Introduction
What to talk about:
What class of proteins it belongs to, how its characterized, other names
-Nuclear hormone receptor
-Component of Mediator complex
Basic function
-transcription regulator of hormone sensitive genes
-has central role in calcium homeostasis
Retailed Diseases
-Rickets, hypocalcemia, secondary hyperparathyroidism, total alopecia
Importance
Overall Structure
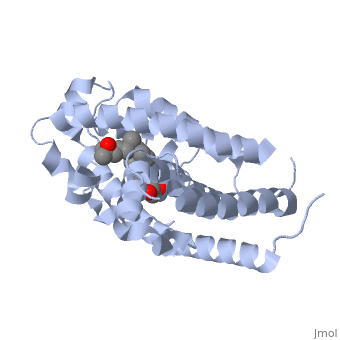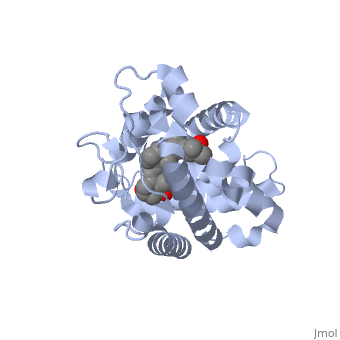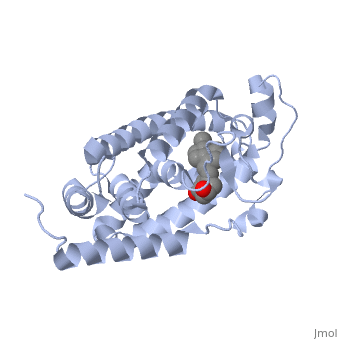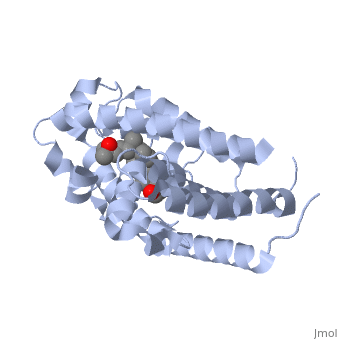
The protein has an active conformation of 1,25 (OH)_2D_3 that has a ligand binding pocket in its active folded state. The ligand interacts with with the activation helix by stabilizing the agonist position. This is accomplished through Van der Waals interactions between the ligand and the activation helix. The activation ligand is a nuclear receptor (VDR).
There is some empty space observed around the aliphatic chain.
Diagram of Protein Protein indicates alpha helices, while yellow indicates beta sheets:
Outline:
-Discuss Primary Structure[
-Discuss Secondary Structure
-Comprised of alpha helices and 1 beta sheet
-Discuss tertiary structure
-No quaternary structure
-427 amino acids, 48289 Da (http://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl?gene=VDR)
The vitamin d receptor contains 427 amino acids with a total molecular weight of 48,289 Da [
Binding Interactions
Protein 1db1 is found to complex with 1,25 Dihydroxy . This molecule has three notable alcohol groups shown in red. Oxygen is electronegative, giving alcohols the ability to participate in hydrogen bonding with the protein. Vitamin D3 has a large number of relations with the residues on the protein chain. First in the sequence are . Tyr143, shown in blue, is the closest to the ligand at 2.83 angstroms. This is sightly large but there is still the possibility of hydrogen bonding. Tyr147 in green and Phe150 in black are also known to have interactions with Vitamin D3 they are farther away and therefore less significant. Next down the peptide chain are . Ser237, shown in green, has significant interactions with vitamin D3 this can be seen by its short distance 2.78 angstroms. Only 40 residues away, more hydrogen bonding is occurring. form bonds with the same oxygen atoms as Tyr143 and Ser237 respectively. This means that the oxygen atoms of vitamin D3, when bound to the receptor, are negatively charged and stabilized by protons. On the opposite end of vitamin D3 there is an additional negatively charged oxygen. Although this oxygen does not participate in hydrogen bonding. , shown in blue and green respectively, Contain aromatic rings. These rings are able to momentarily accept the electrons donated by the oxygen because they can delocalize the charge. This creates two pseudo-covalent bonds that is approximately 2.81 angstroms. When looking at , it can be seen that all of the binding sights are centered around oxygen
Additional Features
Hereditary hypocalcemic Vitamin D resistant rickets (HHVDRR) is a condition that mostly occurs in children and results in soft and weak bone formation, which often causes deformities in bone. A lack of proper nutrients, Vitamin D in particular, as well as defects in the Vitamin D receptor can cause rickets in humans. This can occur when the VDR is impaired in its ability to activate transcription in response to the 1,25-(OH)2D3 ligand [1]. VDR regulates the hormonal form of Vitamin D, through modifying the transcription of the target to a certain sequence of DNA, called the Vitamin D responsive element (VDRE). This activation requires an additional receptor, which is a Retinoid X Receptor (RXR) to bind to the heterodimer [1]. A mutation in the transcription of the protein has the potential to result in the disease known as type 2 rickets. The mutation results in the not forming properly. The failure in the transcription of this process from the failing of the binding of the heterodimer can cause this disease. Current research shows that there are two mechanisms that can cause Rickets to occur within the body. The first is a point mutation of an amino acid in the zinc finger region of the VDR that reduces the binding of the heterodimer, which is found in the residues 21-85 [1]. The other is a premature stop codon in the DNA sequences that does not allow for the full transcription, which can have an effect of reducing the affinity of the heterodimer binding [1].
Outline:
-Vitamin D receptor is a transcription factor that when complexes with with vitamin D it helps regulate calcium uptake
-Interactions with the DNA
-Discuss mutations in Vitamin D receptor (Rickets)
-Regulating hair cycle
-Examine attempts to regulate Vitamin D receptor
Quiz Question 1
Quiz question: More information is needed to focus what the quiz should be about. Possibly related to how the secondary structure is comprised almost entirely of alpha helices, and how that relates to the amino acid sequences.
See Also
Credits
Introduction - Kate Daborowski
Overall Structure - Aaron Thole and Benjamin Rizkin
Drug Binding Site - Roger Crocker
Additional Features - Patrick Murphy
Quiz Question 1 - name of team member
References
- ↑ Rochel N, Wurtz JM, Mitschler A, Klaholz B, Moras D. The crystal structure of the nuclear receptor for vitamin D bound to its natural ligand. Mol Cell. 2000 Jan;5(1):173-9. PMID:10678179
VDR Gene http://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl?gene=VDR (accessed Apr 2, 2016).
Vitamin D Receptor http://pdb101.rcsb.org/motm/155 (accessed Apr 4, 2016).
3D Binding Pocket http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore/jmol.do?structureId=1DB1&residueNr=VDX (accessed Apr 4, 2016).