Sandbox Reserved 1175
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
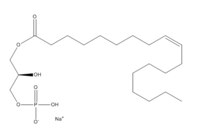
==Lysophosphatodic Acid== | ==Lysophosphatodic Acid== | ||
==Function== | ==Function== | ||
| - | LPA, a signaling phospholipid, can attach to three specific G-protein-coupled receptors. LPA can activate multiple pathways in particular, Ras and Pho which belong to the family of GTPases. Another use of LPA is it can help in stimulation of cell migration <ref name=" | + | LPA, a signaling phospholipid, can attach to three specific G-protein-coupled receptors. LPA can activate multiple pathways in particular, Ras and Pho which belong to the family of GTPases. Another use of LPA is it can help in stimulation of cell migration <ref name="Moolenaar"> DOI: 10.1002/bies.20081 </ref>. |
== Structure == | == Structure == | ||
<scene name='72/721546/Lpa-helices/1'>Helices</scene> | <scene name='72/721546/Lpa-helices/1'>Helices</scene> | ||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
==Clinical Testing== | ==Clinical Testing== | ||
| - | LPA is still in the clinical stage of testing. So far the LPA receptors have had physiological effects on every organism that it has been tested with. There have been studies done looking at what happens with infertility, fibrosis, pain, and cancer when they come into contact with LPA receptors. LPA receptors are commonly found in serum and saliva. <ref name= " | + | LPA is still in the clinical stage of testing. So far the LPA receptors have had physiological effects on every organism that it has been tested with. There have been studies done looking at what happens with infertility, fibrosis, pain, and cancer when they come into contact with LPA receptors. LPA receptors are commonly found in serum and saliva. <ref name= "Moolenaar"/>. |
===Pain=== | ===Pain=== | ||
Since LPA receptors are present in the nervous system, they are able to help manage neuropathic pain <ref name= "Inoue"> DOI:10.1038/nm1060 </ref>. | Since LPA receptors are present in the nervous system, they are able to help manage neuropathic pain <ref name= "Inoue"> DOI:10.1038/nm1060 </ref>. | ||
Revision as of 06:41, 29 March 2016
| This Sandbox is Reserved from Jan 11 through August 12, 2016 for use in the course CH462 Central Metabolism taught by R. Jeremy Johnson at the Butler University, Indianapolis, USA. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1160 through Sandbox Reserved 1184. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Human Lysophosphatodic Acid Receptor 1
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Moolenaar WH, van Meeteren LA, Giepmans BN. The ins and outs of lysophosphatidic acid signaling. Bioessays. 2004 Aug;26(8):870-81. PMID:15273989 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/bies.20081
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Chrencik JE, Roth CB, Terakado M, Kurata H, Omi R, Kihara Y, Warshaviak D, Nakade S, Asmar-Rovira G, Mileni M, Mizuno H, Griffith MT, Rodgers C, Han GW, Velasquez J, Chun J, Stevens RC, Hanson MA. Crystal Structure of Antagonist Bound Human Lysophosphatidic Acid Receptor 1. Cell. 2015 Jun 18;161(7):1633-43. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.06.002. PMID:26091040 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2015.06.002
- ↑ Inoue M, Rashid MH, Fujita R, Contos JJ, Chun J, Ueda H. Initiation of neuropathic pain requires lysophosphatidic acid receptor signaling. Nat Med. 2004 Jul;10(7):712-8. Epub 2004 Jun 13. PMID:15195086 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nm1060
- ↑ Tager AM, LaCamera P, Shea BS, Campanella GS, Selman M, Zhao Z, Polosukhin V, Wain J, Karimi-Shah BA, Kim ND, Hart WK, Pardo A, Blackwell TS, Xu Y, Chun J, Luster AD. The lysophosphatidic acid receptor LPA1 links pulmonary fibrosis to lung injury by mediating fibroblast recruitment and vascular leak. Nat Med. 2008 Jan;14(1):45-54. Epub 2007 Dec 9. PMID:18066075 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nm1685