This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Heat shock factor
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
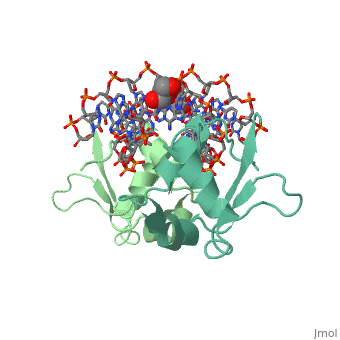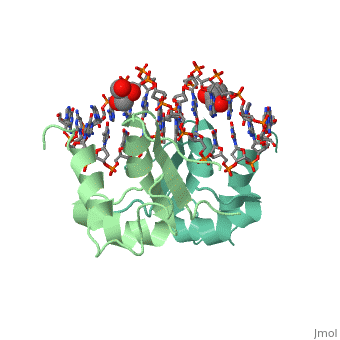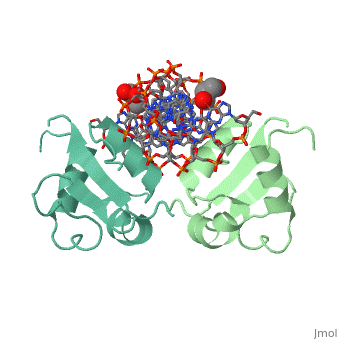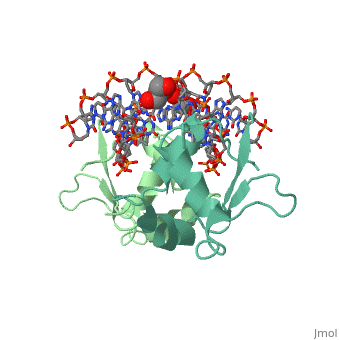
'''Heat shock factor''' (HSF) are transcriptional activators of heat shock genes. HSF bind to heat shock sequence elements throughout the genome with a consensus array of three oppositely oriented sequence AGGAN and activate transcription. Each HSF monomer contains one C-terminal and 3 N-terminal leucine zippers. Two sequences flanking the N-terminal leucine zippers contain the consensus nuclear localization signal (NLS). The DNA-binding domain (DBD) of HSF lies in the N-terminal of the first NLS region<ref>PMID:8441385</ref>. | '''Heat shock factor''' (HSF) are transcriptional activators of heat shock genes. HSF bind to heat shock sequence elements throughout the genome with a consensus array of three oppositely oriented sequence AGGAN and activate transcription. Each HSF monomer contains one C-terminal and 3 N-terminal leucine zippers. Two sequences flanking the N-terminal leucine zippers contain the consensus nuclear localization signal (NLS). The DNA-binding domain (DBD) of HSF lies in the N-terminal of the first NLS region<ref>PMID:8441385</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Relevance == | ||
| + | Depletion of HSF-1 is associated with accumulation of pathogenic androgen receptor in neurodegenerative diseases<ref>PMID:23360996</ref>. | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
Revision as of 10:56, 20 March 2016
| |||||||||||