We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Nos1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
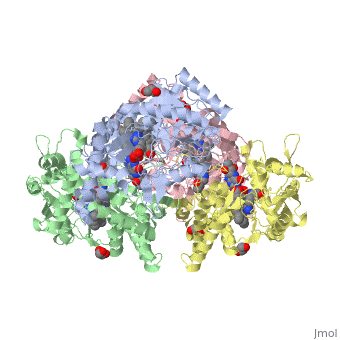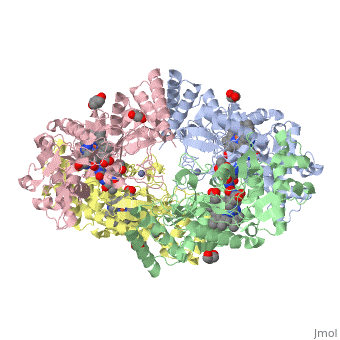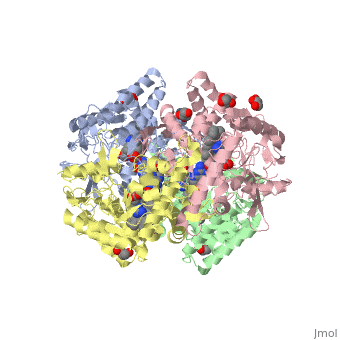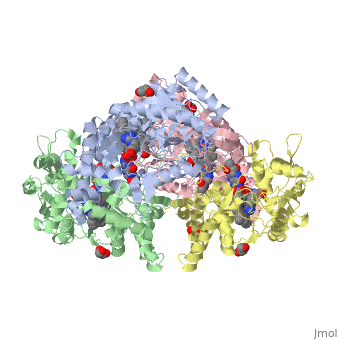
| + | Nos exists as a homodimer. This homodimer consists of two regions. One region is an N-terminal oxygenase domain and the other is a C-terminal reductase. The N-terminal oxygenase domain is an extended beta sheet cage with binding sites for heme and pterin. Nos has a N-terminal catalytic domain with a heme active site. Nos 1 also has a cofactor site nearby for tetrahydrobiopterin (H4B). Nos has a C-terminal reductase domain containing FMN, FAD and NADPH binding sites. Electrons are passed from FAD to FMN and then to the heme. This electron flow is controlled by the binding of CaM and Ca2+ in the linker region between the two major domains. The linker between the oxygenase and reductase domains contains a calmodulin-binding sequence. Nos1 is found in neuronal tissue. | ||
This is a sample scene created with SAT to <scene name="/12/3456/Sample/1">color</scene> by Group, and another to make <scene name="/12/3456/Sample/2">a transparent representation</scene> of the protein. You can make your own scenes on SAT starting from scratch or loading and editing one of these sample scenes. | This is a sample scene created with SAT to <scene name="/12/3456/Sample/1">color</scene> by Group, and another to make <scene name="/12/3456/Sample/2">a transparent representation</scene> of the protein. You can make your own scenes on SAT starting from scratch or loading and editing one of these sample scenes. | ||
Revision as of 16:36, 12 April 2016
Your Heading Here (maybe something like 'Structure')
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Hanson, R. M., Prilusky, J., Renjian, Z., Nakane, T. and Sussman, J. L. (2013), JSmol and the Next-Generation Web-Based Representation of 3D Molecular Structure as Applied to Proteopedia. Isr. J. Chem., 53:207-216. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijch.201300024
- ↑ Herraez A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2006 Jul;34(4):255-61. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644. PMID:21638687 doi:10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644