This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Phosphoglycerate Kinase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
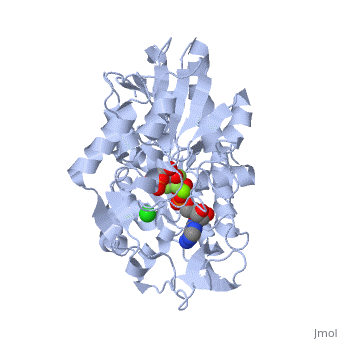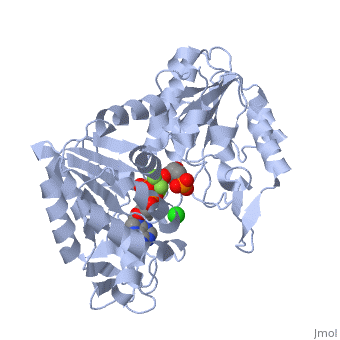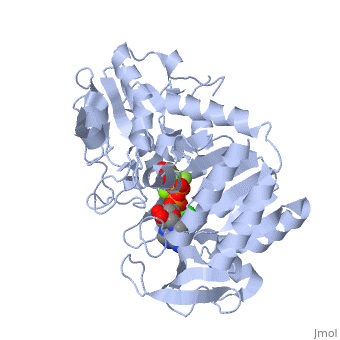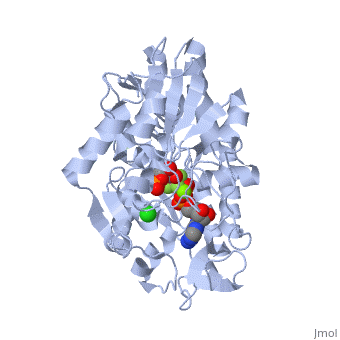
| - | <StructureSection load='2y3i' size=' | + | <StructureSection load='2y3i' size='450' side='right' scene='' caption='Human phosphoglycerate kinase complex with phosphoglyceric acid, ADP (stick model) AlF4-, Cl- and Mg+2 ions (green) (PDB code [[2y3i]])'> |
== PGK in the Glycolysis Cycle == | == PGK in the Glycolysis Cycle == | ||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
The overall structure of Phosphoglycerate kinase is very distinctive. It is a monomeric protein consisting of approximately 400 amino acids, with a molecular weight of about 45kD <ref> Auerbach, Gunter et al. 1997. Closed Structure of phosphoglycerate kinase from Thermotoga maritima reveals the catalytic mechanism and determinants of thermal stability. Structure. 5:1475-1483.</ref>. The structure is distinctly bilobed with a depressed region between the two lobes or domains. The lobes/domains are clearly connected at only two locations: <scene name='Shane_Harmon_Sandbox/Domain_links/1'>Beta Sheet L, Residues 189-202 and between Alpha Helix 14 and 15, Residues 404-408</scene>. The SCOP classification of PGK is alpha and beta, indicating that its <scene name='Shane_Harmon_Sandbox/Scop_classifcation/1'>secondary structure</scene>is composed of roughly equal numbers alpha and beta sheets. | The overall structure of Phosphoglycerate kinase is very distinctive. It is a monomeric protein consisting of approximately 400 amino acids, with a molecular weight of about 45kD <ref> Auerbach, Gunter et al. 1997. Closed Structure of phosphoglycerate kinase from Thermotoga maritima reveals the catalytic mechanism and determinants of thermal stability. Structure. 5:1475-1483.</ref>. The structure is distinctly bilobed with a depressed region between the two lobes or domains. The lobes/domains are clearly connected at only two locations: <scene name='Shane_Harmon_Sandbox/Domain_links/1'>Beta Sheet L, Residues 189-202 and between Alpha Helix 14 and 15, Residues 404-408</scene>. The SCOP classification of PGK is alpha and beta, indicating that its <scene name='Shane_Harmon_Sandbox/Scop_classifcation/1'>secondary structure</scene>is composed of roughly equal numbers alpha and beta sheets. | ||
| - | PGK structure shows an open-to-close transition upon hinge bending. PG assumes the open conformation upon release of PGA and ATP. The closed conformation active site contains PGA, ADP and AlF<sub>4</sub>-1 ion which mimics the phosphate ion<ref>PMID:21549713</ref> | + | PGK structure shows an open-to-close transition upon hinge bending. PG assumes the open conformation upon release of PGA and ATP. The closed conformation active site contains PGA, ADP and AlF<sub>4</sub>-1 ion which mimics the phosphate ion<ref>PMID:21549713</ref>. |
| + | *<scene name='38/387911/Cv/2'>Phosphoglycerate binding site</scene>. | ||
| + | *<scene name='38/387911/Cv/4'>AlF4- binding site</scene>. | ||
| + | *<scene name='38/387911/Cv/7'>ADP binding site</scene>. | ||
| + | *<scene name='38/387911/Cv/9'>Whole binding site</scene>. Water molecules shown as red spheres. | ||
== Reaction Mechanism == | == Reaction Mechanism == | ||
Revision as of 08:15, 5 September 2016
| |||||||||||
3D structures of phosphoglycerate kinase
Updated on 05-September-2016
Additional Resources
For additional information, see: Carbohydrate Metabolism
References
- ↑ Auerbach, Gunter et al. 1997. Closed Structure of phosphoglycerate kinase from Thermotoga maritima reveals the catalytic mechanism and determinants of thermal stability. Structure. 5:1475-1483.
- ↑ Lallemand P, Chaloin L, Roy B, Barman T, Bowler MW, Lionne C. Interaction of human 3-phosphoglycerate kinase with its two substrates: is substrate antagonism a kinetic advantage? J Mol Biol. 2011 Jun 24;409(5):742-57. Epub 2011 Apr 27. PMID:21549713 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2011.04.048
- ↑ Voet, Donald et al. 2008. Fundamentals of Biochemistry. 3rd ed. 499
- ↑ Auerbach, Gunter et al. 1997. Closed Structure of phosphoglycerate kinase from Thermotoga maritima reveals the catalytic mechanism and determinants of thermal stability. Structure. 5:1475-1483.
- ↑ Blake and Rice. 1981. Phosphoglycerate kinase. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. 293:93-104.
- ↑ Vas, M, Varga, A et al. 2010. Insight into the Mechanism of of Domain Movements and their Role in Enzyme Function: Example of 3-Phosphoglycerate kinase. Current Protein and Peptide Science. Jan 21, 2010. (Epub ahead of publication).
- ↑ Harnan, G. et al. 1992. Domain Motions in Phosphoglycerate Kinase: Determination of Interdomain Distance Distribution by Site Specific Labeling and Time Resolved Flourescense Energy Transfer. PNAS. 89:11764-11768.
- ↑ Auerbach, Gunter et al. 1997. Closed Structure of phosphoglycerate kinase from Thermotoga maritima reveals the catalytic mechanism and determinants of thermal stability. Structure. 5:1475-1483.
- ↑ Auerbach, Gunter et al. 1997. Closed Structure of phosphoglycerate kinase from Thermotoga maritima reveals the catalytic mechanism and determinants of thermal stability. Structure. 5:1475-1483.
- ↑ Scopes, Robert. 1977. The Steady State Kinetics of Yeast Phosphoglycerate Kinase. European Journal of Biochemistry. 85, 503-516
- ↑ Macioszek, Jerzy et al. 1990. Kinetics of the Two-Enzyme Phosphoglycerate Kinase/Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Couple. Plant Physiology 94: 291-296.
- ↑ Shaobo, Wu et al. 2009. PGK1 expression responds to freezing, anoxia, and dehydration stresses in freeze tolerant wood frog, Rana sylvatica. Journal of Experimental Zoology. 311, 57-67
- ↑ Hogg, PJ. 2002. Biological Regulation through protein disulfide bond cleavage. Redox Report. 7(2), 71-77.
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Shane Harmon, Michal Harel, Joel L. Sussman, Brandon Tritle, David Canner, Alexander Berchansky