Introduction
The telomerase is a complex composed of an RNA primer and protein that adds G-rich repeated DNA sequences to a 3' DNA strand in eukaryotic cells [1]. This ribonucleoprotein acts as a reverse transcriptase that creates a DNA sequence complementary to its RNA primer in its catalytic subunit, TERT [2]. The sequences attached to the end of DNA is non-coding DNA that functions as protection from mutation and degradation. As DNA replications occurs, the polymerase that copies in the 5' to 3' direction, cannot copy the end of the lagging strand which leaves unpaired bases that may code for a specific gene [3]. Multiple unpaired ends can form hydrogen bonds or even swap genetic material. The telomerase fixes this issue and lengthens the strands, because the replication process slowly shortens the ends of chromosomes. This enzyme also plays a role in coordinating cell division. Complementary issues of aging and cancer describe the inactivation or over-activation of telomerase activity [3].
History
In the 1930s, Barbara McClintock was the first to point out that the ends of chromosomes are somewhat different. Over forty years later, Olovnikov (1973) and Watson (1972) indicated an 'end replication problem' in which the lagging strand of DNA cannot be fully copied [2]. This concept led to a waterfall of studies and information vitally important to cellular regulation. In 1978, acclaimed chemist and front-runner in telomerase studies, Elizabeth H. Blackburn, discovered the telomere in Tetrahymena thermophila. By 1985, Blackburn and Carol Greider noted the enzymatic activity that created the telomeric sequences, and in 1987, the two women officially identified the telomerase as a ribonucleaoprotein with an essential RNA and and protein component. Elizabeth Blackburn, Carol Greider, and Jack Szostak won the 2009 Noble Prize in Physiology or Medicine for their lifetime work regarding the telomere and telomerase [3].
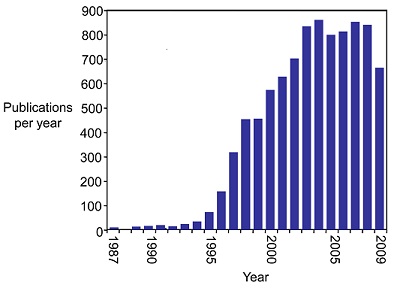
Since 1987, the study of the telomerase has exploded (see figure below)(3) mainly due to its connections to cancer. A multitude of studies in the mid-1990s indicated that many types of cancer cells show increased telomerase activity. By 2001, "telomerase activity had been observed in greater than 90% of patient samples from a wide range of different cancers" [3]. As a result, strategies to create telomerase inhibitors have been a focus in cancer research. One strategy that has seen success is creating oligonucleotides complementary to the RNA component that acts as a template for telomere formation. As of 2009, a handful of drugs containing these oligonucleotides were clinically approved as cancer treatment, and many more were in pre-clinical trials [3].
Structure
Overall Structure
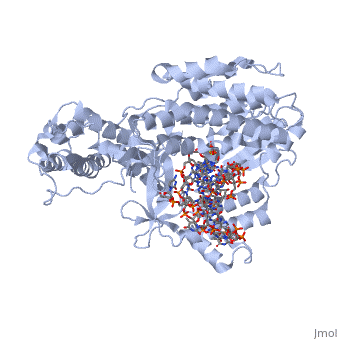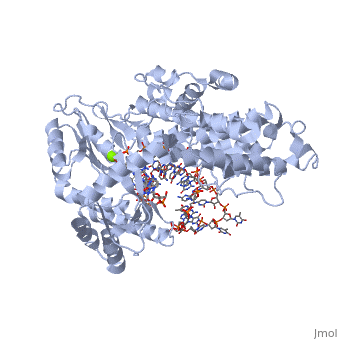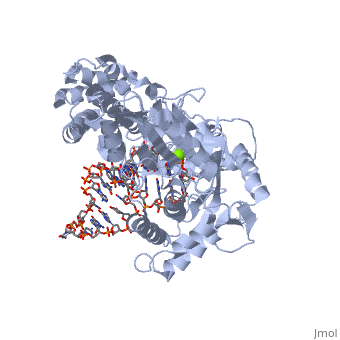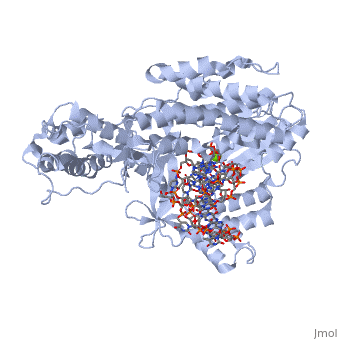
(protein in blue; RNA in green; DNA in red) acts as both a monomer and dimer. The monomer refers to the overall protein and its catalytic subunit TERT, made up of an amino acid polymer, containing approximately 5,000 atoms. This protein binds with the RNA template, , that TERT uses to add DNA to form a dimer-like structure [4]. The RNA has a molecular size between 200 and 500 kDA, depending on the organism [1]. Both the protein and RNA components are highly conserved structures among phylogenetic groups. is organized into a ring-like structure that shares common features with other reverse transcriptases (in viruses for example) and DNA polymerases. The RNA-DNA heteroduplex lies in the interior of the ring and positions the 3' end of the DNA primer at the active site to the telomerse can be enlongated. The substrate binding within the ring can accomodate 7 to 8 bases of double-stranded nucleic acid [4].
Architecture of TERT Structure
contains 3 domains: reverse transcriptase domain (in green), and carboxy-terminal extension (CTE)(in blue), RNA binding domain (TRBD)(in red). Similar to its structural homologs, as noted above, the ring contains fingers, palm, and thumb sections [4]. The reverse transcriptase domain represents the fingers and palm. It consists of a mixture of alpha helices and beta strands The TRBD domain is a helical structure that binds double and single stranded RNA, and is essential for RNP assembly and repeat addition processivity [5]. This fingers and palm is one of the most conserved portions across similar phylogeny. The thumb corresponds to the CTE, which is an elongated helical bundle that contains several surface-exposed long loops. Lastly, the TRBD is a helical structure that binds double and single stranded RNA. CTE and TRBD, the two terminal ends of the protein come together to form the ring-like structure [5].
For details on the reverse transcriptase domain see Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase.
Active Site Chemistry
The includes three invariant aspartic acids (D251,D343,and D344)(in blue), Mg2+ ligand, and hydrophobic tyrosine and valine (Y256 and V342)(in green). The aspartic acids aid in catalysis by interacting with the nucleotide bases. Replacing these residues with alanine results in a complete loss in TERT activity, which indicates that they are extremely important in the reverse transcription reaction. The magnesium ligand stabilizes the newly forming DNA strand by interacting with the negatively charges phosphate backbone. Lastly, the hydrophobic residues are hypothesized to structually hold the binding site together hydrophobically and possibly accommodating the base of the nucleotide substrate.
The reverse transcription process begins by the telomerase RNA binding to the 3' end of the overhanging DNA sequence. Once primed, the G-rich sequence (~6-8 nucleotides) polymerizes the end of the DNA. The RNA primer then translocates down the new DNA sequence and polymerizes again. This process repeats until the entire telomere is formed. After one side of the telomere is formed, the telomerase attaches the complementary nucleotide bases to complete the double-stranded telomere at the end of the DNA double helix.