Sandbox Reserved 428
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
(→'''Vitamin D receptor/vitamin D (1db1)''') |
|||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
[[Student Projects for UMass Chemistry 423 Spring 2016]] | [[Student Projects for UMass Chemistry 423 Spring 2016]] | ||
| + | <StructureSection load='1db1' size='350' side='right' caption='caption for Molecular Playground (PDB entry [[1db1]])' scene=''> | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
| - | <Structure load='1db1' size='300' frame='true' align='right' caption='pdbcode 1db1, Insert caption here' scene='Insert optional scene name here' /> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
-Rickets, hypocalcemia, secondary hyperparathyroidism, total alopecia<br> | -Rickets, hypocalcemia, secondary hyperparathyroidism, total alopecia<br> | ||
<i>Importance</i><br> | <i>Importance</i><br> | ||
| - | <br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br> | ||
<scene name='48/483885/Color1/6'>Amino/Carboxy Color Scene</scene> | <scene name='48/483885/Color1/6'>Amino/Carboxy Color Scene</scene> | ||
==Overall Structure== | ==Overall Structure== | ||
| - | + | Diagram of Protein Protein indicates alpha helices, while yellow indicates beta sheets: | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
Outline: | Outline: | ||
-Discuss Primary Structure[ | -Discuss Primary Structure[ | ||
| Line 38: | Line 35: | ||
-427 amino acids, 48289 Da (http://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl?gene=VDR) | -427 amino acids, 48289 Da (http://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl?gene=VDR) | ||
| - | <br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br> | ||
==Binding Interactions== | ==Binding Interactions== | ||
| - | <Structure load='1db1' size='300' frame='true' align='right' caption='pdbcode, Insert caption here' scene='Insert optional scene name here' /> | ||
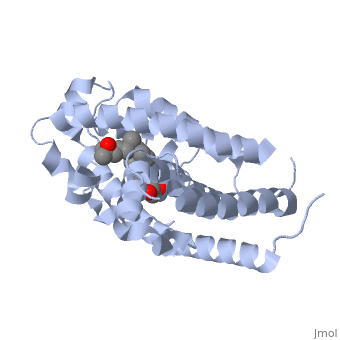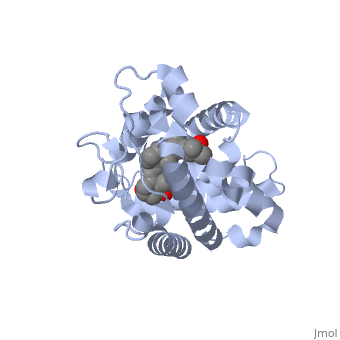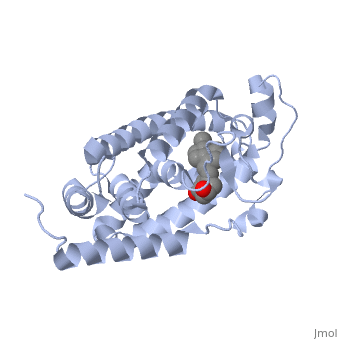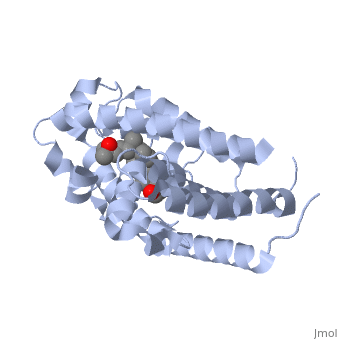
Protein 1db1 is found to complex with 1,25 Dihydroxy <scene name='48/483885/Vitamin_d3/1'>Vitamin D3</scene>. This molecule has three notable alcohol groups that have the ability to participate in interactions with the protein. Vitamin D3 has a large number of relations with the residues on the protein chain. First in the sequence are <scene name='48/483885/Residues_140-151/2'>residues 140-151</scene>. Tyr143, shown in blue, is the closest to the ligand at 2.83 angstroms. This is sightly large but there is still the possibility of hydrogen bonding. Tyr147 in green and Phe150 in black are also known to have interactions with Vitamin D3 they are farther away and therefore less significant. Outline: as has been started, the interactions of the various residues will be covered. The types of bonds that 1db1 and VDX form will be elaborated as well | Protein 1db1 is found to complex with 1,25 Dihydroxy <scene name='48/483885/Vitamin_d3/1'>Vitamin D3</scene>. This molecule has three notable alcohol groups that have the ability to participate in interactions with the protein. Vitamin D3 has a large number of relations with the residues on the protein chain. First in the sequence are <scene name='48/483885/Residues_140-151/2'>residues 140-151</scene>. Tyr143, shown in blue, is the closest to the ligand at 2.83 angstroms. This is sightly large but there is still the possibility of hydrogen bonding. Tyr147 in green and Phe150 in black are also known to have interactions with Vitamin D3 they are farther away and therefore less significant. Outline: as has been started, the interactions of the various residues will be covered. The types of bonds that 1db1 and VDX form will be elaborated as well | ||
| - | <br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br> | ||
==Additional Features== | ==Additional Features== | ||
| - | <Structure load='1db1' size='300' frame='true' align='right' caption='pdbcode, Insert caption here' scene='Insert optional scene name here' /> | ||
A mutation in the transcription of the protein has the potential to result in the disease known as type 2 rickets. The mutation results in the <scene name='48/483885/Heterodimer/1'>Heterodimer</scene> not forming properly. Therefore VDR cannot complex with VDX. | A mutation in the transcription of the protein has the potential to result in the disease known as type 2 rickets. The mutation results in the <scene name='48/483885/Heterodimer/1'>Heterodimer</scene> not forming properly. Therefore VDR cannot complex with VDX. | ||
Outline: | Outline: | ||
| Line 54: | Line 47: | ||
| - | <br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br> | ||
==Quiz Question 1== | ==Quiz Question 1== | ||
| - | <Structure load='1db1' size='300' frame='true' align='right' caption='pdbcode, Insert caption here' scene='Insert optional scene name here' /> | ||
Quiz question: More information is needed to focus what the quiz should be about. Possibly related to how the secondary structure is comprised almost entirely of alpha helices, and how that relates to the amino acid sequences. | Quiz question: More information is needed to focus what the quiz should be about. Possibly related to how the secondary structure is comprised almost entirely of alpha helices, and how that relates to the amino acid sequences. | ||
| - | <br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br> | ||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
Revision as of 21:55, 2 March 2016
| This Sandbox is Reserved from January 19, 2016, through August 31, 2016 for use for Proteopedia Team Projects by the class Chemistry 423 Biochemistry for Chemists taught by Lynmarie K Thompson at University of Massachusetts Amherst, USA. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 425 through Sandbox Reserved 439. |
Vitamin D receptor/vitamin D (1db1)[1]
by Roger Crocker, Kate Daborowski, Patrick Murphy, Benjamin Rizkin and Aaron Thole
Student Projects for UMass Chemistry 423 Spring 2016
| |||||||||||