We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Gyrase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
==Function== | ==Function== | ||
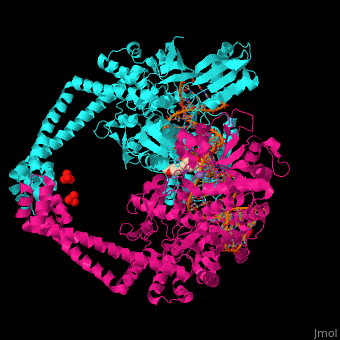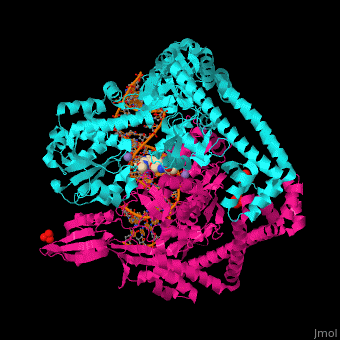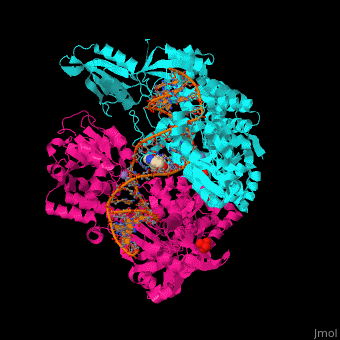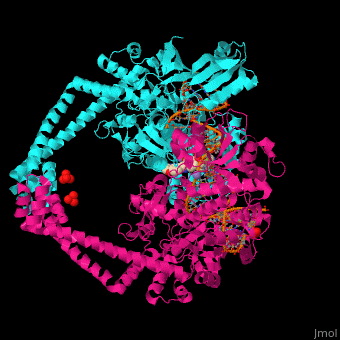
| - | '''Gyrase (Gyr)''' is a type of topoisomerase II in prokaryotes which unwinds double stranded DNA. The DNA Gyr cutting allows the formation of a negative DNA supercoil which enables replication of DNA. Gyr consists of 2 subunits: GyrA and GyrB. Reverse gyrase (Top-RG) is a type of topoisomerase I which catalyses the formation of positive DNA supercoil. <ref>PMID: | + | '''Gyrase (Gyr)''' is a type of topoisomerase II in prokaryotes which unwinds double stranded DNA. The DNA Gyr cutting allows the formation of a negative DNA supercoil which enables replication of DNA<StructureSection load='2pm4' size='350' side='right' caption='Human α-defensin 1 (PDB entry [[2pm4]])' scene='50/509378/Cv/4'>. Gyr consists of 2 subunits: GyrA and GyrB. '''Reverse gyrase''' (Top-RG) is a type of topoisomerase I which catalyses the formation of positive DNA supercoil. <ref>PMID:15673717</ref> See also [[Isomerases]]. |
==Relevance== | ==Relevance== | ||
Revision as of 07:46, 20 March 2016
| |||||||||||
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, David Canner, Joel L. Sussman