We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Prolyl Endopeptidase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | <StructureSection load='3eq7' size=' | + | <StructureSection load='3eq7' size='450' side='right' caption='Prolyl endopeptidase complex with Pro-(decarboxy-Pro)-type inhibitor (PDB entry [[3eq7]])' scene=''> |
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
== Structure == | == Structure == | ||
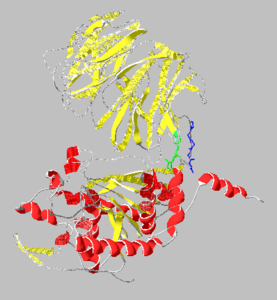
[[Image:1yr2_ribbon2.png|thumb|left|300x300px|alt=Alt text|Catalytic(bottom) and β-propeller domains(top) with peptide linkages between the domains shown in green and blue]] | [[Image:1yr2_ribbon2.png|thumb|left|300x300px|alt=Alt text|Catalytic(bottom) and β-propeller domains(top) with peptide linkages between the domains shown in green and blue]] | ||
| + | {{Clear}} | ||
Prolyl endopeptidases are relatively large enzymes(75 kDa) and contain two distinct domains: a catalytic domain and a β-propeller domain<ref name="Besedin">PMID:12658988</ref>. | Prolyl endopeptidases are relatively large enzymes(75 kDa) and contain two distinct domains: a catalytic domain and a β-propeller domain<ref name="Besedin">PMID:12658988</ref>. | ||
Revision as of 08:37, 28 July 2016
| |||||||||||
3D structures of prolyl endopeptidase
Updated on 28-July-2016
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Shan L, Mathews II, Khosla C. Structural and mechanistic analysis of two prolyl endopeptidases: role of interdomain dynamics in catalysis and specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Mar 8;102(10):3599-604. Epub 2005 Feb 28. PMID:15738423
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Besedin DV, Rudenskaia GN. [Proline-specific endopeptidases] Bioorg Khim. 2003 Jan-Feb;29(1):3-20. PMID:12658988
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 Gass J, Khosla C. Prolyl endopeptidases. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2007 Feb;64(3):345-55. PMID:17160352 doi:10.1007/s00018-006-6317-y
- ↑ Shan L, Marti T, Sollid LM, Gray GM, Khosla C. Comparative biochemical analysis of three bacterial prolyl endopeptidases: implications for coeliac sprue. Biochem J. 2004 Oct 15;383(Pt 2):311-8. PMID:15245330 doi:10.1042/BJ20040907
- ↑ Ehren J, Moron B, Martin E, Bethune MT, Gray GM, Khosla C. A food-grade enzyme preparation with modest gluten detoxification properties. PLoS One. 2009 Jul 21;4(7):e6313. PMID:19621078 doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0006313
- ↑ Ehren J, Govindarajan S, Moron B, Minshull J, Khosla C. Protein engineering of improved prolyl endopeptidases for celiac sprue therapy. Protein Eng Des Sel. 2008 Dec;21(12):699-707. Epub 2008 Oct 4. PMID:18836204 doi:10.1093/protein/gzn050
- ↑ Kanai K, Aranyi P, Bocskei Z, Ferenczy G, Harmat V, Simon K, Batori S, Naray-Szabo G, Hermecz I. Prolyl oligopeptidase inhibition by N-acyl-pro-pyrrolidine-type molecules. J Med Chem. 2008 Dec 11;51(23):7514-22. PMID:19006380 doi:10.1021/jm800944x
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Stacey Shantz, Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, Joel L. Sussman, Andrea Gorrell, David Canner