User:Brittany Stankavich/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
=== [http://proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/Image:Tak_875.png TAK-875] === | === [http://proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/Image:Tak_875.png TAK-875] === | ||
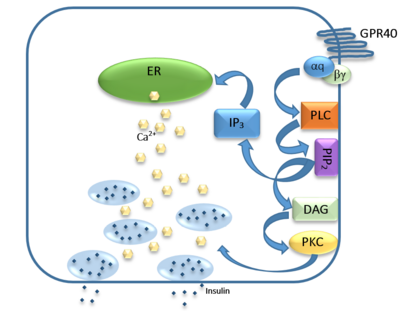
| - | <scene name='72/727085/Hgpr40_begin/3'>Tak-875</scene> is a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Partial_agonist partial agonist] of GPR40 and tested for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. The binding of TAK-875 to hGPR40 occurs by the ligand entering the binding site through the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cell_membrane membrane bilayer]. This membrane insertion is performed via a method similar to ligand binding to [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sphingosine-1-phosphate_receptor sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor 1], retinal loading of [http://proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/4j4q GPCR opsin], and the entry of anandamide in [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cannabinoid_receptor cannabinoid receptors], in which <scene name='72/727085/Hgpr40_a/6'>extracellular loops</scene> block the binding from the extracellular matrix <ref>PMID:22344443</ref>. The binding mechanism through the bilayer may be selectively favoring the free fatty acid because of the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chemical_polarity#Nonpolar_molecules non-polar] regions of the ligand. | + | <scene name='72/727085/Hgpr40_begin/3'>Tak-875</scene> is a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Partial_agonist partial agonist] of GPR40 and tested for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. The binding of TAK-875 to hGPR40 occurs by the ligand entering the binding site through the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cell_membrane membrane bilayer]. This membrane insertion is performed via a method similar to ligand binding to [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sphingosine-1-phosphate_receptor sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor 1], retinal loading of [http://proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/4j4q GPCR opsin], and the entry of anandamide in [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cannabinoid_receptor cannabinoid receptors], in which <scene name='72/727085/Hgpr40_a/6'>extracellular loops</scene> block the binding from the extracellular matrix <ref>PMID:22344443</ref>. The binding mechanism through the bilayer may be selectively favoring the free fatty acid because of the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chemical_polarity#Nonpolar_molecules non-polar] regions of the ligand (Figure 2). |
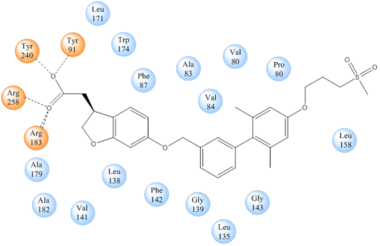
| - | TAK-875 binds to | + | TAK-875 binds to the <scene name='72/727085/Hgpr40_entry/2'>noncanonical binding site </scene> created between transmembrane (TM) domains 3-5 and the extracellular loop 2 (ECL2) of hGPR40. The ECL2 and auxiliary loop form a roof causing TAK-875 to enter through TM3 and TM4, first passing through the lipid bilayer. The carboxylate of TAK-875 is buried within a very hydrophobic region and in a complex complex <scene name='72/727085/Hgpr40_binding_relay/6'>charge network</scene> involving Glu172, Ser187, Asn241, and Asn 244 from hGPR40 forming ionic and polar interactions by coordinating TAK-875 with Arg183, Arg258, Tyr91, and Tyr240. |
Revision as of 11:49, 22 April 2016
- User:Brittany Stankavich/Sandbox 1
hGPR40 Homo sapiens
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 Srivastava A, Yano J, Hirozane Y, Kefala G, Gruswitz F, Snell G, Lane W, Ivetac A, Aertgeerts K, Nguyen J, Jennings A, Okada K. High-resolution structure of the human GPR40 receptor bound to allosteric agonist TAK-875. Nature. 2014 Jul 20. doi: 10.1038/nature13494. PMID:25043059 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature13494
- ↑ Ren XM, Cao LY, Zhang J, Qin WP, Yang Y, Wan B, Guo LH. Investigation of the Binding Interaction of Fatty Acids with Human G Protein-Coupled Receptor 40 Using a Site-Specific Fluorescence Probe by Flow Cytometry. Biochemistry. 2016 Mar 17. PMID:26974599 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.6b00079
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 Ichimura A, Hirasawa A, Hara T, Tsujimoto G. Free fatty acid receptors act as nutrient sensors to regulate energy homeostasis. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2009 Sep;89(3-4):82-8. doi:, 10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2009.05.003. Epub 2009 May 19. PMID:19460454 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2009.05.003
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 4.7 4.8 Morgan NG, Dhayal S. G-protein coupled receptors mediating long chain fatty acid signalling in the pancreatic beta-cell. Biochem Pharmacol. 2009 Dec 15;78(12):1419-27. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2009.07.020., Epub 2009 Aug 4. PMID:19660440 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2009.07.020
- ↑ Ren XM, Cao LY, Zhang J, Qin WP, Yang Y, Wan B, Guo LH. Investigation of the Binding Interaction of Fatty Acids with Human G Protein-Coupled Receptor 40 Using a Site-Specific Fluorescence Probe by Flow Cytometry. Biochemistry. 2016 Mar 17. PMID:26974599 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.6b00079
- ↑ Hanson MA, Roth CB, Jo E, Griffith MT, Scott FL, Reinhart G, Desale H, Clemons B, Cahalan SM, Schuerer SC, Sanna MG, Han GW, Kuhn P, Rosen H, Stevens RC. Crystal structure of a lipid G protein-coupled receptor. Science. 2012 Feb 17;335(6070):851-5. PMID:22344443 doi:10.1126/science.1215904
- ↑ Li X, Zhong K, Guo Z, Zhong D, Chen X. Fasiglifam (TAK-875) Inhibits Hepatobiliary Transporters: A Possible Factor Contributing to Fasiglifam-Induced Liver Injury. Drug Metab Dispos. 2015 Nov;43(11):1751-9. doi: 10.1124/dmd.115.064121. Epub 2015, Aug 14. PMID:26276582 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1124/dmd.115.064121
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Takano R, Yoshida M, Inoue M, Honda T, Nakashima R, Matsumoto K, Yano T, Ogata T, Watanabe N, Hirouchi M, Yoneyama T, Ito S, Toda N. Discovery of DS-1558: A Potent and Orally Bioavailable GPR40 Agonist. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2015 Jan 13;6(3):266-70. doi: 10.1021/ml500391n. eCollection, 2015 Mar 12. PMID:25815144 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ml500391n