We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
User:Daniel Schemenauer/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
= metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 5 ''Homo sapiens''= | = metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 5 ''Homo sapiens''= | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
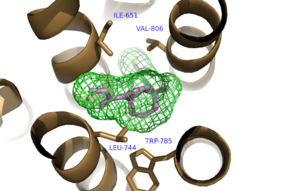
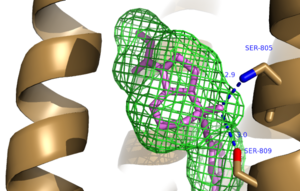
| - | G-coupled protein receptors [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/G_protein–coupled_receptor GPCR] are trans-membrane proteins that are integral to cell signaling. The human genome encodes for approximately 750 GPCRS, 350 of which are known to respond to extracellular ligands.<ref name="GPCRRep">PMID: 12679517 </ref>. GPCRs are divided into four major classes; Class A,B,C, and F.<ref name="MSGPCR">PMID:23407534</ref>. Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 5 (mGlu<sub>5</sub>) is a class C GPCR that is involved in the G<sub>q</sub> pathway <ref name="CCGPCR">PMID:12782243</ref>. mGlu<sub>5</sub>is highly expressed in neuronal and glial cells in the central nervous system, where glutamate serves as the major neurotransmitter. When glutamate binds to the extracellular domain of mGlu<sub>5</sub>, consisting of the Venus Fly Trap <ref name="Primary">PMID: 25042998 </ref>, a conformational change through the tram-membrane domains activates the coupled G-protein. This G-protein disassociates and the alpha subunit activates [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phospholipase_C Phospholipase C] which has the final outcome of increased neuronal activity<ref name="MSGPCR">PMID:23407534</ref>. | + | G-coupled protein receptors [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/G_protein–coupled_receptor GPCR] are trans-membrane proteins that are integral to cell signaling. The human genome encodes for approximately 750 GPCRS, 350 of which are known to respond to extracellular ligands.<ref name="GPCRRep">PMID: 12679517 </ref>. GPCRs are divided into four major classes based on sequence similarity and transduction mechanism; Class A,B,C, and F.<ref name="MSGPCR">PMID:23407534</ref>. Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 5 (mGlu<sub>5</sub>) is a class C GPCR that is involved in the G<sub>q</sub> pathway <ref name="CCGPCR">PMID:12782243</ref>. mGlu<sub>5</sub>is highly expressed in neuronal and glial cells in the central nervous system, where glutamate serves as the major neurotransmitter. When glutamate binds to the extracellular domain of mGlu<sub>5</sub>, consisting of the Venus Fly Trap <ref name="Primary">PMID: 25042998 </ref>, a conformational change through the tram-membrane domains activates the coupled G-protein. This G-protein disassociates and the alpha subunit activates [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phospholipase_C Phospholipase C] which has the final outcome of increased neuronal activity<ref name="MSGPCR">PMID:23407534</ref>. |
Revision as of 12:25, 28 March 2016
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Vassilatis DK, Hohmann JG, Zeng H, Li F, Ranchalis JE, Mortrud MT, Brown A, Rodriguez SS, Weller JR, Wright AC, Bergmann JE, Gaitanaris GA. The G protein-coupled receptor repertoires of human and mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Apr 15;100(8):4903-8. Epub 2003 Apr 4. PMID:12679517 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0230374100
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Venkatakrishnan AJ, Deupi X, Lebon G, Tate CG, Schertler GF, Babu MM. Molecular signatures of G-protein-coupled receptors. Nature. 2013 Feb 14;494(7436):185-94. doi: 10.1038/nature11896. PMID:23407534 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature11896
- ↑ Pin JP, Galvez T, Prezeau L. Evolution, structure, and activation mechanism of family 3/C G-protein-coupled receptors. Pharmacol Ther. 2003 Jun;98(3):325-54. PMID:12782243
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Dore AS, Okrasa K, Patel JC, Serrano-Vega M, Bennett K, Cooke RM, Errey JC, Jazayeri A, Khan S, Tehan B, Weir M, Wiggin GR, Marshall FH. Structure of class C GPCR metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 transmembrane domain. Nature. 2014 Jul 31;511(7511):557-62. doi: 10.1038/nature13396. Epub 2014 Jul 6. PMID:25042998 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature13396