Class B GPCRs
G protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) are the largest class of integral membrane proteins. GPCRs are divided into five families; the rhodopsin family (class A), the secretin family (class B), the glutamate family (class C), the frizzled/taste family (class F), and the adhesion family.[1] Roughly 5% of the human genome encodes g protein-coupled receptors, which are responsible for the transduction of endogenous signals and the instigation of cellular responses.[1] All GPCRs contain a similar seven α-helical transmembrane domain that once bound to its ligand, undergoes a conformational change and tranduces a signal to coupled, heterotrimeric G proteins. The initiation of intracellular signal pathways occur in response to stimuli such as light, Ca2+, amino acids, nucleotides, odorants, peptides, and other proteins, and accomplishes many interesting physiological roles. [1]
Class B GPCRs contain 15 distinct receptors for peptide hormones and generate their signal pathway through the activation of adenylate cyclase (AC) which increases the intracellular concentration of cAMP, inositol phosphate, and calcium levels. [2] These secondary messengers are essential elements of intracellular signal cascades for human diseases including type II diabetes mellitus, osteoporosis, obesity, cancer, neurological degeneration, cardiovascular diseases, headaches, and psychiatric disorders; making their regulation through drug targeting of particular interest as disease targets. [3] Structural approaches to the development of agonists and antagonists have however been hampered by the lack of accurate Class B TMD visualizations. Recent crystal structure images of corticoptropin-releasing factor receptor 1 (PDB: 4K5Y) and human glucagon receptor (PDB: 4L6R) were accomplished through x-ray crystallography. [4] [5]
Glucagon Receptor (GCGR)
The glucagon class B GPCR (GCGR) is involved in glucose homeostasis through the binding of the signal peptide glucagon. Glucagon is released from pancreatic α-cells when blood glucose levels fall after a period of fasting or several hours following intake of dietary carbohydrates.[6] Once the peptide hormone is released, it binds to GCGR, a 485 amino acid protein found in the liver, kidney, intestinal smooth muscle, brain, and adipose tissues. [7] Upon binding, signaling is initiated to heterotrimeric G-proteins containing Gαs. [8] GCGR can regulate additional signal pathways, including G-proteins of the Gαi family through the adoption of differing receptor conformations. [9]
Glucagon's main role is the regulation of blood glucose levels.[6] Glucagon lowers the concentration of fructose 2,6-bisphosphate which is an allosteric inhibitor of the gluconeogenic enzyme fructose 1,6-bisphosphotase and activates phosphofructose kinase 1, which increases glucose levels via glycolysis.[6] Glucagon is also a regulator of the production of cholesterol, which is an energetically intensive process. When energy resources are low, downregulation of cholesterol production begins with glucagon binding to GCGR, which stimulates the phosphorylation of HMG-CoA.[6] HMG-CoA is inactivated by phosphorylation and moderates cholesterol production to conserve energy.[6] Glucagon also takes part in fatty acid mobilization by affecting levels of adipose tissue in the organism. Activation of GCGR by glucagon initiates triacylglycerol breakdown and the phosphorylation of perilipin and lipases via cAMP signal pathways.[6] This allows the body to export fatty acids to the liver and other crucial tissues for energy use and makes more glucose available for use in brain functioning.[6]
Structure
The class B GPCRs, including GCGR, are different from other GPCRs in several ways. The first is that class B GPCRs contain a protrusion known as a 'stalk,' a three α-helical turn elongation of the N-terminus that protrudes past the extracellular (EC) membrane.[5] Structural integrity of this domain in GCGR is A135P mutations impact stalk stability by removing an important salt bridge between Glu133 - Lys136.[5] A second difference between class B and other GPCRs is that the extracellular loop 1 (ECL1) is 3-4 times longer than comparable loops in class A GPCRs, and also affects ligand binding affinity.[5] Most notably, class B GPCRs contain a which is solvent filled and accessible from the extracellular side.[3] This central splay is notably absent , and represents a tantalizing target for agonists/antagonists.[3]
Because of the difficulty in stabilizing and crystallizing Class B TMDs, very little is known about the conformational changes that transduce cell signals endogenously. GCGR is known to regulate additional signal pathways through the adoption of differing receptor conformations and to interact with receptor activity-modifying proteins (RAMPs) altering the signaling bias of the receptor.[9]
Glucagon Binding
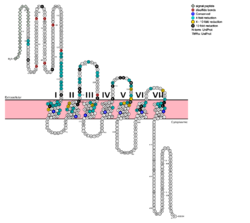
Fig. 1: Snake Plot of GCGR TMD. Residues of particular importance in glucagon binding affinity are found in green, yellow, and black. Residues in red are the location of critical disulfide bonds, while blue residues were found to be highly conserved across all class B GPCRs.
[5]
Fig. 2: functioning as anchoring site for glucagon's n-terminal residues.

Fig. 3: Surface visualization of glucagon visualizing the three dimensional shape of the N-terminal tail that interacts with the binding site of GCGR central cavity.
The large, soluble N-terminal extracellular domains (ECD) of GCGR provide initial ligand selectivity with the deep, ligand pocket (Fig. 2) of the TMD providing secondary recognition.
[7] In a comprehensive mutagenesis and glucagon-binding study, a total of 129 mutations of GCGR were tested. 41 of these covering 28 different locations in the GCGR TMD were found to have at least a fourfold decrease in glucagon binding affinity
[5]. (see Fig. 1) It is the face of the central cavity that harbors the majority of the residues which play an important role in glucagon binding.
[5] The binding site was shown to be a dynamic area traveling from the middle of the stalk region (Tyr 138) to deep within the 7TM core (Glu 362), encompassing positions along ECL1, ECL2 and ECL3 and helices I, II, III, V, VI and VII.
Mutagenesis and photo cross-linking studies determined essential, conserved residues in glucagon and have been in red.[5] Glucagon residues His 1, Gln 3, Phe 6, and Tyr 10 are critical to successful binding interaction with the GCGR while others are important for structural rigidity. The n-terminus of glucagon (Fig. 3) leads to a protuberance that fits into the deep, interior cavity of the GCGR 7TMD (Fig. 2) where four residues reside that play strong roles in ligand binding affinity. There is a to the entrance of the cavity, providing a firm anchor during peptide docking. (also see Fig. 2)
Clinical relevance
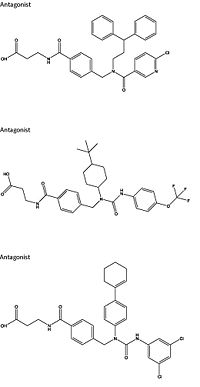
Figure 4: Three small molecule antagonists reported in 2007.
[10].
Because GCGR can interact with multiple types of G protein subfamilies, discovering small molecule inhibitors could lead to a wide range of focused therapies.[11] Blocking conformations that favor interaction with specific G proteins could allow the knockdown of targeted signal pathways. For example, GCGR is known to interact with inhibitory Gαi proteins that antagonize cAMP production.[11] The finding of an agonist for this pathway could lead to breakthroughs in the treatment of diabetes mellitus. Recently some fundamental work has been done with RAMPs which were shown to alter ligand preference in class B GPCRs.[12] Specifically, RAMP2 association has been shown to alter the pharmacology of all GCGR ligands (glucagon and oxyntomodulin). RAMP2 association altered cAMP production, indicating an effect on signaling bias and g protein coupling.[12]
Attempts to target the GCGR have proven relatively unsuccessful. Three small molecule modulators were reported with the hope of enhanced pharmaceutical regulation.[10] (Fig. 4) It is not clear if this work has resulted in additional pharmacological modalities, but any progress has been modest, at best. Some gains have been made in targeting glucagon-like peptide-1 receptors (a GPCR closely related to GCGR) but with the caveat of severe, adverse side-effects.[11] Encouraging results have recently come from Eli Lilly and Company who have been testing a small molecule antagonist of the GCGR (LY2409021) in phase two trials with some success, providing hope for some more specific control of diabetes mellitus.[10] In addition to diabetes mellitus, future development of signal bias modulators promise to provide focused therapies for obesity and heart disease, as well as related secondary pathological conditions such as hypertension and cancer.
See Also
PSI Structural Biology Database
G protein-coupled receptors
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Zhang Y, Devries ME, Skolnick J. Structure modeling of all identified G protein-coupled receptors in the human genome. PLoS Comput Biol. 2006 Feb;2(2):e13. Epub 2006 Feb 17. PMID:16485037 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.0020013
- ↑ Bortolato A, Dore AS, Hollenstein K, Tehan BG, Mason JS, Marshall FH. Structure of Class B GPCRs: new horizons for drug discovery. Br J Pharmacol. 2014 Jul;171(13):3132-45. doi: 10.1111/bph.12689. PMID:24628305 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/bph.12689
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Hollenstein K, de Graaf C, Bortolato A, Wang MW, Marshall FH, Stevens RC. Insights into the structure of class B GPCRs. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2014 Jan;35(1):12-22. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2013.11.001. Epub, 2013 Dec 18. PMID:24359917 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tips.2013.11.001
- ↑ Hollenstein K, Kean J, Bortolato A, Cheng RK, Dore AS, Jazayeri A, Cooke RM, Weir M, Marshall FH. Structure of class B GPCR corticotropin-releasing factor receptor 1. Nature. 2013 Jul 25;499(7459):438-43. doi: 10.1038/nature12357. Epub 2013 Jul 17. PMID:23863939 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature12357
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 5.6 5.7 Siu FY, He M, de Graaf C, Han GW, Yang D, Zhang Z, Zhou C, Xu Q, Wacker D, Joseph JS, Liu W, Lau J, Cherezov V, Katritch V, Wang MW, Stevens RC. Structure of the human glucagon class B G-protein-coupled receptor. Nature. 2013 Jul 25;499(7459):444-9. doi: 10.1038/nature12393. Epub 2013 Jul 17. PMID:23863937 doi:10.1038/nature12393
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 6.6 'Lehninger A., Nelson D.N, & Cox M.M. (2008) Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry. W. H. Freeman, fifth edition.'
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Yang DH, Zhou CH, Liu Q, Wang MW. Landmark studies on the glucagon subfamily of GPCRs: from small molecule modulators to a crystal structure. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2015 Sep;36(9):1033-42. doi: 10.1038/aps.2015.78. Epub 2015, Aug 17. PMID:26279155 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/aps.2015.78
- ↑ Ahren B. Islet G protein-coupled receptors as potential targets for treatment of type 2 diabetes. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2009 May;8(5):369-85. doi: 10.1038/nrd2782. Epub 2009 Apr, 14. PMID:19365392 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nrd2782
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Xu Y, Xie X. Glucagon receptor mediates calcium signaling by coupling to G alpha q/11 and G alpha i/o in HEK293 cells. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2009 Dec;29(6):318-25. doi:, 10.3109/10799890903295150. PMID:19903011 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/10799890903295150
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 Lau J, Behrens C, Sidelmann UG, Knudsen LB, Lundt B, Sams C, Ynddal L, Brand CL, Pridal L, Ling A, Kiel D, Plewe M, Shi S, Madsen P. New beta-alanine derivatives are orally available glucagon receptor antagonists. J Med Chem. 2007 Jan 11;50(1):113-28. PMID:17201415 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/jm058026u
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 Weston C, Lu J, Li N, Barkan K, Richards GO, Roberts DJ, Skerry TM, Poyner D, Pardamwar M, Reynolds CA, Dowell SJ, Willars GB, Ladds G. Modulation of Glucagon Receptor Pharmacology by Receptor Activity-modifying Protein-2 (RAMP2). J Biol Chem. 2015 Sep 18;290(38):23009-22. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.624601. Epub, 2015 Jul 21. PMID:26198634 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M114.624601
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 Wootten D, Lindmark H, Kadmiel M, Willcockson H, Caron KM, Barwell J, Drmota T, Poyner DR. Receptor activity modifying proteins (RAMPs) interact with the VPAC2 receptor and CRF1 receptors and modulate their function. Br J Pharmacol. 2013 Feb;168(4):822-34. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2012.02202.x. PMID:22946657 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1476-5381.2012.02202.x




