This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Raghad zoubi
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | ==Example page for α- | + | ==Example page for α-Amylase== |
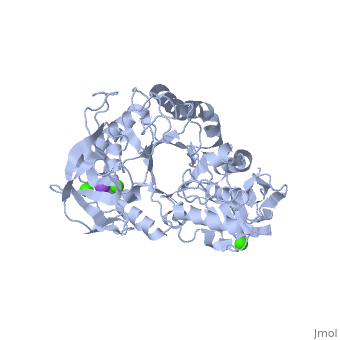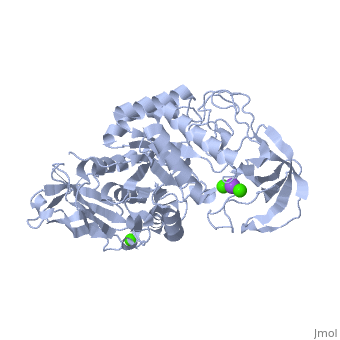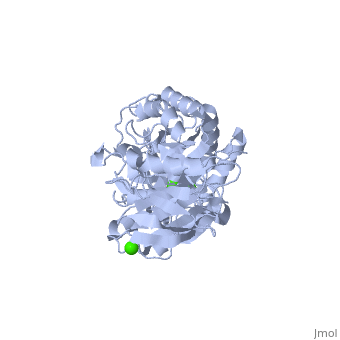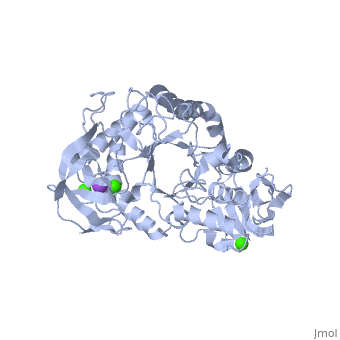
| - | <StructureSection load='1hvx' size='340' side='right' caption='α- | + | <StructureSection load='1hvx' size='340' side='right' caption='α-Amylase complex with Ca+2 (green) and Na+ (purple) ions (PDB code [[1hvx]])' scene=''> |
'''α-Amylase''' is a protein enzyme EC 3.2.1.1 that hydrolyses alpha bonds of large, alpha-linked polysaccharides, such as starch and glycogen, yielding glucose and maltose. It is the major form of amylase found in humans and other mammals.It is also present in seeds containing starch as a food reserve, and is secreted by many fungi. <ref>http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alpha-amylase</ref> | '''α-Amylase''' is a protein enzyme EC 3.2.1.1 that hydrolyses alpha bonds of large, alpha-linked polysaccharides, such as starch and glycogen, yielding glucose and maltose. It is the major form of amylase found in humans and other mammals.It is also present in seeds containing starch as a food reserve, and is secreted by many fungi. <ref>http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alpha-amylase</ref> | ||
Current revision
Example page for α-Amylase
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alpha-amylase
- ↑ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Amylase
- ↑ "The use of enzymes in detergents". Faculty of Engineering, Science and the Built Environment, London South Bank University. 20 December 2004. Archived from the original on 20 October 2009. Retrieved 21 November 2009.