmodium falciparum Atg3 peptide
| |||||||||||
References
1. Hain AU, Weltzer RR, Hammond H, Jayabalasingham B, Dinglasan RR, Graham DR, Colquhoun DR, Coppens I, Bosch J Structural characterization and inhibition of the plasmodium atg8-atg3 interaction. J.Struct.Biol. (2012) 180 p.551
2. Machiko Sakoh-Nakatogawa, Kazuaki Matoba, Eri Asai, Hiromi Kirisako, Junko Ishii, Nobuo N Noda, Fuyuhiko Inagaki, Hitoshi Nakatogawa & Yoshinori Ohsumi Atg12–Atg5 conjugate enhances E2 activity of Atg3 by rearranging its catalytic site Nature Structural & Molecular Biology 20, 433-439 (2013) doi :10.1083/nsmb.2527
3. Oliver H. Weiergräber, Jeannine Mohrlüder and Dieter Willbold Atg8 Family Proteins — Autophagy and Beyond, DOI: 10.5772/55647 Biochemistry, Genetics and Molecular Biology » "Autophagy - A Double-Edged Sword - Cell Survival or Death?", book edited by Yannick Bailly, ISBN 978-953-51-1062-0, Published: April 17, 2013 under CC BY 3.0 license.
4. Herman Denis, http://hermandenis.perso.sfr.fr/204.%20Ann.%20IV.%20Autophagie.pdf
5. Patrice Codogno Les gènes ATG et la macro-autophagie Med Sci (Paris). 2004 August; 20(8-9): 734–736. Published online 2004 August 15. doi: 10.1051/medsci/2004208-9734
6. Hain AU, Bartee D, Sanders NG, Miller AS, Sullivan DJ, Levitskaya J, Meyers CF, Bosch J. Identification of an Atg8-Atg3 protein-protein interaction inhibitor from the medicines for Malaria Venture Malaria Box active in blood and liver stage Plasmodium falciparum parasites. J Med Chem. 2014 Jun 12;57(11):4521-31. doi: 10.1021/jm401675a. Epub 2014 May 19
7. Masaya Yamaguchi, Nobuo N. Noda, Hitoshi Nakatogawa, Hiroyuki Kumeta, Yoshinori Ohsumi and Fuyuhiko Inagaki Autophagy-related Protein 8 (Atg8) Family Interacting Motif in Atg3 Mediates the Atg3-Atg8 Interaction and Is Crucial for the Cytoplasm-to-Vacuole Targeting Pathway. The Journal of Biological Chemistry vol.28. 2010, September 17. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.11367
8. Hain AU1, Weltzer RR, Hammond H, Jayabalasingham B, Dinglasan RR, Graham DR, Colquhoun DR, Coppens I, Bosch J. Structural characterization and inhibition of the Plasmodium Atg8-Atg3 interaction. J Struct Biol. 2012 Dec;180(3):551-62. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2012.09.001. Epub 2012 Sep 13.PMID:22982544
9. Machiko Sakoh-Nakatogawa, Kazuaki Matoba, Eri Asai, Hiromi Kirisako, Junko Ishii, Nobuo N Noda, Fuyuhiko Inagaki, Hitoshi Nakatogawa & Yoshinori Ohsumi. Atg12–Atg5 conjugate enhances E2 activity of Atg3 by rearranging its catalytic site. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology. 2013 February. doi:10.1038/nsmb.2527