Elongation factor
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
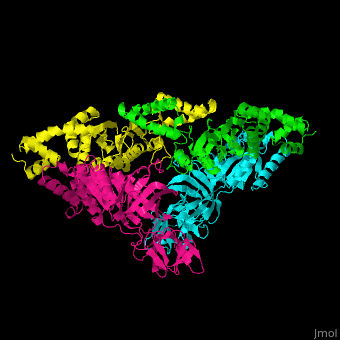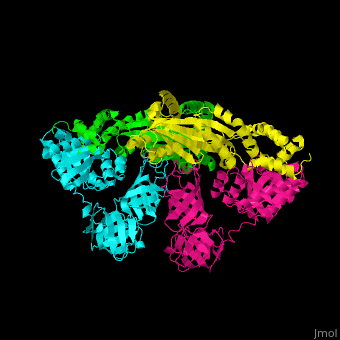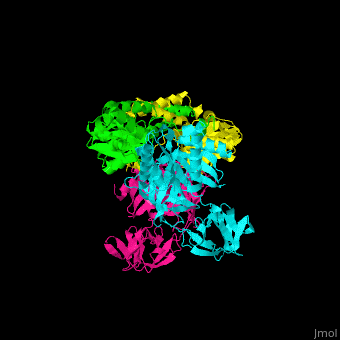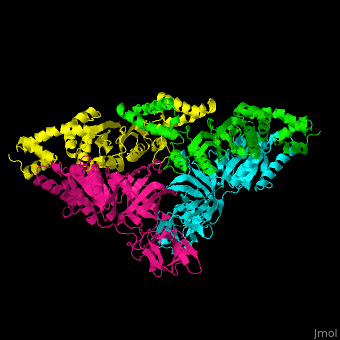
| - | <StructureSection load='1efu' size='350' side='right' caption='Structure of EF-Tu ( | + | <StructureSection load='1efu' size='350' side='right' caption='Structure of EF-Tu (cyan and magenta) with EF-Ts (green and yellow) (PDB entry [[1efu]])' scene='51/517376/Cv/1'> |
'''Elongation factors''' (EF) facilitate translational elongation during the formation of peptide bonds in the ribosome.<br /> | '''Elongation factors''' (EF) facilitate translational elongation during the formation of peptide bonds in the ribosome.<br /> | ||
Revision as of 10:37, 9 February 2016
| |||||||||||
3D structures of elongation factor
Updated on 09-February-2016
References
- ↑ Takeshita D, Tomita K. Assembly of Q{beta} viral RNA polymerase with host translational elongation factors EF-Tu and -Ts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Sep 7;107(36):15733-8. Epub 2010 Aug 23. PMID:20798060 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1006559107
- ↑ Jorgensen R, Merrill AR, Andersen GR. The life and death of translation elongation factor 2. Biochem Soc Trans. 2006 Feb;34(Pt 1):1-6. PMID:16246167 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1042/BST20060001