Function
PDE5 is 5th isoform of the 12 known phosphodiesterases. This enzyme family is responsible for cyclic AMP and cyclic GMP(cGMP) hydrolysis into AMP and GMP. :PE5 specifically catalyzes the hydrolysis of cGMP into 5'GMP. cGMP is an usual second messager in cell signalling pathways, like NO synthesis. By degradating such nucleotide,this phosphodiesterase of class I regulates nucletotic concentration of the cell, through an allosteric regulation system.
PDE5 function affects the smooth muscles, blood vessels or penis, uterus and intestines.
Structural highlights
PDE5 is a homodimeric protein of 875 amino acids long.
This protein is composed of several important domains:
- pol-GLY (10-24 amino acids) in Ntermini (structural importance).
- GAFA (164-314 amino acids)
- GAFB (346-503 amino acids)
- Catalytic domain (588-853 amino acids) in Ctermini involved in cGMP hydrolysis.
The full structure of PDE5 has not been crystallized contrary to this of isolated domains of the protein.
GAFA and GAFB are homologous domains and allosteric binding sites of cGMP.
The of the catalytic domain allows us to see that this domain is mostly constituted by alpha helix and turns.
Catalytic activity
PDE5 is a phosphodiesterase. cGMP could bind the catalytic domain thanks to hydrogen bonds made with Gln775 and Gln817[1] and coordination bonds made with Zn2+ and Mg2+ cations in the catalytic site. In order to see these interactions, report to Sildenafil in Inhibitors and medical application.
cGMP is hydrolyzed in GMP. The catalytic chemical reaction deals with breaking a phosphodiester bound in cGMP between the 3'O of the guanoside and the phosphate of cGMP: cGMP + H20 => GMP.
The catalytic domain is able to bind ligands thanks to an (hydrophylic domain. Moreover with this it appears the cGMP binding site in the catalytic domain is more conservedthan the the rest of the domain that could be variable. Sildenafil is in yellow
Some residues could be affected by post traductional modifications :
phosphorylation : S60, S86, S92, S102, S104, S108, T111, T127, T137, S869.
acylation : K364.
ubiquitinylation : K714.
The ubiquitinylation) of and the phosphorylation of (in yellow) are present in the catalytic site and the phosphorylation of S819 is involved in cGMP binding.
Inhibitors and medical application
Inhibitors of PDE5 prevent cGMP from binding the catalytic site by competititve inhibition. They have more affinity for this domain than cGMP.
Sildenafil (active substance of Viagra) binds to PDE5 catalytic domain through:
- made between Gln775 and Gln817 of PDE5 and Sildenafil
- Mg2+: coordination bond made with in catalytic site
- Zn2+: coordination bond made with in catalytic site
Allosteric regulation
Positive regulation
PDE5 contains several cGMP binding sites that do not have the same effect on its activity. These allosteric domains are GAF A and GAF B play a role in PDE5 activity. Especially GAF A(see the picture below) binds cGMP, by establishing hydrogens bonds between cGMP and the residues T,I,[2] colored in the picture below
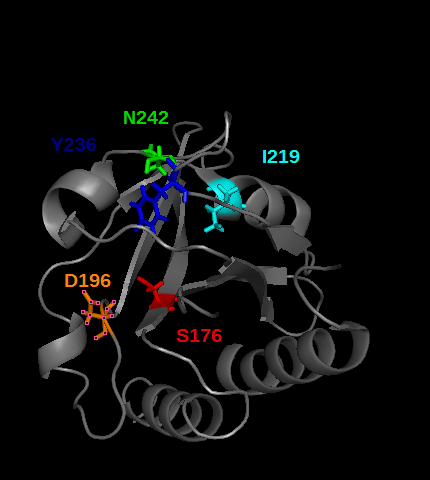
cGMP binding to GAF A triggers an allosteric modification that lead to the seperation of the dimeric catalytic site of the enzyme, so that it free cGMP access to the catalytic site.
This cGMP binding to allosteric sites increases the enzyme affinity to cGMP.
Plus,the phosphorylation the Ser92 by the PKG kinase[3] leads to increase the catalytic activity of the enzyme.
Negative regulation
In large excess of cGMP, cGMP is sequestred by the allosteric sites and can no longer reach the catalytic site[4]. An other model including both PKG and the myosine phosphatase[5] shows that PKG realises an inhibitive phosphorylation of PDE5. In this way, the cell can regulate cGMP concentration by a negative feedback.

