We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1170
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
=== Mechanisms of Insulin Secretion === | === Mechanisms of Insulin Secretion === | ||
| - | One proposed pathway of insulin secretion by hGPR40 involves the activation of the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gq_alpha_subunit G<sub>aq/11</sub>] protein complex. This complex then activates [[phospholipase C]] (PLC) which in turn | + | One proposed pathway of insulin secretion by hGPR40 involves the activation of the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gq_alpha_subunit G<sub>aq/11</sub>] protein complex. This complex then activates [[phospholipase C]] (PLC) which in turn hydrolyses [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phosphatidylinositol_4,5-bisphosphate phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate] to inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate (IP<sub>3</sub>) and diacylglycerol (DAG). IP<sub>3</sub> can then mediate the [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3560308/ influx of Ca<sup>2+</sup>] by moving into the cytoplasm, binding to the endoplasmic reticulum, and allowing for the release of Ca<sup>2+</sup> into the cytosol.<ref name="Burant"/> This increase in [Ca<sup>2+</sup>] amplifies the similar increase in [Ca<sup>2+</sup>] that results from high concentrations of glucose. In this way, hGPR40 mimics glucose dependent insulin secretion.<ref name="Itoh">PMID:12629551</ref> Overall, hGPR40 helps to amplify the Ca<sup>2+</sup> signal so that the cell secretes more insulin. |
Another pathway through which hGPR40 may induce insulin expression is through phospholipase D1 (PLD1). When free fatty acids bind to hGPR40, hGPR40 directly phosphorylates and activates PLD1. The PLD1 plays a role in controlling the organization of an actin network that plays in role in insulin secretion.<ref name="Burant"/> | Another pathway through which hGPR40 may induce insulin expression is through phospholipase D1 (PLD1). When free fatty acids bind to hGPR40, hGPR40 directly phosphorylates and activates PLD1. The PLD1 plays a role in controlling the organization of an actin network that plays in role in insulin secretion.<ref name="Burant"/> | ||
Revision as of 13:33, 12 April 2016
Human GPR40 (hGPR40), also known as Free Fatty Acid Receptor 1 (FFAR1)
| |||||||||||
References
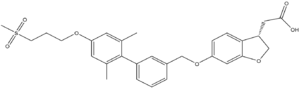
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 Srivastava A, Yano J, Hirozane Y, Kefala G, Gruswitz F, Snell G, Lane W, Ivetac A, Aertgeerts K, Nguyen J, Jennings A, Okada K. High-resolution structure of the human GPR40 receptor bound to allosteric agonist TAK-875. Nature. 2014 Jul 20. doi: 10.1038/nature13494. PMID:25043059 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature13494
- ↑ Morgan NG, Dhayal S. G-protein coupled receptors mediating long chain fatty acid signalling in the pancreatic beta-cell. Biochem Pharmacol. 2009 Dec 15;78(12):1419-27. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2009.07.020., Epub 2009 Aug 4. PMID:19660440 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2009.07.020
- ↑ Kebede M, Ferdaoussi M, Mancini A, Alquier T, Kulkarni RN, Walker MD, Poitout V. Glucose activates free fatty acid receptor 1 gene transcription via phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase-dependent O-GlcNAcylation of pancreas-duodenum homeobox-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Feb 14;109(7):2376-81. doi:, 10.1073/pnas.1114350109. Epub 2012 Jan 30. PMID:22308370 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1114350109
- ↑ Ma Z, Lin DC, Sharma R, Liu J, Zhu L, Li AR, Kohn T, Wang Y, Liu JJ, Bartberger MD, Medina JC, Zhuang R, Li F, Zhang J, Luo J, Wong S, Tonn GR, Houze JB. Discovery of the imidazole-derived GPR40 agonist AM-3189. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2016 Jan 1;26(1):15-20. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2015.11.050., Epub 2015 Nov 17. PMID:26620255 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2015.11.050
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 Burant CF. Activation of GPR40 as a therapeutic target for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2013 Aug;36 Suppl 2:S175-9. doi: 10.2337/dcS13-2037. PMID:23882043 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.2337/dcS13-2037
- ↑ Hong YH, Nishimura Y, Hishikawa D, Tsuzuki H, Miyahara H, Gotoh C, Choi KC, Feng DD, Chen C, Lee HG, Katoh K, Roh SG, Sasaki S. Acetate and propionate short chain fatty acids stimulate adipogenesis via GPCR43. Endocrinology. 2005 Dec;146(12):5092-9. Epub 2005 Aug 25. PMID:16123168 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1210/en.2005-0545
- ↑ Lin DC, Guo Q, Luo J, Zhang J, Nguyen K, Chen M, Tran T, Dransfield PJ, Brown SP, Houze J, Vimolratana M, Jiao XY, Wang Y, Birdsall NJ, Swaminath G. Identification and pharmacological characterization of multiple allosteric binding sites on the free fatty acid 1 receptor. Mol Pharmacol. 2012 Nov;82(5):843-59. doi: 10.1124/mol.112.079640. Epub 2012 Aug , 2. PMID:22859723 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1124/mol.112.079640
- ↑ Sum CS, Tikhonova IG, Neumann S, Engel S, Raaka BM, Costanzi S, Gershengorn MC. Identification of residues important for agonist recognition and activation in GPR40. J Biol Chem. 2007 Oct 5;282(40):29248-55. Epub 2007 Aug 15. PMID:17699519 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M705077200
- ↑ Sum CS, Tikhonova IG, Costanzi S, Gershengorn MC. Two arginine-glutamate ionic locks near the extracellular surface of FFAR1 gate receptor activation. J Biol Chem. 2009 Feb 6;284(6):3529-36. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M806987200. Epub 2008, Dec 8. PMID:19068482 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M806987200
- ↑ Itoh Y, Kawamata Y, Harada M, Kobayashi M, Fujii R, Fukusumi S, Ogi K, Hosoya M, Tanaka Y, Uejima H, Tanaka H, Maruyama M, Satoh R, Okubo S, Kizawa H, Komatsu H, Matsumura F, Noguchi Y, Shinohara T, Hinuma S, Fujisawa Y, Fujino M. Free fatty acids regulate insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells through GPR40. Nature. 2003 Mar 13;422(6928):173-6. Epub 2003 Feb 23. PMID:12629551 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature01478
- ↑ Kaku K, Enya K, Nakaya R, Ohira T, Matsuno R. Efficacy and safety of fasiglifam (TAK-875), a G protein-coupled receptor 40 agonist, in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled by diet and exercise: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase III trial. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2015 Jul;17(7):675-81. doi: 10.1111/dom.12467. Epub 2015 Apr, 23. PMID:25787200 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/dom.12467