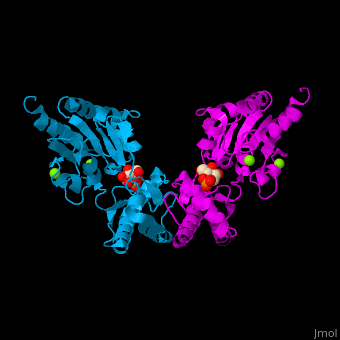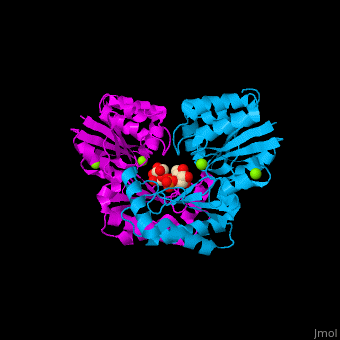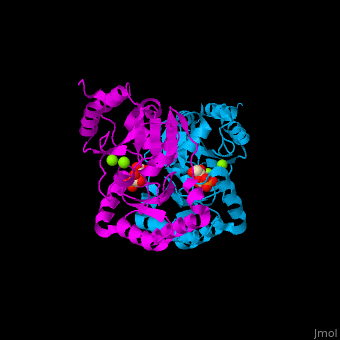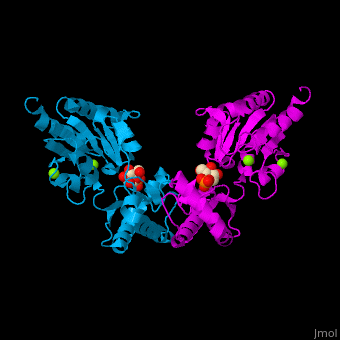We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Phosphomannomutase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
| - | The PMM structure contains a core domain and a cap domain. It is known that in order for the substrate to bind, the cap must dissociate from the core domain and then re-associate to seal the active site from solvent molecules. The active site of PMM is located at the interface of the core and cap domains of the molecule<ref>PMID:16540464</ref>. | + | The PMM structure contains a <scene name='48/481638/Cv/2'>core domain and a cap domain</scene>. It is known that in order for the substrate to bind, the cap must dissociate from the core domain and then re-associate to seal the active site from solvent molecules. The active site of PMM is located at the interface of the core and cap domains of the molecule<ref>PMID:16540464</ref>. |
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
Revision as of 08:29, 4 September 2016
| |||||||||||
3D Structures of phosphomannomutase
Updated on 04-September-2016
References
- ↑ Matthijs G, Schollen E, Pardon E, Veiga-Da-Cunha M, Jaeken J, Cassiman JJ, Van Schaftingen E. Mutations in PMM2, a phosphomannomutase gene on chromosome 16p13, in carbohydrate-deficient glycoprotein type I syndrome (Jaeken syndrome). Nat Genet. 1997 May;16(1):88-92. PMID:9140401 doi:10.1038/ng0597-88
- ↑ Silvaggi NR, Zhang C, Lu Z, Dai J, Dunaway-Mariano D, Allen KN. The X-ray crystal structures of human alpha-phosphomannomutase 1 reveal the structural basis of congenital disorder of glycosylation type 1a. J Biol Chem. 2006 May 26;281(21):14918-26. Epub 2006 Mar 15. PMID:16540464 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M601505200