Nisin
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
| - | <StructureSection load='1wco' size='340' side='right' caption='60/607847/Nisin_structure/4' scene=''> | + | <StructureSection load='1wco' size='340' side='right' caption='60/607847/Nisin_structure/4 in complex with lipid (PDB code [[1wco]])' scene=''> |
| - | + | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| - | + | '''Nisin''' is a polycylic antibacterial peptide, with 34 amino acid residues used as a food preservative. | |
Nisin is produced by fermentation using the bacterium ''Lactococcus lactis''. | Nisin is produced by fermentation using the bacterium ''Lactococcus lactis''. | ||
| - | While in general most | + | While in general most bacteriocins inhibit only closely related species, nisin is a rare example of a "broad-spectrum" bacteriocin effective against many Gram-positive organisms, including lactic acid bacteria (commonly associated with spoilage), ''Listeria monocytogenes'' (a known pathogen), ''Staphylococcus aureus,'' ''Bacillus cereus'', ''Clostridium botulinum'', etc. It is also particularly effective against spores. Gram-negative bacteria are protected by their outer membrane but may become susceptible to nisin action after a heat shock or when this is coupled with the chelator EDTA. Nisin is soluble in water and can be effective at levels nearing the parts-per-billion range<ref>PMID:184764</ref>. |
== Disease == | == Disease == | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
== Relevance == | == Relevance == | ||
| - | In the food industry, it is obtained from the culturing of ''L. lactis'' on natural substrates, such as milk or dextrose, and is not chemically synthesized. | + | In the food industry, it is obtained from the culturing of ''L. lactis'' on natural substrates, such as milk or dextrose, and is not chemically synthesized. Nisin is studied as a novel antibiotic due to its antimicrobial activity and as a therapeutic against neck and head squamous cell carcinoma<ref>PMID:3544465</ref>. |
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
Revision as of 09:08, 25 February 2016
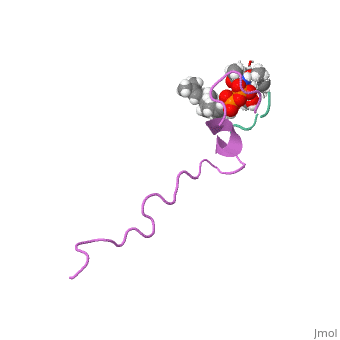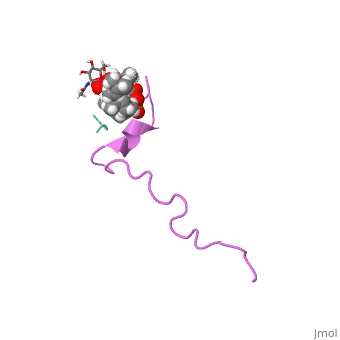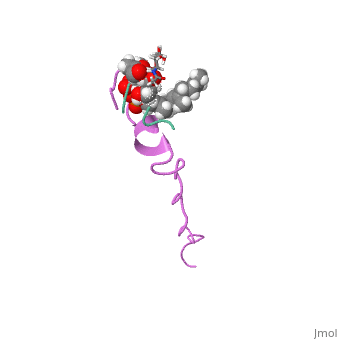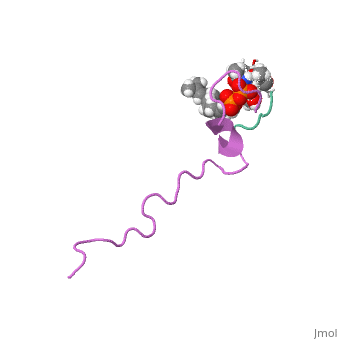
Nisin
| |||||||||||
3D structure of nisin
1wco - Nisin + lipid - Lactococcus lactis - NMR
References
- ↑ Wilson HJ, Goodman RM, Israel HW. Pinwheel inclusions in morphogenesis: a possible alternative to induction by viruses. Arch Virol. 1976;51(4):347-54. PMID:184764
- ↑ Bacon EJ, Richmond SJ, Wood DJ, Stirling P, Bevan BJ, Chalmers WS. Serological detection of phage infection in Chlamydia psittaci recovered from ducks. Vet Rec. 1986 Dec 20-27;119(25-26):618-20. PMID:3544465