Sandbox Reserved 1131
From Proteopedia
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
This enzyme has been recently discovered so it has not been fully understood and characterized yet. | This enzyme has been recently discovered so it has not been fully understood and characterized yet. | ||
| + | <table><tr><td colspan='2'> | ||
</td></tr><tr id='ligand'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Ligand|Ligands:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><scene name='pdbligand=SO4:SULFATE+ION'>SO4</scene></td></tr> | </td></tr><tr id='ligand'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Ligand|Ligands:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><scene name='pdbligand=SO4:SULFATE+ION'>SO4</scene></td></tr> | ||
<tr id='NonStdRes'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Non-Standard_Residue|NonStd Res:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><scene name='pdbligand=MSE:SELENOMETHIONINE'>MSE</scene></td></tr> | <tr id='NonStdRes'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Non-Standard_Residue|NonStd Res:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><scene name='pdbligand=MSE:SELENOMETHIONINE'>MSE</scene></td></tr> | ||
Revision as of 19:01, 30 January 2016
|
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 15/12/2015, through 15/06/2016 for use in the course "Structural Biology" taught by Bruno Kieffer at the University of Strasbourg, ESBS. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1120 through Sandbox Reserved 1159. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
(Human) Phosphohistidine phosphatase 1 belongs to the Janus family, it has 2 isoforms produced by alternative splicing, and 6 transcripts. It is encoded by the PHPT1 gene, located on the 9th chromosome. This enzyme has been recently discovered so it has not been fully understood and characterized yet.
| Ligands: | |
| NonStd Res: | |
| Gene: | PHPT1, PHP14 (HUMAN) |
| Resources: | FirstGlance, OCA, PDBe, RCSB, PDBsum, TOPSAN |
Contents |
Structure
|
Generality
Phosphohistidine phosphatase 1 is a 14kDa homotrimeric protein, whose monomers contain all 125 amino acids. Furthermore, one monomer contains 4 α helices, 6 β strands and 2 turns.
Sequence of the PHPT1 gene
>>sp|Q9NRX4|PHP14_HUMAN 14 kDa phosphohistidine phosphatase OS=Homo sapiens GN=PHPT1 PE=1 SV=1 MAVADLALIPDVDIDSDGVFKYVLIRVHSAPRSGAPAAESKEIVRGYKWAEYHADIYDKV
SGDMQKQGCDCECLGGGRISHQSQDKKIHVYGYSMAYGPAQHAISTEKIKAKYPDYEVTW
ANDGY
Domains
PHPT1 contains an acetylation site and a N-acetylalanine site. There is also an Janus/Ocnus family region, characteristic.
It has one substrate binding site, and one proton acceptor active site.
Function
It is an hydrolase. This characteristic structure allows it to have many activities : phosphoprotein and phosphohistidine phosphatase, calcium channel inhibition, ion channel binding. It is located in the cytosol and in extracellular exosome
Active site
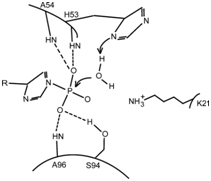
The active site is located between the beginning of helix α1 and loop L5. The catalytic residue is His(53), and the anchor sites of P(i) are the amine groups of His(53), Ala(54) and Ala(96) and the Hydroxy group of Ser(94), which form hydrogen bonds with it.
Ligands and binding
There are 6 SO4 lingands, called SO4 201 to 206. 2 lingand fix to each monomer (2ai6), inducing a conformational change of all the monomers (2hw4). Then, the lingands bind to each other, forming a trimer (2NMM). O4 S is a 96 Da molecule, with two negative charges. The four oxygens allow good fixation on the monomers, with hydrogen bounds.
Catalyic mechanism
The P(i) substrate binds to the active site thanks to the formation of four H-bonds. The imidazole ring of His(53) acts as a base to activate a water molecule, which will in turn do a nucleophilic attack on the substrate. The amine group of the residue Lys(21) can help stabilize the transition state.
Degradation of defective PHPT1
A possible degratation of PHPT1, thanks to quality control and cellular system self-guarding, can happen at two levels. A primary degradation of non-sens mutated PHPT1 mRNA is possible, at the RNA level. Then, the formed protein can be destroyed by the ptoteasome, if it is defective.
Implication in biological fonctions and pathways
Histidine reversible phosphorylation plays important roles in several signal transductions and other cellular functions.
Tissue expression
It is mainly expressed in the cytosol of cells located in the pancreas, the heart, and skeletal muscles.
Inhibition of epithelial Ca²⁺ channel TRPV5
This channel is activated by the kinase NDPK-B, which phosphorylates his(711) in the C-terminal tail of TRPV5. PHPT1 inhibits the activity of TRPV5 by dephosphorylating the same residue, resulting in a decrease in Ca²⁺ flux. This mechanism plays a role in the regulation of Ca²⁺ reabsorption by the kidney.
Inhibition of the K+ channel KCa3.1
PHPT1 dephosphorylates his(358) on KCa3.1, a Ca²⁺-dependant K+ channel that is activated by the phosphorylation on the same residue by NDPK-B. KCa3.1 helps maintain the negative membrane potential, and plays an important role in CD4 T cells signalling. This dephosphorylation inhibits the activity of the KCa3.1 channel and decreases the Ca²⁺ afflux, negatively regulating human CD4 T cells.
NB:dephosphorylation on a non-histidine residue
A study has proved that PHPT1 dephosphorylate histone H1 and polylysine, which do not contain Histidine residue, meaning that the protin has a broader specificity than the one that we know yet.
Diseases and medical applications
Lung Cancer
It has been proved that PHPT1 concentration is linked to lung cancer. Indeed, PHPT1 is associated with the carcinogenesis and metastasis of this cancer, it promotes cell migration and invasion. In cancerous cells, the expression of PHPT1 is almost two fold the one in in normal cells. Therefore, a therapy has been recently developped, aiming the inhibition or the silencing of PHPT1, and it is hoped to be benefic for lung cancer patient.
References
1. GeneCard : http://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl?gene=PHPT1&keywords=Phosphohistidine,phosphatase
2. UniProt : http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q9NRX4
3. Xu AJ, Xia XH, DU ST, Gu JC, 2010 Nov ;123(22):3247-51. Clinical significance of PHPT1 protein expression in lung cancer. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21163124
4. Inturi R, Wäneskog M, Vlachakis D, Ali Y, Ek P, Punga T, Bjerling P, Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2014 Dec;57:69-75. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2014.10.009. Epub 2014 Oct 14. A splice variant of the human phosphohistidine phosphatase 1 (PHPT1) is degraded by the proteasome. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25450458
5. Ek P, Ek B, Zetterqvist Ö, Ups J Med Sci. 2015 Mar;120(1):20-7. doi: 10.3109/03009734.2014.996720. Epub 2015 Jan 9. Phosphohistidine phosphatase 1 (PHPT1) also dephosphorylates phospholysine of chemically phosphorylated histone H1 and polylysine. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25574816
6. Kamath V, Kyathanahalli CN, Jayaram B, Syed I, Olson LK, Ludwig K, Klumpp S, Krieglstein J, Kowluru A, Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2010 Aug;299(2):E276-86. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00091.2010. Epub 2010 May 25. Regulation of glucose- and mitochondrial fuel-induced insulin secretion by a cytosolic protein histidine phosphatase in pancreatic beta-cells. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20501872
7. Klumpp S, Faber D, Fischer D, Litterscheid S, Krieglstein J, Brain Res. 2009 Apr 6;1264:7-12. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2008.12.052. Epub 2008 Dec 30. Role of protein histidine phosphatase for viability of neuronal cells. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19138678
8. Srivastava S, Zhdanova O, Di L, Li Z, Albaqumi M, Wulff H, Skolnik EY, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Sep 23;105(38):14442-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0803678105. Epub 2008 Sep 16. Protein histidine phosphatase 1 negatively regulates CD4 T cells by inhibiting the K+ channel KCa3.1. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18796614
9. Gong W, Li Y, Cui G, Hu J, Fang H, Jin C, Xia B. Biochem J. 2009 Mar 1;418(2):337-44. doi: 10.1042/BJ20081571. Solution structure and catalytic mechanism of human protein histidine phosphatase 1. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18991813
10. Ma R, Kanders E, Sundh UB, Geng M, Ek P, Zetterqvist O, Li JP. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005 Nov 25;337(3):887-91. Epub 2005 Sep 30. Mutational study of human phosphohistidine phosphatase: effect on enzymatic activity. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16219293
11. Cai X, Srivastava S, Surindran S, Li Z, Skolnik EY. Mol Biol Cell. 2014 Apr;25(8):1244-50. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E13-04-0180. Epub 2014 Feb 12. Regulation of the epithelial Ca²⁺ channel TRPV5 by reversible histidine phosphorylation mediated by NDPK-B and PHPT1. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24523290