We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1160
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Human metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 transmembrane domain == | == Human metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 transmembrane domain == | ||
| - | <StructureSection load='4oo9' size='300' frame='true' side='right' caption='Human metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 transmembrane domain' scene='72/721531/Protien_clean_sce/ | + | <StructureSection load='4oo9' size='300' frame='true' side='right' caption='Human metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 transmembrane domain' scene='72/721531/Protien_clean_sce/5'> |
Receiving and responding to extracellular messages is critical to the proper function of the nervous system. Glutamate is the primary excitory neurotransmitter of the Central Nervous System (CNS), and metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 is a key member of the glutamate signaling pathway<ref name="Dore" />. Metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 is a homodimeric [[GPCR]] that resides in the cellular membrane <ref name="Dore" />. mGlu5 is a member of the Class C GPCR family and can further be categorized into the Group I subgroup<ref name="Wu" />. | Receiving and responding to extracellular messages is critical to the proper function of the nervous system. Glutamate is the primary excitory neurotransmitter of the Central Nervous System (CNS), and metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 is a key member of the glutamate signaling pathway<ref name="Dore" />. Metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 is a homodimeric [[GPCR]] that resides in the cellular membrane <ref name="Dore" />. mGlu5 is a member of the Class C GPCR family and can further be categorized into the Group I subgroup<ref name="Wu" />. | ||
The functionality of the mGlu5 receptor is determined by conformational changes throughout multiple domains. mGlu5 will bind glutamate through its extracellular Venus flytrap domain and the signal will be transduced across the membrane to a heterotrimeric G protein, which will ultimately lead to calcium release and the activation of [[PKC]]<ref name="Wu" />. The signal is relayed through a Gq/11 pathway<ref name="Dore" />. Activated PKC will elicit a excitory post-synaptic response and modulate long term potentiation<ref name="Wu" />. | The functionality of the mGlu5 receptor is determined by conformational changes throughout multiple domains. mGlu5 will bind glutamate through its extracellular Venus flytrap domain and the signal will be transduced across the membrane to a heterotrimeric G protein, which will ultimately lead to calcium release and the activation of [[PKC]]<ref name="Wu" />. The signal is relayed through a Gq/11 pathway<ref name="Dore" />. Activated PKC will elicit a excitory post-synaptic response and modulate long term potentiation<ref name="Wu" />. | ||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
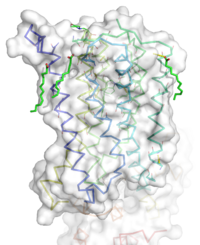
[[Image:STR.png|200 px|left|thumb|'''Figure 1''': Overall Structure of the mGlu5 TMD. The polar heads on the Oliec acids orient the image with the top oriented extracellularly, the middle portion inserted into the membrane, and the lower portion oriented intracellularly. The white exterior represents the surface of the protien, and the multicolored lines interior to the surface represent the backbones 7 transmembrane alpha helices. ]] | [[Image:STR.png|200 px|left|thumb|'''Figure 1''': Overall Structure of the mGlu5 TMD. The polar heads on the Oliec acids orient the image with the top oriented extracellularly, the middle portion inserted into the membrane, and the lower portion oriented intracellularly. The white exterior represents the surface of the protien, and the multicolored lines interior to the surface represent the backbones 7 transmembrane alpha helices. ]] | ||
=== Overview === | === Overview === | ||
| - | The mGlu5 TMD contains 7 <scene name='72/721531/Protien_7_helices/3'> alpha helices</scene> that spans the membrane. The protein was crystallized with <scene name='72/721531/Protien_clean_sce/ | + | The mGlu5 TMD contains 7 <scene name='72/721531/Protien_7_helices/3'> alpha helices</scene> that spans the membrane. The protein was crystallized with <scene name='72/721531/Protien_clean_sce/5'>Oleic acid</scene>. On the top portion of the protein several critical extracellular loops connect the TMD to the CRD. The binding pocket can be found near the middle of the protein, and is mainly comprised of hydrophobic amino acids with more polar amino acids found in the upper and lower portions of the binding site. Inserted into the biding pocket is the negative allosteric modulator [http://www.en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mavoglurant mavoglurant]. The TMD is in an inactive conformation, since mavoglurant is bound. Also, the deletion of the flexible domains leaves the mGlu5 receptor unable to bind to its [[GPCR]]. The inactive state is maintained by multiple ionic locks whose positions determine the active versus inactive conformation. |
=== Extracellular Domain === | === Extracellular Domain === | ||
These are the <scene name='72/721532/Ecl_trail_1/7'>Extracellular Loops</scene> with extracellular loops (ECLs) 1, 2, and 3 highlighted in purple. Additionally in the ECL domain, a <scene name='72/721532/Ecl_trail_1/6'>disulfide bond</scene> is attached to both Helix 3 and the amino acid chain between Helix 5 and the N terminus. The disulfide bond is highlighted in yellow, and it is conserved in all classes of glutamate receptor 5 transmembrane domains<ref name="Wu" />. | These are the <scene name='72/721532/Ecl_trail_1/7'>Extracellular Loops</scene> with extracellular loops (ECLs) 1, 2, and 3 highlighted in purple. Additionally in the ECL domain, a <scene name='72/721532/Ecl_trail_1/6'>disulfide bond</scene> is attached to both Helix 3 and the amino acid chain between Helix 5 and the N terminus. The disulfide bond is highlighted in yellow, and it is conserved in all classes of glutamate receptor 5 transmembrane domains<ref name="Wu" />. | ||
Revision as of 12:12, 12 April 2016
Human metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 transmembrane domain
| |||||||||||