This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
User:Brittany Stankavich/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
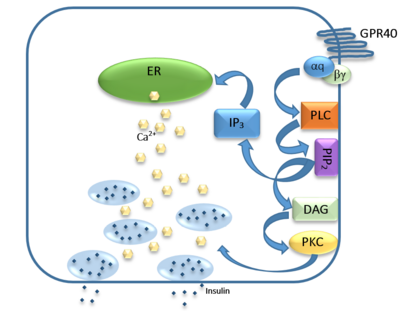
| - | GPR40 is most prevalent in [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Beta_cell pancreatic β-cells] where free fatty acids (FFAs) | + | GPR40 is most prevalent in [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Beta_cell pancreatic β-cells] where free fatty acids (FFAs) have pleiotropic effects. While acute intake of FFAs stimulates insulin release, chronic exposure to high levels of FFAs results in the impairment of β-cell function and insulin secretory response. GPR40 mediates the effect of both acute and chronic levels of FFAs. FFAs amplify glucose-stimulated insulin secretion from pancreatic β-cells by activating GPR40. |
| - | When GPR40 is inhibited, insulin secretion no longer increases in response to fatty acid stimulation. This decreased activity of GPR40 leads to a decreased risk of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hyperinsulinemia hyperinsulinemia], [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fatty_liver fatty liver disease], [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hypertriglyceridemia hypertriglyceridemia], [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hyperglycemia hyperglycemia], and [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Impaired_glucose_tolerance glucose tolerance] in obese patients. On the contrary, overexpression of GPR40 leads to impaired β-cell function, hyperinsulinemia, and diabetes | + | When GPR40 is inhibited, insulin secretion no longer increases in response to fatty acid stimulation. This decreased activity of GPR40 leads to a decreased risk of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hyperinsulinemia hyperinsulinemia], [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fatty_liver fatty liver disease], [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hypertriglyceridemia hypertriglyceridemia], [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hyperglycemia hyperglycemia], and [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Impaired_glucose_tolerance glucose tolerance] in obese patients. On the contrary, overexpression of GPR40 leads to impaired β-cell function, hyperinsulinemia, and diabetes. These results suggest that GPR40 plays an important role in the mechanism that links obesity and type 2 diabetes and thus is a popular drug target being studied. |
== Signal Transduction == | == Signal Transduction == | ||
Revision as of 00:45, 21 April 2016
- User:Brittany Stankavich/Sandbox 1
hGPR40 Homo sapiens
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Ren XM, Cao LY, Zhang J, Qin WP, Yang Y, Wan B, Guo LH. Investigation of the Binding Interaction of Fatty Acids with Human G Protein-Coupled Receptor 40 Using a Site-Specific Fluorescence Probe by Flow Cytometry. Biochemistry. 2016 Mar 17. PMID:26974599 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.6b00079
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Morgan NG, Dhayal S. G-protein coupled receptors mediating long chain fatty acid signalling in the pancreatic beta-cell. Biochem Pharmacol. 2009 Dec 15;78(12):1419-27. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2009.07.020., Epub 2009 Aug 4. PMID:19660440 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2009.07.020
- ↑ Hanson MA, Roth CB, Jo E, Griffith MT, Scott FL, Reinhart G, Desale H, Clemons B, Cahalan SM, Schuerer SC, Sanna MG, Han GW, Kuhn P, Rosen H, Stevens RC. Crystal structure of a lipid G protein-coupled receptor. Science. 2012 Feb 17;335(6070):851-5. PMID:22344443 doi:10.1126/science.1215904
- ↑ Li X, Zhong K, Guo Z, Zhong D, Chen X. Fasiglifam (TAK-875) Inhibits Hepatobiliary Transporters: A Possible Factor Contributing to Fasiglifam-Induced Liver Injury. Drug Metab Dispos. 2015 Nov;43(11):1751-9. doi: 10.1124/dmd.115.064121. Epub 2015, Aug 14. PMID:26276582 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1124/dmd.115.064121
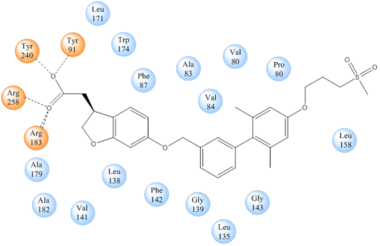
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Takano R, Yoshida M, Inoue M, Honda T, Nakashima R, Matsumoto K, Yano T, Ogata T, Watanabe N, Hirouchi M, Yoneyama T, Ito S, Toda N. Discovery of DS-1558: A Potent and Orally Bioavailable GPR40 Agonist. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2015 Jan 13;6(3):266-70. doi: 10.1021/ml500391n. eCollection, 2015 Mar 12. PMID:25815144 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ml500391n