Ann Taylor sandbox 117
From Proteopedia
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | {{STRUCTURE_2age | PDB=2age | SCENE= }} | ||
==Succinyl-AAPR-trypsin acyl-enzyme== | ==Succinyl-AAPR-trypsin acyl-enzyme== | ||
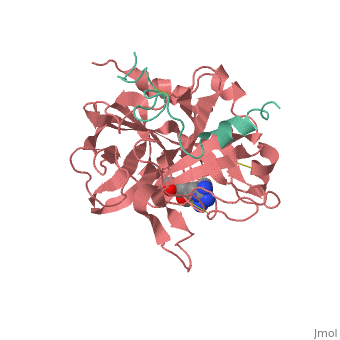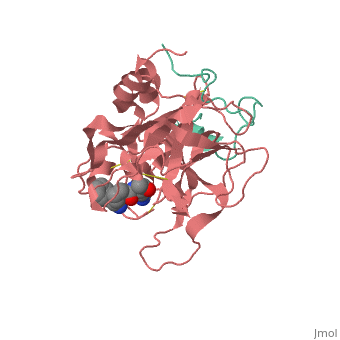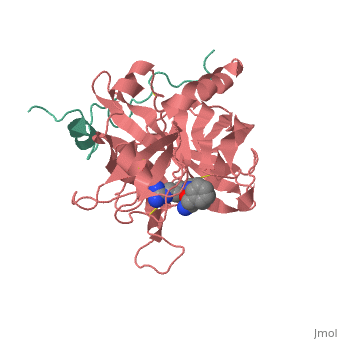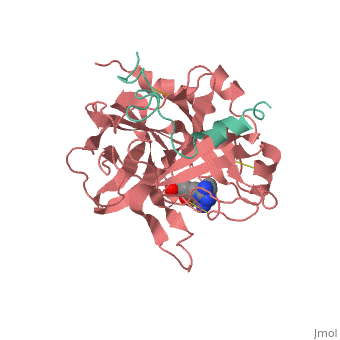
| - | Structures of trypsin acyl-enzymes are used to reconstruct events in the catalytic cycle of serine protease. The structural comparisons provide insight into active site adjustments involved in catalysis. The motions of the catalytic serine and histidine residues coordinated with translation of the substrate reaction center are seen to favor the forward reaction. The structures also clarify how the hydrolytic water attacks in the deacylation reaction. The PDB code is <scene name='Ann_Taylor_sandbox_117/2age/1'>2AGE</scene>. Movements of the enzyme catalytic residues are subtle but significant: <scene name='Ann_Taylor_sandbox_117/Ser-195_rotation/1'>Ser-195 rotation</scene> and <scene name='Ann_Taylor_sandbox_117/His-57/4'>His-57 side chain swivels</scene>. The result is to shift the His-47 N, from its initial favorable distance for activation of the serine, 0.6 A nearer to the amine leaving group and attacking water for subsequent reaction steps. | + | '''Serine proteases''', or '''proteinases''', so called due to the presence of a serine residue in the active site, are a class of enzymes that catalyse the hydrolysis of peptide bonds in proteins. Structures of trypsin acyl-enzymes are used to reconstruct events in the catalytic cycle of serine protease. The structural comparisons provide insight into active site adjustments involved in catalysis. The motions of the catalytic serine and histidine residues coordinated with translation of the substrate reaction center are seen to favor the forward reaction. The structures also clarify how the hydrolytic water attacks in the deacylation reaction. The PDB code is <scene name='Ann_Taylor_sandbox_117/2age/1'>2AGE</scene>. Movements of the enzyme catalytic residues are subtle but significant: <scene name='Ann_Taylor_sandbox_117/Ser-195_rotation/1'>Ser-195 rotation</scene> and <scene name='Ann_Taylor_sandbox_117/His-57/4'>His-57 side chain swivels</scene>. The result is to shift the His-47 N, from its initial favorable distance for activation of the serine, 0.6 A nearer to the amine leaving group and attacking water for subsequent reaction steps. <ref>PMID: 16636277</ref> |
<applet load="1ppb" size="350" color="white" frame="true" align="left" spinBox="true" | <applet load="1ppb" size="350" color="white" frame="true" align="left" spinBox="true" | ||
caption="Human Thrombin with PPACK inhibitor" /> | caption="Human Thrombin with PPACK inhibitor" /> | ||
| - | '''Serine proteases''', or '''proteinases''', so called due to the presence of a serine residue in the active site, are a class of enzymes that catalyse the hydrolysis of peptide bonds in proteins. | ||
| - | + | ==References== | |
| - | + | <references/> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
Revision as of 15:25, 12 February 2016
| |||||||||
| 2age, resolution 1.15Å () | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligands: | |||||||||
| Non-Standard Residues: | |||||||||
| Activity: | Trypsin, with EC number 3.4.21.4 | ||||||||
| Related: | 2agg, 2agi, 2ah4
| ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Resources: | FirstGlance, OCA, PDBsum, RCSB | ||||||||
| Coordinates: | save as pdb, mmCIF, xml | ||||||||
Succinyl-AAPR-trypsin acyl-enzyme
Serine proteases, or proteinases, so called due to the presence of a serine residue in the active site, are a class of enzymes that catalyse the hydrolysis of peptide bonds in proteins. Structures of trypsin acyl-enzymes are used to reconstruct events in the catalytic cycle of serine protease. The structural comparisons provide insight into active site adjustments involved in catalysis. The motions of the catalytic serine and histidine residues coordinated with translation of the substrate reaction center are seen to favor the forward reaction. The structures also clarify how the hydrolytic water attacks in the deacylation reaction. The PDB code is . Movements of the enzyme catalytic residues are subtle but significant: and . The result is to shift the His-47 N, from its initial favorable distance for activation of the serine, 0.6 A nearer to the amine leaving group and attacking water for subsequent reaction steps. [1]
|