We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1165
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<StructureSection load='4l6r' size='350' side='right' caption='Class B 7TM' scene='72/721535/Opening_orientation/1'> | <StructureSection load='4l6r' size='350' side='right' caption='Class B 7TM' scene='72/721535/Opening_orientation/1'> | ||
| - | =Human Glucagon Class B G Protein-Coupled Receptors (GPCRs)= | + | ==Human Glucagon Class B G Protein-Coupled Receptors (GPCRs)== |
| - | =Introduction= | + | ===Introduction=== |
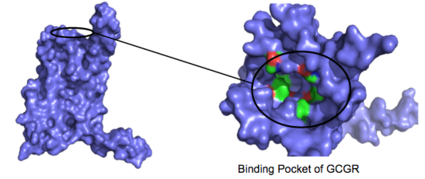
<scene name='72/721536/Class_b_receptor/1'>Human glucagon class B G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs)</scene>, also known as [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Secretin_receptor_family secretin-like receptors], are a subfamily of the more well known class A ([https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rhodopsin-like_receptors rhodopsin-like]) glucagon receptor family<ref name="Intro">PMID: 24359917</ref> . Located in the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Liver liver], class B glucagon receptors (GCGRs) are activated by the binding of the hormonal peptide [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glucagon glucagon] which leads to the release of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glucose glucose] into the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Circulatory_system bloodstream] and plays an essential role in [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Blood_sugar_regulation glucose homeostasis]. Class B GCGRs are composed of a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Liver seven transmembrane domain] (7TM) and [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Liver extracellular domain] (ECD) that are of vital importance in glucagon binding. In comparison, class A vs. class B glucagon receptors share less than fifteen percent sequence homology, but both share this 7TM which is a primary area of comparison between the two <ref name="Intro">PMID: 24359917</ref>. The understanding of class A family of GCGRs structure-function [https://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/Structural_Biochemistry/Enzyme_Catalytic_Mechanism mechanism] has made great progress over the past few years, but understanding of class B has fallen behind. | <scene name='72/721536/Class_b_receptor/1'>Human glucagon class B G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs)</scene>, also known as [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Secretin_receptor_family secretin-like receptors], are a subfamily of the more well known class A ([https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rhodopsin-like_receptors rhodopsin-like]) glucagon receptor family<ref name="Intro">PMID: 24359917</ref> . Located in the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Liver liver], class B glucagon receptors (GCGRs) are activated by the binding of the hormonal peptide [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glucagon glucagon] which leads to the release of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glucose glucose] into the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Circulatory_system bloodstream] and plays an essential role in [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Blood_sugar_regulation glucose homeostasis]. Class B GCGRs are composed of a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Liver seven transmembrane domain] (7TM) and [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Liver extracellular domain] (ECD) that are of vital importance in glucagon binding. In comparison, class A vs. class B glucagon receptors share less than fifteen percent sequence homology, but both share this 7TM which is a primary area of comparison between the two <ref name="Intro">PMID: 24359917</ref>. The understanding of class A family of GCGRs structure-function [https://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/Structural_Biochemistry/Enzyme_Catalytic_Mechanism mechanism] has made great progress over the past few years, but understanding of class B has fallen behind. | ||
Revision as of 10:55, 29 March 2016
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Hollenstein K, de Graaf C, Bortolato A, Wang MW, Marshall FH, Stevens RC. Insights into the structure of class B GPCRs. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2014 Jan;35(1):12-22. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2013.11.001. Epub, 2013 Dec 18. PMID:24359917 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tips.2013.11.001
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 Siu FY, He M, de Graaf C, Han GW, Yang D, Zhang Z, Zhou C, Xu Q, Wacker D, Joseph JS, Liu W, Lau J, Cherezov V, Katritch V, Wang MW, Stevens RC. Structure of the human glucagon class B G-protein-coupled receptor. Nature. 2013 Jul 25;499(7459):444-9. doi: 10.1038/nature12393. Epub 2013 Jul 17. PMID:23863937 doi:10.1038/nature12393
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Miller LJ, Dong M, Harikumar KG. Ligand binding and activation of the secretin receptor, a prototypic family B G protein-coupled receptor. Br J Pharmacol. 2012 May;166(1):18-26. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01463.x. PMID:21542831 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01463.x
- ↑ Thomsen J, Kristiansen K, Brunfeldt K, Sundby F. The amino acid sequence of human glucagon. FEBS Lett. 1972 Apr 1;21(3):315-319. PMID:11946536
- ↑ Bortolato A, Dore AS, Hollenstein K, Tehan BG, Mason JS, Marshall FH. Structure of Class B GPCRs: new horizons for drug discovery. Br J Pharmacol. 2014 Jul;171(13):3132-45. doi: 10.1111/bph.12689. PMID:24628305 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/bph.12689
- ↑ Mukund S, Shang Y, Clarke HJ, Madjidi A, Corn JE, Kates L, Kolumam G, Chiang V, Luis E, Murray J, Zhang Y, Hotzel I, Koth CM, Allan BB. Inhibitory mechanism of an allosteric antibody targeting the glucagon receptor. J Biol Chem. 2013 Nov 4. PMID:24189067 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M113.496984
- ↑ Hoare SR. Allosteric modulators of class B G-protein-coupled receptors. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2007 Sep;5(3):168-79. doi: 10.2174/157015907781695928. PMID:19305799 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.2174/157015907781695928
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 Yang L, Yang D, de Graaf C, Moeller A, West GM, Dharmarajan V, Wang C, Siu FY, Song G, Reedtz-Runge S, Pascal BD, Wu B, Potter CS, Zhou H, Griffin PR, Carragher B, Yang H, Wang MW, Stevens RC, Jiang H. Conformational states of the full-length glucagon receptor. Nat Commun. 2015 Jul 31;6:7859. doi: 10.1038/ncomms8859. PMID:26227798 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/ncomms8859