This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Sandbox Reserved 427
From Proteopedia
(→Binding Interactions) |
|||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
| - | <Structure load='1j7e' size='300' frame='true' align='right' caption='1j7e, Vitamin D Binding Protein' scene=' | + | <Structure load='1j7e' size='300' frame='true' align='right' caption='1j7e, Vitamin D Binding Protein' scene='Insert optional scene name here' /> |
Vitamin D binding protein Overview: | Vitamin D binding protein Overview: | ||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
==Overall Structure== | ==Overall Structure== | ||
| - | <Structure load='1j7e' size='300' frame='true' align='right' caption='1j7e, Vitamin D Binding Protein' scene=' | + | <Structure load='1j7e' size='300' frame='true' align='right' caption='1j7e, Vitamin D Binding Protein' scene='Insert optional scene name here' /> |
The tertiary structure consists of mainly <scene name="48/483884/Alpha_helices/2">alpha helices</scene>, which can be seen in pink. The quaternary structure of the protein consists of <scene name='48/483884/Twosubunits/1'>two subunits</scene> forming a complex. The structure is about 58 kDA in size and made up of 458 amino acids. | The tertiary structure consists of mainly <scene name="48/483884/Alpha_helices/2">alpha helices</scene>, which can be seen in pink. The quaternary structure of the protein consists of <scene name='48/483884/Twosubunits/1'>two subunits</scene> forming a complex. The structure is about 58 kDA in size and made up of 458 amino acids. | ||
=====Alpha Helical Domains===== | =====Alpha Helical Domains===== | ||
Revision as of 18:20, 25 February 2016
| This Sandbox is Reserved from January 19, 2016, through August 31, 2016 for use for Proteopedia Team Projects by the class Chemistry 423 Biochemistry for Chemists taught by Lynmarie K Thompson at University of Massachusetts Amherst, USA. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 425 through Sandbox Reserved 439. |
Contents |
Vitamin D binding protein (1j7e)[1]
missing team member names
Student Projects for UMass Chemistry 423 Spring 2016
Introduction
|
Vitamin D binding protein Overview:
1) purposes
2) History (various name changes since discovery)
3) overview of structure:
green scenes for , ball and stick, secondary structure
4) Brief mention of unique binding characteristics.
5) Therapeutic uses
Overall Structure
|
The tertiary structure consists of mainly , which can be seen in pink. The quaternary structure of the protein consists of forming a complex. The structure is about 58 kDA in size and made up of 458 amino acids.
Alpha Helical Domains
The Vitamin D binding protein consists of three alpha helical domains which are homologous. Domain I containing 10 aloha helices, Domain II 9, and Domain III 4 being shorter than the other domains.
Vitamin D Binding Protein and Human Serum Albumin
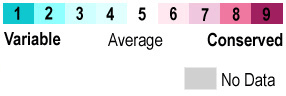
The overall structure is closely related to that of the human serum albumin, to which it is homologous. The proteins are very similar yet the three dimensional structure differs somewhat to facilitate binding. Looking at it can be seen that the outer edges are more variable while the core has more conserved sections.
Actin Binding
The tertiary structure of the protein is optimized for it binding with actin, efficiently folding into a complex requiring little change of the structure.
Binding Interactions
|
The Vitamin D Binding Site
Describe the chemical make-up of the binding. Talk about hydrophobic interactions with vitamin D3 ligands. Hydrogen bond formation with 250HD3. Also discuss steric strain and binding affinity.
Biological Relevance of The Vitamin D Binding Site
Vitamin D hormone 1,25(OH)2D3 used to treat renal osteodystrophy, hypoparathyroidism and osteoporosis. Discuss selectivity and binding affinity of synthesized molecules
Additional Features
|
Synthesis
Synthesized in the liver. Will also include details about folding, posttranslational modification and chaperone proteins, if any.
Actin Binding Interactions
Vitamin D binding protein is also capable of interacting with actin at the domains shown in . This function occurs mainly in the bloodstream, as DBP binds to globular actin present in the plasma. It presents an important mechanism for clearing actin from necrotic or apoptotic tissue (Meier et all 2006)
Other Interactions
"Macrophage modulation Chemotaxis of C5 derived peptides Transport of fatty acids and endotoxins Inhibition of platelet induced aggregation Osteoclast Activation" from Meier et al 2006 Figure 2
Role in Disease
Altered levels in hepatic failure, AHF, trauma, immune function. Deficient mice show no phenotype. White and Cooke.
Other Notable Ligands
Quiz Question 1
|
Vitamin D binding protein is very similar to based on sequence similarity as well as an almost identical tertiary structure. However, HSA binds to actin instead, and is actually unable to bind to Vitamin D3. Based on what you have learned about the binding nature in domain I of Vitamin D Binding Protein, hypothesize a reason why HSA is unable to bind to Vitamin D3, but Vitamin D binding protein can. The following scenes should help guide your thinking = Domain I Helices 2,3,4 HSA; Domain I Helices 2,3,4 Vitamin D binding Protein.
See Also
Credits
Introduction - Uday Prakhya
Overall Structure - Elizabeth Swanson
Drug Binding Site - Alex Debreceni
Additional Features - Nick Rivelli
Quiz Question 1 - Robert Green
References
- ↑ Verboven C, Rabijns A, De Maeyer M, Van Baelen H, Bouillon R, De Ranter C. A structural basis for the unique binding features of the human vitamin D-binding protein. Nat Struct Biol. 2002 Feb;9(2):131-6. PMID:11799400 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nsb754
[1] Gomme PT, Bertolini J. 2004. Therapeutic potential of vitamin D-binding protein. Trends Biotechnol. 22:340–345.
[2] Haddad JG. 1995. Plasma vitamin D-binding protein (Gc-globulin): Multiple tasks. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 53:579–582.
[3] Otterbein LR, Cosio C, Graceffa P, Dominguez R. 2002. Crystal structures of the vitamin D-binding protein and its complex with actin: structural basis of the actin-scavenger system. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 99:8003–8008.
[4] Speeckaert M, Huang G, Delanghe JR, Taes YEC. 2006. Biological and clinical aspects of the vitamin D binding protein (Gc-globulin) and its polymorphism. Clin. Chim. Acta 372:33–42.
[5] Verboven C, Rabijns A, De Maeyer M, Van Baelen H, Bouillon R, De Ranter C. 2002. A structural basis for the unique binding features of the human vitamin D-binding protein. Nat. Struct. Biol. 9:131–6.
[6] White P, Cooke N. 2000. The multifunctional properties and characteristics of vitamin D-binding protein. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 11:320–327.
