Human Glucagon Class B G Protein-Coupled Receptors (GPCRs)
Introduction
Human glucagon class B G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as secretin-like receptors, are a subfamily of GPCRs and very similar in structure to the more well known class A (rhodopsin-like) glucagon receptor family. [1] Located in the liver, class B glucagon receptors (GCGRs) are activated by the binding of the hormonal peptide glucagon. Glucagon binding leads to the release of glucose into the bloodstream and plays an essential role in glucose homeostasis. Class B GCGRs are composed of a seven transmembrane domain (7TM) and an extracellular domain (ECD) that are required for glucagon binding.
Structures of Class A vs. Class B GPCRs
Class A vs. class B glucagon receptors share less than fifteen percent sequence homology, but both share a 7TM domain. [1] Understanding for class A family of GCGRs of the structure-function mechanism has made great progress over the past few years, but understanding of class B has fallen behind but is now catching up. [2] Comparison of the helices to that of the helices showed that the general orientation and positioning of the alpha helices are conserved through both classes. Detailed structural alignments of the two GPCR subclasses revealed multiple sequence misalignments in the transmembrane region signifying a variety of structural deviations in the transmembrane helices. [2] The N-terminal end of in class B GCGR, located in the 7TM, is longer than any known class A GPCR structure and stretches three supplementary helical turns above the extracellular (EC) membrane boundary. This region is referred to as the
. The stalk is involved in glucagon binding and helps in defining the orientation of the ECD with respect to the 7TM domain. [2] Also specific to class B GPCRs, a Gly residue at position 393 induces a ; this bend is stabilized by the hydrophobic interaction between the . One of the most distinguishable characteristics of the class B 7TM is the of 25 degrees and its length compared to that of , which is much shorter. This helical tilt results from Glu 406 in helix VIII that is fully conserved in secretin-like receptors and forms two interhelical salt bridges with conserved residues Arg 173 and Arg 346. [2] Despite these differences, a vital region that is conserved in both class B and class A receptors is the disulfide bond between in extracellular loop two (ECL2). This bond stabilizes the receptors entire 7TM fold. Lastly, the locations of the extracellular tips for class B glucagon receptors allow for a much wider and deeper ligand-binding pocket than any of the class A GPCRs. [2] These wide extracellular tip locations specifically occur between two sets of alpha helices, (Figure 1).
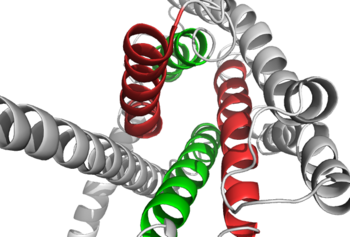
Figure 1: Extracellular tips of the 7TM helices. Helices two and six are shown in green, while helices three and seven are shown in red
How These Structures Lead to Function

Figure 2: Open conformation in contrast to the closed conformation. The movement of the single helix over the top of the transmembrane domain is the most distinguishable characteristic between closed and open conformation. The is not accessible to glucagon in the closed conformation.
[3] Structurally, the 7TM and its signature seven helical structure is involved in signaling via coupling to heterotrimeric G proteins that activate adenylate cyclase to increase the levels of intracellular cyclic AMP. Additionally, this coupling increases levels of IP3 and intracellular calcium levels. [2] The wider and deeper ligand-binding pocket of class B GPCRs allows for a vast array of molecules to be bound that in turn allow for numerous functions activated by peptide receptors. [4] The conformation and orientation of the 7TM and the ECD regions dictate the functionality of the class B G protein-coupled receptor, which has an open and closed conformation of the GCGR (Figure 2). The open conformation is when glucagon can bind to GCGR; in the closed conformation binding does not occur.[4]
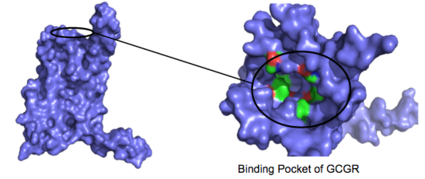
Figure 3: Binding Pocket Residues: Residues with side chains of carbon(utilizing the
hydrophobic effect) are shown in green and side chains containing oxygen (
hydrophilic) are shown in red. The properties of hydrophobicity and hydrophilicity of the residues create the
binding affinity of glucagon.
[4] This image depicts the open conformation of GCGR.
The residues in the binding pocket that are in direct contact with the glucagon molecule are polar (utilizing the attraction of opposite charges or (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dipole dipoles] for glucagon binding) or are hydrophobic (utilizing the hydrophobic effect). The binding site location of the hormone peptide ligand has been identified, and the N-terminus of glucagon is known to bind partly with the ECD while the rest of glucagon binds deep into the (Figure 3). The amino acids at the N-terminus of the class B 7TM have the ability to form hydrogen bonds and ionic interactions, which can be seen in the amino acid sequence of glucagon (Figure 4). [5]

Figure 4: Amino Acid Sequence of GlucagonThe primary sequence of glucagon, ligand to GCGR, is 29 amino acids.
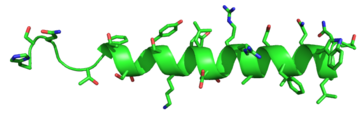
Figure 5: Structure of Glucagon: The side chains of the residues making up glucagon are depicted. Coloration on the side chains indicate certain
atoms that determine the properties the residues hold. The blue indicates a
nitrogen atom (hydrophilic properties), the green on the side chains indicates carbon atoms (non-polar hydrophobic properties), and the red coloration indicates an
oxygen atom (hydrophilic properties).
PDB 1GCN
There are specific amino acid interactions that maximize affinity. This includes the alpha helical structure of the . The alpha helical structure of the stalk interacts directly with glucagon, as it extends nearly three helical turns above the membrane. When the alpha helix of the stalk is disrupted, the affinity of glucagon for GCGR decreases. A mutagenesis study mutating to a proline. Proline disrupts helices. The Ala135Pro mutant had significant lower affinity for glucagon.[2] Furthermore, there are certain interactions that hold the helices of the 7TM in the conformation that maximizes affinity. [4] The high affinity conformation of GCGR is the open conformation, when glucagon can bind. Without these specific interactions between the residues, the open conformation is not stabilized and GCGR remains in the closed conformation, where glucagon cannot bind. [2] The disulfide bond between serves to hold the helices in the proper orientation for binding and stabilizes the open conformation. Additionally, the salt bridges between
hold the open conformation together for higher affinity (Figure 6). [4]
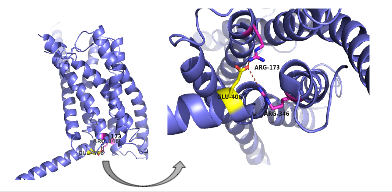
Figure 6: Salt Bridge. The non-covalent interactions between residues form a
tridentate salt bridge. The Glu 406 acts as the central residue in the tridentate salt bridge; Arg 173 and Arg 436 both
chelating with Glu 406. The salt bridge is located on the intracellular side of the transmembrane helices.
Glucagon Signaling Pathway
Glucagon binds to the open conformation of GCGR; the GCGR located on the plasma membrane. Glucagon binding to GCGR induces a conformational change in GCGR. This conformation change induces the active state of the protein. The active state of the protein exchanges a guanosine diphosphate (GDP) for guanosine triphosphate (GTP) that is bound to the alpha subunit. With the GTP in place, the activated alpha subunit dissociates from the heterotrimeric G protein'sbeta and gamma subunits. Following dissociation, the alpha subunit can activate adenylate cyclase. Activated adenylate cyclase, catalyzes the conversion of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) into cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP). cAMP then serves as a secondary messenger to activate, through allosteric binding, cAMP dependent protein kinase A (PKA). PKA activates via phosphorylation the phosphorylase b kinase. The phosphorylase b kinase phosphorylates glycogen phosphorylase b to convert to the active form, phosphorylase a. Phosphorylase a finally catalyzes the release of glucose-1-phosphate into the bloodstream from glycogen polymers (Figure 7).
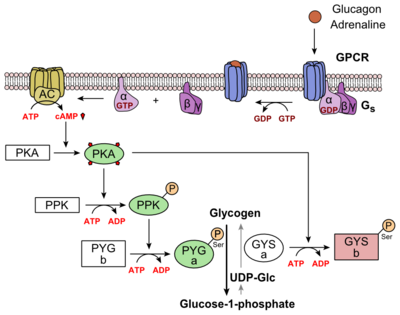
Figure 7: Metabolic Regulation of Glycogen by Glucagon.Depicted is the visualization of the glucagon signaling pathway through the GCGR. The location of the GCGR, the release of the alpha subunit from the beta and gamma subunits, and the enzyme cascade to result in the releasing of glucose are depicted. Abbreviations for the enzymes in the cascade include- PPK: phosphorylase kinase; PYG b: glycogen phosphorylase b; PYG a: glycogen phosphorylase a.
Clinical Relevancy
Of the fifteen human class B GPCRs, eight have been confirmed as potential drug target. [6] However, overall family B GPCRS have been difficult drug targets. This difficulty is partially related to the inherent flexibility in the class B GCGR 7TM. The flexibility comes from the ability of GCGR to be a receptor many ligands. The ECD and it's role in interactions on the extracellular side of receptors may provide evidence to how class B receptors adjust the conformational spectra for various ligands. Researchers hope to show how these conformations can be utilized in potential treatments of a wide array disorders. [6]
Potential Inhibitors for GCGR
There are potential class B GCGR inhibitors that have clinic relevancy. These inhibitors to class B GCGRs have primarily focused on allosteric inhibitors with high specificity and the ability to treat diseases including: stress disorders, managing hyperglycemia, and also alternative mechanisms for treating migraines. [7] Inhibitors include monoclonal antibodies which inhibit glucagon receptors through an allosteric mechanism. [8] There is further research still to be done on GCGR to determine more inhibitors for clinical relevance.







