This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Sandbox Reserved 1160
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
== Discovery == | == Discovery == | ||
| - | The mGlu family of receptors was the first of the Class C [[GPCR]] to be extensively studied<ref name="Wu" />. The first regions of the protein crystallized and studied were the Venus Fly Trap domain and the cystiene -rich domain on the extracellular region of the receptor<ref name="Dore" />.The Venus Flytrap domain is a large extracellular domain that will selectively bind to glutamate<ref name="Wu" />. The CRD is a somewhat smaller domain composed of many | + | The mGlu family of receptors was the first of the Class C [[GPCR]] to be extensively studied<ref name="Wu" />. The first regions of the protein crystallized and studied were the Venus Fly Trap domain and the cystiene -rich domain on the extracellular region of the receptor<ref name="Dore" />.The Venus Flytrap domain is a large extracellular domain that will selectively bind to glutamate<ref name="Wu" />. The CRD is a somewhat smaller domain composed of many ß sheets and cystiene residues <ref name="Wu" />. The CRD acts as a signal mediator between the Venus Flytrap domain and the TMD of mGlu5, by linking to each domain with disulfide bonds<ref name="Wu" />. The hydrophobic nature and flexibility of the transmembrane domain made it difficult to crystallize. Recently, the human metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 transmembrane domain (TMD) was crystallized and a structure elucidated<ref name="Dore" />. Several modifications made to the TMD for successful crystallization. The protein was thermostabilized and flexible domains were removed<ref name="Dore" />. In total residue 2-568 and residues 837-1153 were excised from the structure. Also, a T4 -<scene name='72/721531/Protien_lys/3'>Lysozyme</scene> was inserted into intracellular loop 2 to add stability<ref name="Dore" />. |
== Structure== | == Structure== | ||
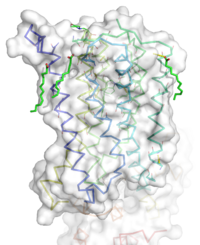
[[Image:STR.png|200 px|left|thumb|'''Figure 1''': Overall Structure of the mGlu5 TMD. The polar heads on the Oliec acids orient the image with the top oriented extracellularly, the middle portion inserted into the membrane, and the lower portion oriented intracellularly. The white exterior represents the surface of the protien, and the multicolored lines interior to the surface represent the backbones 7 transmembrane alpha helices. ]] | [[Image:STR.png|200 px|left|thumb|'''Figure 1''': Overall Structure of the mGlu5 TMD. The polar heads on the Oliec acids orient the image with the top oriented extracellularly, the middle portion inserted into the membrane, and the lower portion oriented intracellularly. The white exterior represents the surface of the protien, and the multicolored lines interior to the surface represent the backbones 7 transmembrane alpha helices. ]] | ||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
The mGlu5 TMD contains 7 <scene name='72/721531/Protien_7_helices/4'> alpha helices</scene> that spans the membrane. The protein was crystallized with <scene name='72/721531/Protien_clean_sce/5'>Oleic acid</scene>. On the top portion of the protein several critical extracellular loops connect the TMD to the CRD. The binding pocket can be found near the middle of the protein, and is mainly comprised of hydrophobic amino acids with more polar amino acids found in the upper and lower portions of the binding site. Inserted into the biding pocket is the negative allosteric modulator [http://www.en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mavoglurant mavoglurant]. The TMD is in an inactive conformation, since mavoglurant is bound. Also, the deletion of the flexible domains leaves the mGlu5 receptor unable to bind to its [[GPCR]]. The inactive state is maintained by multiple ionic locks whose positions determine the active versus inactive conformation. | The mGlu5 TMD contains 7 <scene name='72/721531/Protien_7_helices/4'> alpha helices</scene> that spans the membrane. The protein was crystallized with <scene name='72/721531/Protien_clean_sce/5'>Oleic acid</scene>. On the top portion of the protein several critical extracellular loops connect the TMD to the CRD. The binding pocket can be found near the middle of the protein, and is mainly comprised of hydrophobic amino acids with more polar amino acids found in the upper and lower portions of the binding site. Inserted into the biding pocket is the negative allosteric modulator [http://www.en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mavoglurant mavoglurant]. The TMD is in an inactive conformation, since mavoglurant is bound. Also, the deletion of the flexible domains leaves the mGlu5 receptor unable to bind to its [[GPCR]]. The inactive state is maintained by multiple ionic locks whose positions determine the active versus inactive conformation. | ||
=== Extracellular Domain === | === Extracellular Domain === | ||
| - | These are the <scene name='72/721532/Ecl_trail_7/2'>Extracellular Loops</scene> with extracellular loops (ECLs) 1, 2, and 3 highlighted in purple. Additionally in the ECL domain, a <scene name='72/721531/Ecl_trail_1/5'>disulfide bond</scene> is attached to both Helix 3 and the amino acid chain between Helix 5 and the N-terminus. Helix 3 and Helix 5 are colored in teal and | + | These are the <scene name='72/721532/Ecl_trail_7/2'>Extracellular Loops</scene> with extracellular loops (ECLs) <font color='purple'><b>1</b></font>, <font color='purple'><b>2</b></font>, and <font color='purple'><b>3</b></font> highlighted in <font color='purple'><b>purple</b></font>. Additionally in the ECL domain, a <scene name='72/721531/Ecl_trail_1/5'>disulfide bond</scene> is attached to both Helix 3 and the amino acid chain between Helix 5 and the N-terminus. <font color='teal'><b>Helix 3</b></font> and <font color='red'><b>Helix 5</b></font> are colored in <font color='teal'><b>teal</b></font> and <font color='red'><b>red</b></font> respectively. <font color='blue'><b>N-terminus is represented in blue</b></font>. The <span style="color:yellow;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">disulfide bond is higlighed in yellow</span>, and it is conserved in all classes of glutamate receptor 5 transmembrane domains<ref name="Wu" /> ECLs and the Helices are also factors that dictate how mavolgarent fits in the binding pocket (citations. The position of these factors can change the size of the binding pocket through tightening or widening. |
=== Binding Pocket === | === Binding Pocket === | ||
[[Image: Organic with clipped surface.png|200 px|left|thumb|'''Figure 2.''' Mavolugarent in its binding pocket of the 7TM region of mGLu5 Class C receptor. The binding pocket's surface is clipped in black with the substrate, mavolugarent, in red. The rest of the protein is colored in green. The binding pocket is present in the 7 Helix Transmembrane Domain that would be present in the phosolipid bilayer appearing as an intergral protein. The presence of mavolugarent inhibits the function of the metabotropic glutamate receptor.]] | [[Image: Organic with clipped surface.png|200 px|left|thumb|'''Figure 2.''' Mavolugarent in its binding pocket of the 7TM region of mGLu5 Class C receptor. The binding pocket's surface is clipped in black with the substrate, mavolugarent, in red. The rest of the protein is colored in green. The binding pocket is present in the 7 Helix Transmembrane Domain that would be present in the phosolipid bilayer appearing as an intergral protein. The presence of mavolugarent inhibits the function of the metabotropic glutamate receptor.]] | ||
Revision as of 00:14, 19 April 2016
Human metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 transmembrane domain
| |||||||||||