1dkf
From Proteopedia
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
|PDB= 1dkf |SIZE=350|CAPTION= <scene name='initialview01'>1dkf</scene>, resolution 2.50Å | |PDB= 1dkf |SIZE=350|CAPTION= <scene name='initialview01'>1dkf</scene>, resolution 2.50Å | ||
|SITE= | |SITE= | ||
| - | |LIGAND= <scene name='pdbligand=BMS:4-[(4,4-DIMETHYL-1,2,3,4-TETRAHYDRO-[1,2']BINAPTHALENYL-7-CARBONYL)-AMINO]-BENZOIC+ACID'>BMS</scene> | + | |LIGAND= <scene name='pdbligand=BMS:4-[(4,4-DIMETHYL-1,2,3,4-TETRAHYDRO-[1,2']BINAPTHALENYL-7-CARBONYL)-AMINO]-BENZOIC+ACID'>BMS</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=OLA:OLEIC+ACID'>OLA</scene> |
|ACTIVITY= | |ACTIVITY= | ||
|GENE= | |GENE= | ||
| + | |DOMAIN= | ||
| + | |RELATEDENTRY=[[1lbd|1LBD]], [[2lbd|2LBD]] | ||
| + | |RESOURCES=<span class='plainlinks'>[http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1dkf FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=1dkf OCA], [http://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/1dkf PDBsum], [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=1dkf RCSB]</span> | ||
}} | }} | ||
| Line 14: | Line 17: | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
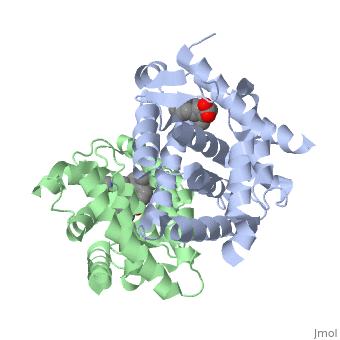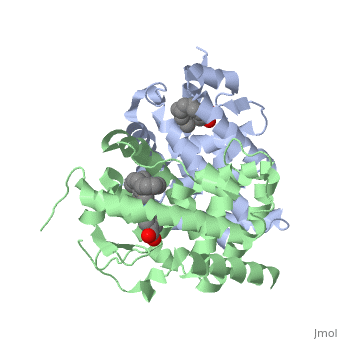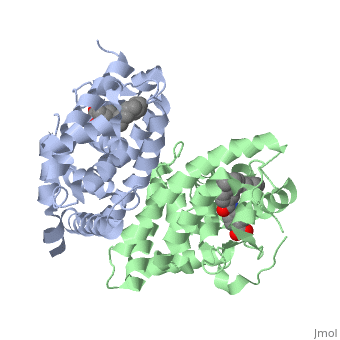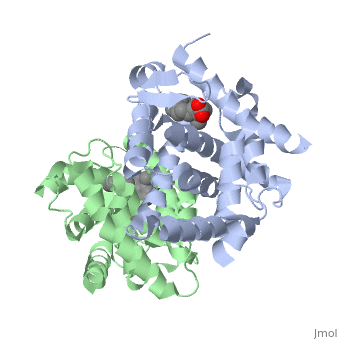
The crystal structure of a heterodimer between the ligand-binding domains (LBDs) of the human RARalpha bound to a selective antagonist and the constitutively active mouse RXRalphaF318A mutant shows that, pushed by a bulky extension of the ligand, RARalpha helix H12 adopts an antagonist position. The unexpected presence of a fatty acid in the ligand-binding pocket of RXRalpha(F318A is likely to account for its apparent "constitutivity." Specific conformational changes suggest the structural basis of pure and partial antagonism. The RAR-RXR heterodimer interface is similar to that observed in most nuclear receptor (NR) homodimers. A correlative analysis of 3D structures and sequences provides a novel view on dimerization among members of the nuclear receptor superfamily. | The crystal structure of a heterodimer between the ligand-binding domains (LBDs) of the human RARalpha bound to a selective antagonist and the constitutively active mouse RXRalphaF318A mutant shows that, pushed by a bulky extension of the ligand, RARalpha helix H12 adopts an antagonist position. The unexpected presence of a fatty acid in the ligand-binding pocket of RXRalpha(F318A is likely to account for its apparent "constitutivity." Specific conformational changes suggest the structural basis of pure and partial antagonism. The RAR-RXR heterodimer interface is similar to that observed in most nuclear receptor (NR) homodimers. A correlative analysis of 3D structures and sequences provides a novel view on dimerization among members of the nuclear receptor superfamily. | ||
| - | |||
| - | ==Disease== | ||
| - | Known disease associated with this structure: Leukemia, acute promyelocytic OMIM:[[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/dispomim.cgi?id=180240 180240]] | ||
==About this Structure== | ==About this Structure== | ||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
[[Category: Vivat, V.]] | [[Category: Vivat, V.]] | ||
[[Category: Wurtz, J M.]] | [[Category: Wurtz, J M.]] | ||
| - | [[Category: BMS]] | ||
| - | [[Category: OLA]] | ||
[[Category: helical sandwich]] | [[Category: helical sandwich]] | ||
[[Category: heterodimer]] | [[Category: heterodimer]] | ||
| Line 43: | Line 41: | ||
[[Category: structural proteomics in europe]] | [[Category: structural proteomics in europe]] | ||
| - | ''Page seeded by [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca OCA ] on Sun Mar | + | ''Page seeded by [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca OCA ] on Sun Mar 30 19:43:16 2008'' |
Revision as of 16:43, 30 March 2008
| |||||||
| , resolution 2.50Å | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligands: | , | ||||||
| Related: | 1LBD, 2LBD
| ||||||
| Resources: | FirstGlance, OCA, PDBsum, RCSB | ||||||
| Coordinates: | save as pdb, mmCIF, xml | ||||||
CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF A HETERODIMERIC COMPLEX OF RAR AND RXR LIGAND-BINDING DOMAINS
Overview
The crystal structure of a heterodimer between the ligand-binding domains (LBDs) of the human RARalpha bound to a selective antagonist and the constitutively active mouse RXRalphaF318A mutant shows that, pushed by a bulky extension of the ligand, RARalpha helix H12 adopts an antagonist position. The unexpected presence of a fatty acid in the ligand-binding pocket of RXRalpha(F318A is likely to account for its apparent "constitutivity." Specific conformational changes suggest the structural basis of pure and partial antagonism. The RAR-RXR heterodimer interface is similar to that observed in most nuclear receptor (NR) homodimers. A correlative analysis of 3D structures and sequences provides a novel view on dimerization among members of the nuclear receptor superfamily.
About this Structure
1DKF is a Protein complex structure of sequences from Homo sapiens and Mus musculus. Full crystallographic information is available from OCA.
Reference
Crystal structure of a heterodimeric complex of RAR and RXR ligand-binding domains., Bourguet W, Vivat V, Wurtz JM, Chambon P, Gronemeyer H, Moras D, Mol Cell. 2000 Feb;5(2):289-98. PMID:10882070
Page seeded by OCA on Sun Mar 30 19:43:16 2008
Categories: Homo sapiens | Mus musculus | Protein complex | Bourguet, W. | Chambon, P. | Gronemeyer, H. | Moras, D. | SPINE, Structural Proteomics in Europe. | Vivat, V. | Wurtz, J M. | Helical sandwich | Heterodimer | Hormone/growth factor receptor | Protein-ligand complex | Spine | Structural genomic | Structural proteomics in europe