We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Prolyl Endopeptidase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | |||
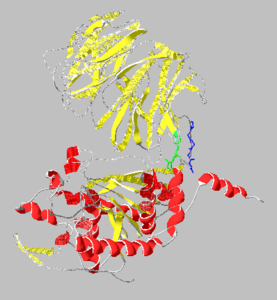
<StructureSection load='3eq7' size='350' side='right' caption='Prolyl endopeptidase complex with Pro-(decarboxy-Pro)-type inhibitor (PDB entry [[3eq7]])' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='3eq7' size='350' side='right' caption='Prolyl endopeptidase complex with Pro-(decarboxy-Pro)-type inhibitor (PDB entry [[3eq7]])' scene=''> | ||
| Line 52: | Line 51: | ||
As well as having a proposed role in the degradation of neuropeptides PEPs have also been linked to several specific neurological disorders. It has been found that patients suffering from depression had decreased PEP activity and those suffering from psychosis have increased PEP activity showing the importance of maintaining a balanced level of PEP activity in the brain. PEP inhibitors are a current point of research in hopes of finding ways to balance brain PEP activity.<ref name="Gass"/> | As well as having a proposed role in the degradation of neuropeptides PEPs have also been linked to several specific neurological disorders. It has been found that patients suffering from depression had decreased PEP activity and those suffering from psychosis have increased PEP activity showing the importance of maintaining a balanced level of PEP activity in the brain. PEP inhibitors are a current point of research in hopes of finding ways to balance brain PEP activity.<ref name="Gass"/> | ||
| + | == Structural highlights == | ||
| + | The active site of PEP contains the serene protease catalytic triad of Ser-His-Asp<ref>PMID:19006380</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | </StructureSection> | ||
==3D structures of prolyl endopeptidase== | ==3D structures of prolyl endopeptidase== | ||
Revision as of 10:07, 12 July 2016
| |||||||||||
3D structures of prolyl endopeptidase
Updated on 12-July-2016
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Shan L, Mathews II, Khosla C. Structural and mechanistic analysis of two prolyl endopeptidases: role of interdomain dynamics in catalysis and specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Mar 8;102(10):3599-604. Epub 2005 Feb 28. PMID:15738423
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Besedin DV, Rudenskaia GN. [Proline-specific endopeptidases] Bioorg Khim. 2003 Jan-Feb;29(1):3-20. PMID:12658988
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 Gass J, Khosla C. Prolyl endopeptidases. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2007 Feb;64(3):345-55. PMID:17160352 doi:10.1007/s00018-006-6317-y
- ↑ Shan L, Marti T, Sollid LM, Gray GM, Khosla C. Comparative biochemical analysis of three bacterial prolyl endopeptidases: implications for coeliac sprue. Biochem J. 2004 Oct 15;383(Pt 2):311-8. PMID:15245330 doi:10.1042/BJ20040907
- ↑ Ehren J, Moron B, Martin E, Bethune MT, Gray GM, Khosla C. A food-grade enzyme preparation with modest gluten detoxification properties. PLoS One. 2009 Jul 21;4(7):e6313. PMID:19621078 doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0006313
- ↑ Ehren J, Govindarajan S, Moron B, Minshull J, Khosla C. Protein engineering of improved prolyl endopeptidases for celiac sprue therapy. Protein Eng Des Sel. 2008 Dec;21(12):699-707. Epub 2008 Oct 4. PMID:18836204 doi:10.1093/protein/gzn050
- ↑ Kanai K, Aranyi P, Bocskei Z, Ferenczy G, Harmat V, Simon K, Batori S, Naray-Szabo G, Hermecz I. Prolyl oligopeptidase inhibition by N-acyl-pro-pyrrolidine-type molecules. J Med Chem. 2008 Dec 11;51(23):7514-22. PMID:19006380 doi:10.1021/jm800944x
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Stacey Shantz, Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, Joel L. Sussman, Andrea Gorrell, David Canner