We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1167
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 50: | Line 50: | ||
== Clinical Relevance == | == Clinical Relevance == | ||
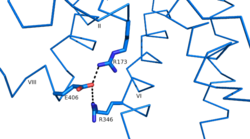
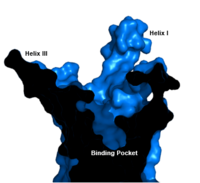
| - | Because of GCGR's role in glucose homeostasis, GCGRis a potential drug target for [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Diabetes_mellitus_type_2 Type 2 diabetes]. Specifically, molecules that antagonize the glucagon receptor may be able to lower blood sugar levels. Among experimental treatments, two antibodies, mAb1 and mAb23, target the ECD domain of the GCGR interrupting glucagon binding<ref name= | + | Because of GCGR's role in glucose homeostasis, GCGRis a potential drug target for [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Diabetes_mellitus_type_2 Type 2 diabetes]. Specifically, molecules that antagonize the glucagon receptor may be able to lower blood sugar levels. Among experimental treatments, two antibodies, mAb1 and mAb23, target the ECD domain of the GCGR interrupting glucagon binding<ref name='other_article'>PMID:22908259</ref>. While the entire cleft of the ECD is blocked by mAb1, mAb3 blocks glucagon binding by stabilizing a conformation of the ECD that promotes receptor inactivation <ref name='other_article'>PMID:22908259</ref>. Another antibody, mAb7, inhibits GCGR allosterically<ref>PMID:24189067</ref>. Through binding to a site outside of the binding pocket, mAb7 inhibits the receptor without interacting with essential glucagon binding residues. Disrupting the normal interactions between the ECD and the 7tm domains, these antibodies inhibit the receptor's function and help to lower blood glucose level. |
As GCGR holds great promise as a therapeutic target, there are currently three drugs under development that are designed to treat Type 2 Diabetes by targeting the human glucagon receptor<ref name='therapeutic_article'>DOI 10.1016/j.tips.2013.11.001</ref>. Although they are still in phase I of their clinical trials, preliminary research has shown promising results<ref>DOI 10.2174/1573399810666141224121927</ref>. | As GCGR holds great promise as a therapeutic target, there are currently three drugs under development that are designed to treat Type 2 Diabetes by targeting the human glucagon receptor<ref name='therapeutic_article'>DOI 10.1016/j.tips.2013.11.001</ref>. Although they are still in phase I of their clinical trials, preliminary research has shown promising results<ref>DOI 10.2174/1573399810666141224121927</ref>. | ||
Revision as of 07:58, 19 April 2016
| This Sandbox is Reserved from Jan 11 through August 12, 2016 for use in the course CH462 Central Metabolism taught by R. Jeremy Johnson at the Butler University, Indianapolis, USA. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1160 through Sandbox Reserved 1184. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Class B Human Glucagon G-Protein Coupled Receptor
References
- ↑ Lotfy M, Kalasz H, Szalai G, Singh J, Adeghate E. Recent Progress in the Use of Glucagon and Glucagon Receptor Antago-nists in the Treatment of Diabetes Mellitus. Open Med Chem J. 2014 Dec 31;8:28-35. doi: 10.2174/1874104501408010028., eCollection 2014. PMID:25674162 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.2174/1874104501408010028
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 Siu FY, He M, de Graaf C, Han GW, Yang D, Zhang Z, Zhou C, Xu Q, Wacker D, Joseph JS, Liu W, Lau J, Cherezov V, Katritch V, Wang MW, Stevens RC. Structure of the human glucagon class B G-protein-coupled receptor. Nature. 2013 Jul 25;499(7459):444-9. doi: 10.1038/nature12393. Epub 2013 Jul 17. PMID:23863937 doi:10.1038/nature12393
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Hollenstein K, de Graaf C, Bortolato A, Wang MW, Marshall FH, Stevens RC. Insights into the structure of class B GPCRs. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2014 Jan;35(1):12-22. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2013.11.001. Epub, 2013 Dec 18. PMID:24359917 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tips.2013.11.001
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Yang L, Yang D, de Graaf C, Moeller A, West GM, Dharmarajan V, Wang C, Siu FY, Song G, Reedtz-Runge S, Pascal BD, Wu B, Potter CS, Zhou H, Griffin PR, Carragher B, Yang H, Wang MW, Stevens RC, Jiang H. Conformational states of the full-length glucagon receptor. Nat Commun. 2015 Jul 31;6:7859. doi: 10.1038/ncomms8859. PMID:26227798 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/ncomms8859
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Koth CM, Murray JM, Mukund S, Madjidi A, Minn A, Clarke HJ, Wong T, Chiang V, Luis E, Estevez A, Rondon J, Zhang Y, Hotzel I, Allan BB. Molecular basis for negative regulation of the glucagon receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Sep 4;109(36):14393-8. Epub 2012 Aug 20. PMID:22908259 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1206734109
- ↑ Mukund S, Shang Y, Clarke HJ, Madjidi A, Corn JE, Kates L, Kolumam G, Chiang V, Luis E, Murray J, Zhang Y, Hotzel I, Koth CM, Allan BB. Inhibitory mechanism of an allosteric antibody targeting the glucagon receptor. J Biol Chem. 2013 Nov 4. PMID:24189067 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M113.496984
- ↑ Mittermayer F, Caveney E, De Oliveira C, Gourgiotis L, Puri M, Tai LJ, Turner JR. Addressing unmet medical needs in type 2 diabetes: a narrative review of drugs under development. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2015;11(1):17-31. doi: 10.2174/1573399810666141224121927. PMID:25537454 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.2174/1573399810666141224121927