We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1167
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
In contrast to class A glucagon receptors which have a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Proline proline] kink, in all [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Secretin_receptor_family secretin-like class B glucagon receptors] there is a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glycine Glycine] at position 393 in Helix VII which allows for a <scene name='72/721537/Gly_393_helical_bend/1'>helical bend</scene>. This glycine helical bend is fully [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conserved_sequence conserved] in all secretin-like class B receptors and is an important part of the FQGxxVxxYCF [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sequence_motif motif]. | In contrast to class A glucagon receptors which have a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Proline proline] kink, in all [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Secretin_receptor_family secretin-like class B glucagon receptors] there is a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glycine Glycine] at position 393 in Helix VII which allows for a <scene name='72/721537/Gly_393_helical_bend/1'>helical bend</scene>. This glycine helical bend is fully [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conserved_sequence conserved] in all secretin-like class B receptors and is an important part of the FQGxxVxxYCF [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sequence_motif motif]. | ||
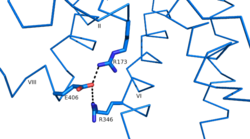
| - | Another important structural component found in all secretin-like class B receptors are the two conserved [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Salt_bridge_%28protein_and_supramolecular%29 salt bridges] found between [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Arginine Arg] 346 and [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glutamic_acid Glu] 406 and Arg 173 and Glu 406 [[Image:Salt Bridge Interactions.png | 250 px|right|thumb|Glu 406 Salt Bridges]]. These salt bridges | + | Another important structural component found in all secretin-like class B receptors are the two conserved [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Salt_bridge_%28protein_and_supramolecular%29 salt bridges] found between [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Arginine Arg] 346 and [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glutamic_acid Glu] 406 and Arg 173 and Glu 406 [[Image:Salt Bridge Interactions.png | 250 px|right|thumb|Glu 406 Salt Bridges]]. These salt bridges are a distinct feature of class B receptors only because their interaction results in the distinct stalk found only in class B receptors<ref name ='structure_article'>PMID:23863937</ref>. |
A conserved [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Disulfide disulfide bond] can be found in 7tm region at <scene name='72/721538/7tm_disulfide_bond/2'>Cys224-Cys294</scene> which helps to stabilize the 7tm fold. This bond is conserved among both class A and class B receptors. Additionally, the ECD region of Class B GCPRs is defined by three conserved disulfide bonds. These bonds occur at <scene name='72/721538/Ecd_disulfide_bond_1/4'>Cys62-Cys104</scene>, <scene name='72/721538/Ecd_disulfide_bond_2/1'>Cys46-Cys71</scene>, and <scene name='72/721538/Ecd_disulfide_bond_3/1'>Cys85-Cys126</scene>. | A conserved [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Disulfide disulfide bond] can be found in 7tm region at <scene name='72/721538/7tm_disulfide_bond/2'>Cys224-Cys294</scene> which helps to stabilize the 7tm fold. This bond is conserved among both class A and class B receptors. Additionally, the ECD region of Class B GCPRs is defined by three conserved disulfide bonds. These bonds occur at <scene name='72/721538/Ecd_disulfide_bond_1/4'>Cys62-Cys104</scene>, <scene name='72/721538/Ecd_disulfide_bond_2/1'>Cys46-Cys71</scene>, and <scene name='72/721538/Ecd_disulfide_bond_3/1'>Cys85-Cys126</scene>. | ||
Revision as of 03:46, 19 April 2016
| This Sandbox is Reserved from Jan 11 through August 12, 2016 for use in the course CH462 Central Metabolism taught by R. Jeremy Johnson at the Butler University, Indianapolis, USA. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1160 through Sandbox Reserved 1184. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Class B Human Glucagon G-Protein Coupled Receptor
References
- ↑ Yang L, Yang D, de Graaf C, Moeller A, West GM, Dharmarajan V, Wang C, Siu FY, Song G, Reedtz-Runge S, Pascal BD, Wu B, Potter CS, Zhou H, Griffin PR, Carragher B, Yang H, Wang MW, Stevens RC, Jiang H. Conformational states of the full-length glucagon receptor. Nat Commun. 2015 Jul 31;6:7859. doi: 10.1038/ncomms8859. PMID:26227798 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/ncomms8859
- ↑ Lotfy M, Kalasz H, Szalai G, Singh J, Adeghate E. Recent Progress in the Use of Glucagon and Glucagon Receptor Antago-nists in the Treatment of Diabetes Mellitus. Open Med Chem J. 2014 Dec 31;8:28-35. doi: 10.2174/1874104501408010028., eCollection 2014. PMID:25674162 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.2174/1874104501408010028
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Siu FY, He M, de Graaf C, Han GW, Yang D, Zhang Z, Zhou C, Xu Q, Wacker D, Joseph JS, Liu W, Lau J, Cherezov V, Katritch V, Wang MW, Stevens RC. Structure of the human glucagon class B G-protein-coupled receptor. Nature. 2013 Jul 25;499(7459):444-9. doi: 10.1038/nature12393. Epub 2013 Jul 17. PMID:23863937 doi:10.1038/nature12393
- ↑ Koth CM, Murray JM, Mukund S, Madjidi A, Minn A, Clarke HJ, Wong T, Chiang V, Luis E, Estevez A, Rondon J, Zhang Y, Hotzel I, Allan BB. Molecular basis for negative regulation of the glucagon receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Sep 4;109(36):14393-8. Epub 2012 Aug 20. PMID:22908259 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1206734109
- ↑ Mukund S, Shang Y, Clarke HJ, Madjidi A, Corn JE, Kates L, Kolumam G, Chiang V, Luis E, Murray J, Zhang Y, Hotzel I, Koth CM, Allan BB. Inhibitory mechanism of an allosteric antibody targeting the glucagon receptor. J Biol Chem. 2013 Nov 4. PMID:24189067 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M113.496984