We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Exonuclease
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
'''Exonucleases''' (ExN) cleave nucleotides at the end of a polynucleotide chain<ref>PMID:14770007</ref>. In ''E. coli'' there are ExN I to VIII. ExN were found in human and yeast as well. | '''Exonucleases''' (ExN) cleave nucleotides at the end of a polynucleotide chain<ref>PMID:14770007</ref>. In ''E. coli'' there are ExN I to VIII. ExN were found in human and yeast as well. | ||
| - | + | <br /> | |
* '''ExN-I''' cleaves single-stranded DNA.<br /> | * '''ExN-I''' cleaves single-stranded DNA.<br /> | ||
* '''ExN-II''' is associated with DNA polymerase.<br /> | * '''ExN-II''' is associated with DNA polymerase.<br /> | ||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
* '''ExN-V''' cleaves linear double-stranded DNA.<br /> | * '''ExN-V''' cleaves linear double-stranded DNA.<br /> | ||
* '''ExN-VIII''' requires a free 5’ OH group for reacting.<br /> | * '''ExN-VIII''' requires a free 5’ OH group for reacting.<br /> | ||
| + | * For '''phage ExN''' see [[Sand box 211]]. | ||
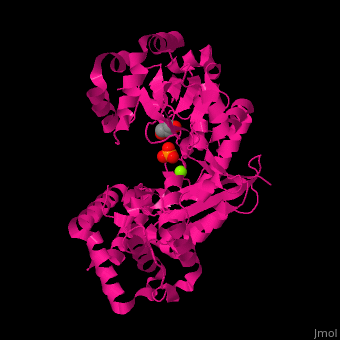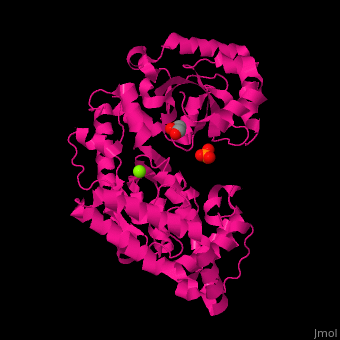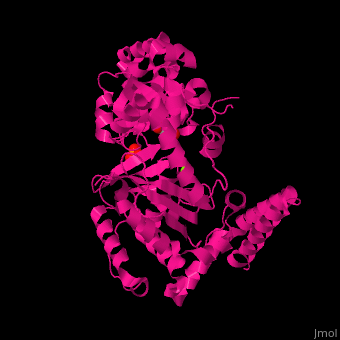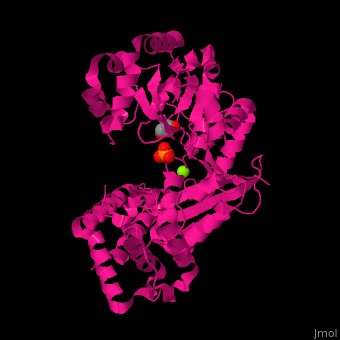
<scene name='46/466467/Cv/2'>Mg coordination site</scene> in ''E. coli'' exonuclease I (PDB code [[1fxx]]).<ref>PMID:11101894</ref> Water molecules shown as red spheres. | <scene name='46/466467/Cv/2'>Mg coordination site</scene> in ''E. coli'' exonuclease I (PDB code [[1fxx]]).<ref>PMID:11101894</ref> Water molecules shown as red spheres. | ||
Revision as of 10:24, 21 February 2016
| |||||||||||
3D Structures of exonuclease
Updated on 21-February-2016
References
- ↑ Mukherjee D, Fritz DT, Kilpatrick WJ, Gao M, Wilusz J. Analysis of RNA exonucleolytic activities in cellular extracts. Methods Mol Biol. 2004;257:193-212. PMID:14770007 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1385/1-59259-750-5:193
- ↑ Breyer WA, Matthews BW. Structure of Escherichia coli exonuclease I suggests how processivity is achieved. Nat Struct Biol. 2000 Dec;7(12):1125-8. PMID:11101894 doi:10.1038/81978