We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1165
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
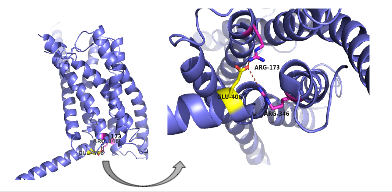
| - | [[Image:Screen Shot 2016-03-29 at 3.24.43 PM.png|(|):|400 px|center|thumb|'''Figure 5: Salt Bridge'''. The non-covalent interactions between residues Glu 406, Arg 173, and Arg 346 form a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Denticity tridentate] salt bridge. The Glu 406 acts as the central residue in the tridentate salt bridge; Arg 173 and Arg 436 both | + | [[Image:Screen Shot 2016-03-29 at 3.24.43 PM.png|(|):|400 px|center|thumb|'''Figure 5: Salt Bridge'''. The non-covalent interactions between residues Glu 406, Arg 173, and Arg 346 form a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Denticity tridentate] salt bridge. The Glu 406 acts as the central residue in the tridentate salt bridge; Arg 173 and Arg 436 both [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chelation chelating] with Glu 406. The salt bridge is located on the intracellular side of the transmembrane helices.]] |
| Line 45: | Line 45: | ||
=Clinical Relevancy= | =Clinical Relevancy= | ||
Of the fifteen human class B GPCRs, eight have been confirmed as potential [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Biological_target drug target]. <ref name="Drug">PMID: 24628305</ref> However, overall family B GPCRS have been difficult drug targets. This difficulty is partially related to the inherent flexibility in the class B GCGR 7TM. The flexibility comes from the ability of GCGR to be a receptor many ligands. The ECD and it's role in interactions on the extracellular side of receptors may provide evidence to how class B receptors adjust the conformational spectra for various ligands. Researchers hope to show how these conformations can be utilized in potential treatments of a wide array [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_mental_disorders disorders]. <ref name="Drug">PMID: 24628305</ref> | Of the fifteen human class B GPCRs, eight have been confirmed as potential [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Biological_target drug target]. <ref name="Drug">PMID: 24628305</ref> However, overall family B GPCRS have been difficult drug targets. This difficulty is partially related to the inherent flexibility in the class B GCGR 7TM. The flexibility comes from the ability of GCGR to be a receptor many ligands. The ECD and it's role in interactions on the extracellular side of receptors may provide evidence to how class B receptors adjust the conformational spectra for various ligands. Researchers hope to show how these conformations can be utilized in potential treatments of a wide array [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_mental_disorders disorders]. <ref name="Drug">PMID: 24628305</ref> | ||
| - | =Potential Inhibitors= | + | =Potential Inhibitors for GCGR= |
There are potential class B GCGR [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Enzyme_inhibitor inhibitors] that have clinic relevancy. These inhibitors to class B GCGRs have primarily focused on [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Allosteric_regulation allosteric inhibitors] with high specificity and the ability to treat diseases including: [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stress-related_disorders stress disorders], managing [http://www.webmd.com/diabetes/guide/diabetes-hyperglycemia hyperglycemia], and also alternative mechanisms for treating [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Migraine migraines]. <ref name="Inhibitors">PMID: 24189067</ref> Inhibitors include [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Monoclonal_antibody monoclonal antibodies] which inhibit glucagon receptors through an allosteric mechanism. <ref name="Last">PMID: 19305799</ref> Further research still to be done on | There are potential class B GCGR [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Enzyme_inhibitor inhibitors] that have clinic relevancy. These inhibitors to class B GCGRs have primarily focused on [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Allosteric_regulation allosteric inhibitors] with high specificity and the ability to treat diseases including: [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stress-related_disorders stress disorders], managing [http://www.webmd.com/diabetes/guide/diabetes-hyperglycemia hyperglycemia], and also alternative mechanisms for treating [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Migraine migraines]. <ref name="Inhibitors">PMID: 24189067</ref> Inhibitors include [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Monoclonal_antibody monoclonal antibodies] which inhibit glucagon receptors through an allosteric mechanism. <ref name="Last">PMID: 19305799</ref> Further research still to be done on | ||
==Research== | ==Research== | ||
Revision as of 03:45, 19 April 2016
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Hollenstein K, de Graaf C, Bortolato A, Wang MW, Marshall FH, Stevens RC. Insights into the structure of class B GPCRs. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2014 Jan;35(1):12-22. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2013.11.001. Epub, 2013 Dec 18. PMID:24359917 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tips.2013.11.001
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 Siu FY, He M, de Graaf C, Han GW, Yang D, Zhang Z, Zhou C, Xu Q, Wacker D, Joseph JS, Liu W, Lau J, Cherezov V, Katritch V, Wang MW, Stevens RC. Structure of the human glucagon class B G-protein-coupled receptor. Nature. 2013 Jul 25;499(7459):444-9. doi: 10.1038/nature12393. Epub 2013 Jul 17. PMID:23863937 doi:10.1038/nature12393
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Yang L, Yang D, de Graaf C, Moeller A, West GM, Dharmarajan V, Wang C, Siu FY, Song G, Reedtz-Runge S, Pascal BD, Wu B, Potter CS, Zhou H, Griffin PR, Carragher B, Yang H, Wang MW, Stevens RC, Jiang H. Conformational states of the full-length glucagon receptor. Nat Commun. 2015 Jul 31;6:7859. doi: 10.1038/ncomms8859. PMID:26227798 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/ncomms8859
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 Miller LJ, Dong M, Harikumar KG. Ligand binding and activation of the secretin receptor, a prototypic family B G protein-coupled receptor. Br J Pharmacol. 2012 May;166(1):18-26. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01463.x. PMID:21542831 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01463.x
- ↑ Thomsen J, Kristiansen K, Brunfeldt K, Sundby F. The amino acid sequence of human glucagon. FEBS Lett. 1972 Apr 1;21(3):315-319. PMID:11946536
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Bortolato A, Dore AS, Hollenstein K, Tehan BG, Mason JS, Marshall FH. Structure of Class B GPCRs: new horizons for drug discovery. Br J Pharmacol. 2014 Jul;171(13):3132-45. doi: 10.1111/bph.12689. PMID:24628305 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/bph.12689
- ↑ Mukund S, Shang Y, Clarke HJ, Madjidi A, Corn JE, Kates L, Kolumam G, Chiang V, Luis E, Murray J, Zhang Y, Hotzel I, Koth CM, Allan BB. Inhibitory mechanism of an allosteric antibody targeting the glucagon receptor. J Biol Chem. 2013 Nov 4. PMID:24189067 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M113.496984
- ↑ Hoare SR. Allosteric modulators of class B G-protein-coupled receptors. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2007 Sep;5(3):168-79. doi: 10.2174/157015907781695928. PMID:19305799 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.2174/157015907781695928