Ketosteroid Isomerase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | <StructureSection load='1qjg' size=' | + | <StructureSection load='1qjg' size='350' side='right' scene='' caption='Ketosteroid isomerase complex with transition state analog equilenin and sulfate (PDB code [[1qjg]])'> |
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
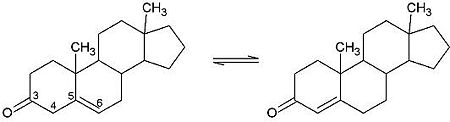
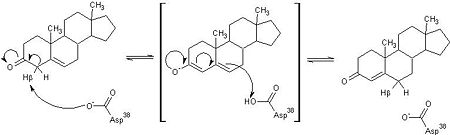
<scene name='User:Laura_M._Haynes/Sandbox_1/Ksi/4'>Ketosteroid isomerase</scene> (KSI, EC#5.3.3.1) is an enzyme that catalyzes the isomerization of 3-oxo-Δ<sup>5</sup> ketosteroids to their hormonally active Δ<sup>4</sup>-conjugated isomers, as illustrated below.<ref name="Pollack">PMID:15381400</ref>, <ref name="Talalay">PMID:13276386 </ref> | <scene name='User:Laura_M._Haynes/Sandbox_1/Ksi/4'>Ketosteroid isomerase</scene> (KSI, EC#5.3.3.1) is an enzyme that catalyzes the isomerization of 3-oxo-Δ<sup>5</sup> ketosteroids to their hormonally active Δ<sup>4</sup>-conjugated isomers, as illustrated below.<ref name="Pollack">PMID:15381400</ref>, <ref name="Talalay">PMID:13276386 </ref> | ||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
[[Image:Reaction.jpg|left|450px|thumb]] | [[Image:Reaction.jpg|left|450px|thumb]] | ||
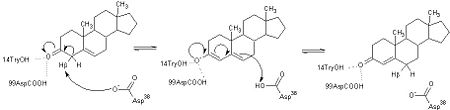
| - | This reaction is essential in the biosynthesis of steroids in mammals where KSI is a membrane-bound complex.<ref name="Ha">PMID:11751047</ref> In bacteria, however, KSI exists as a soluble protein is involves in catabolism of steroids.<ref name="Ha" /> It was first isolated in and has been extensively studied in [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Comamonas_testosteroni ''Commamonas tetosteroni''] (TI), a bacteria that is capable of growth with testosterone as its sole carbon source.<ref name="Stanier1966">PMID:11751047</ref> Structural and kinetic studies of this and its homolog from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pseudomonas_putida ''Pseudomonas putida''] with which it shares 34% sequence and near identical structural homology.<ref name="Pollack" />,<ref name="Ha" /> It is one of the most efficient known enzymes with an essentially diffusion limited rate of catalysis.<ref name="Talalay" />,<ref name="Wu">PMID:9103200 </ref> It is capable of increasing the catalytic rate by eleven orders of magnitude.<ref name="Murzin">PMID:9666335 </ref> The high degree of efficiency is believed to be due to a preference for the transition state to move towards products rather than reactants although the exact mechanism of this preference is unclear.<ref name="Pollack" /> Its high catalytic efficiency and unique active site geometry have made it fertile ground for examining the validity of the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Low-barrier_hydrogen_bond low barrier hydrogen bond] hypothesis<ref name="Cleland1998">PMID:9748211 </ref> and electrostatic preorganization.<ref name="Kraut2006">PMID:16602823 </ref>. | + | This reaction is essential in the biosynthesis of steroids in mammals where KSI is a membrane-bound complex.<ref name="Ha">PMID:11751047</ref> In bacteria, however, KSI exists as a soluble protein is involves in catabolism of steroids.<ref name="Ha" /> It was first isolated in and has been extensively studied in [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Comamonas_testosteroni ''Commamonas tetosteroni''] (TI), a bacteria that is capable of growth with testosterone as its sole carbon source.<ref name="Stanier1966">PMID:11751047</ref> Structural and kinetic studies of this and its homolog from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pseudomonas_putida ''Pseudomonas putida''] with which it shares 34% sequence and near identical structural homology.<ref name="Pollack" />,<ref name="Ha" /> It is one of the most efficient known enzymes with an essentially diffusion limited rate of catalysis.<ref name="Talalay" />,<ref name="Wu">PMID:9103200 </ref> It is capable of increasing the catalytic rate by eleven orders of magnitude.<ref name="Murzin">PMID:9666335 </ref> The high degree of efficiency is believed to be due to a preference for the transition state to move towards products rather than reactants although the exact mechanism of this preference is unclear.<ref name="Pollack" /> Its high catalytic efficiency and unique active site geometry have made it fertile ground for examining the validity of the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Low-barrier_hydrogen_bond low barrier hydrogen bond] hypothesis<ref name="Cleland1998">PMID:9748211 </ref> and electrostatic preorganization.<ref name="Kraut2006">PMID:16602823 </ref>. See also [[Isomerases]]. |
==Structure== | ==Structure== | ||
Revision as of 11:49, 10 February 2016
| |||||||||||
3D structures of ketosteroid isomerase
Updated on 10-February-2016
References
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 Pollack RM. Enzymatic mechanisms for catalysis of enolization: ketosteroid isomerase. Bioorg Chem. 2004 Oct;32(5):341-53. PMID:15381400 doi:10.1016/j.bioorg.2004.06.005
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 TALALAY P, WANG VS. Enzymic isomerization of delta5-3-ketosteroids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1955 Oct;18(2):300-1. PMID:13276386
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 3.7 3.8 Ha NC, Choi G, Choi KY, Oh BH. Structure and enzymology of Delta5-3-ketosteroid isomerase. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2001 Dec;11(6):674-8. PMID:11751047
- ↑ Ha NC, Choi G, Choi KY, Oh BH. Structure and enzymology of Delta5-3-ketosteroid isomerase. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2001 Dec;11(6):674-8. PMID:11751047
- ↑ 5.00 5.01 5.02 5.03 5.04 5.05 5.06 5.07 5.08 5.09 5.10 Wu ZR, Ebrahimian S, Zawrotny ME, Thornburg LD, Perez-Alvarado GC, Brothers P, Pollack RM, Summers MF. Solution structure of 3-oxo-delta5-steroid isomerase. Science. 1997 Apr 18;276(5311):415-8. PMID:9103200
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 Murzin AG. How far divergent evolution goes in proteins. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 1998 Jun;8(3):380-7. PMID:9666335
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Cleland WW, Frey PA, Gerlt JA. The low barrier hydrogen bond in enzymatic catalysis. J Biol Chem. 1998 Oct 2;273(40):25529-32. PMID:9748211
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 Kraut DA, Sigala PA, Pybus B, Liu CW, Ringe D, Petsko GA, Herschlag D. Testing electrostatic complementarity in enzyme catalysis: hydrogen bonding in the ketosteroid isomerase oxyanion hole. PLoS Biol. 2006 Apr;4(4):e99. Epub 2006 Mar 28. PMID:16602823 doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0040099
- ↑ Cho HS, Choi G, Choi KY, Oh BH. Crystal structure and enzyme mechanism of Delta 5-3-ketosteroid isomerase from Pseudomonas testosteroni. Biochemistry. 1998 Jun 9;37(23):8325-30. PMID:9622484 doi:10.1021/bi9801614
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Aurora R, Rose GD. Helix capping. Protein Sci. 1998 Jan;7(1):21-38. PMID:9514257 doi:10.1002/pro.5560070103
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Kim DH, Jang DS, Nam GH, Choi KY. Folding mechanism of ketosteroid isomerase from Comamonas testosteroni. Biochemistry. 2001 Apr 24;40(16):5011-7. PMID:11305917
- ↑ Massiah MA, Abeygunawardana C, Gittis AG, Mildvan AS. Solution structure of Delta 5-3-ketosteroid isomerase complexed with the steroid 19-nortestosterone hemisuccinate. Biochemistry. 1998 Oct 20;37(42):14701-12. PMID:9778345 doi:10.1021/bi981447b
- ↑ Kim SW, Cha SS, Cho HS, Kim JS, Ha NC, Cho MJ, Joo S, Kim KK, Choi KY, Oh BH. High-resolution crystal structures of delta5-3-ketosteroid isomerase with and without a reaction intermediate analogue. Biochemistry. 1997 Nov 18;36(46):14030-6. PMID:9369474 doi:10.1021/bi971546+
- ↑ Sigala PA, Kraut DA, Caaveiro JM, Pybus B, Ruben EA, Ringe D, Petsko GA, Herschlag D. Testing geometrical discrimination within an enzyme active site: constrained hydrogen bonding in the ketosteroid isomerase oxyanion hole. J Am Chem Soc. 2008 Oct 15;130(41):13696-708. Epub 2008 Sep 23. PMID:18808119 doi:10.1021/ja803928m
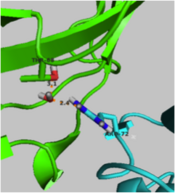
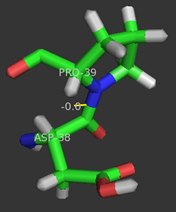
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 Nam GH, Cha SS, Yun YS, Oh YH, Hong BH, Lee HS, Choi KY. The conserved cis-Pro39 residue plays a crucial role in the proper positioning of the catalytic base Asp38 in ketosteroid isomerase from Comamonas testosteroni. Biochem J. 2003 Oct 15;375(Pt 2):297-305. PMID:12852789 doi:10.1042/BJ20030263
- ↑ Cho HS, Ha NC, Choi G, Kim HJ, Lee D, Oh KS, Kim KS, Lee W, Choi KY, Oh BH. Crystal structure of delta(5)-3-ketosteroid isomerase from Pseudomonas testosteroni in complex with equilenin settles the correct hydrogen bonding scheme for transition state stabilization. J Biol Chem. 1999 Nov 12;274(46):32863-8. PMID:10551849
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 Zhao Q, Abeygunawardana C, Talalay P, Mildvan AS. NMR evidence for the participation of a low-barrier hydrogen bond in the mechanism of delta 5-3-ketosteroid isomerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Aug 6;93(16):8220-4. PMID:8710850
- ↑ Zhao Q, Abeygunawardana C, Talalay P, Mildvan AS. NMR evidence for the participation of a low-barrier hydrogen bond in the mechanism of delta 5-3-ketosteroid isomerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Aug 6;93(16):8220-4. PMID:8710850
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 Kraut DA, Sigala PA, Fenn TD, Herschlag D. Dissecting the paradoxical effects of hydrogen bond mutations in the ketosteroid isomerase oxyanion hole. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Feb 2;107(5):1960-5. Epub 2010 Jan 11. PMID:20080683
- ↑ Sigala PA, Caaveiro JM, Ringe D, Petsko GA, Herschlag D. Hydrogen bond coupling in the ketosteroid isomerase active site. Biochemistry. 2009 Jul 28;48(29):6932-9. PMID:19469568 doi:10.1021/bi900713j
- ↑ 21.0 21.1 Cherney MM, Garen CR, James MN. Crystal structure of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Rv0760c at 1.50 A resolution, a structural homolog of Delta(5)-3-ketosteroid isomerase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008 Nov;1784(11):1625-32. Epub 2008 Jun 6. PMID:18589008 doi:10.1016/j.bbapap.2008.05.012
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Laura M. Haynes, Michal Harel, Joel L. Sussman, Alexander Berchansky