Fosamax (alendronate sodium)
From Proteopedia
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | + | <table style="width:200px; border:1px solid black; float:right; "> | |
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td colspan="2">FOSAMAX</td> | <td colspan="2">FOSAMAX</td> | ||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
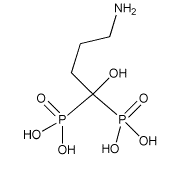
| - | Fosamax (Alendronate Sodium or Alendronic Acid) is a pharmaceutical drug administered to prevent and treat osteodegenerative diseases such as [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Osteoporosis Osteoporosis]. Functioning as a nitrogen-containing, second generation [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bisphosphonate bisphosphonate], Fosamax binds to [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hydroxylapatite hydroxyapatite] in bone and promotes apoptosis in [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Osteoclast osteoclasts] (cells specialized in skeletal breakdown), thereby delaying the degradation of bone tissue. While incorporated in bone matrix, alendronate is not pharmacologically active, thus, it must be continuously administered to suppress osteoclasts on newly formed resorption surfaces <ref>https://www.drugs.com/fosamax.html</ref>. | + | Fosamax (Alendronate Sodium or Alendronic Acid) is a pharmaceutical drug administered to prevent and treat osteodegenerative diseases such as [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Osteoporosis Osteoporosis]. Functioning as a nitrogen-containing, second generation [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bisphosphonate bisphosphonate], Fosamax binds to [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hydroxylapatite hydroxyapatite] in bone and promotes apoptosis in [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Osteoclast osteoclasts] (cells specialized in skeletal breakdown), thereby delaying the degradation of bone tissue. While incorporated in bone matrix, alendronate is not pharmacologically active, thus, it must be continuously administered to suppress osteoclasts on newly formed resorption surfaces <ref>https://www.drugs.com/fosamax.html</ref>. [[Image:http://baddrugrecall.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/01/fosamax.jpg]] |
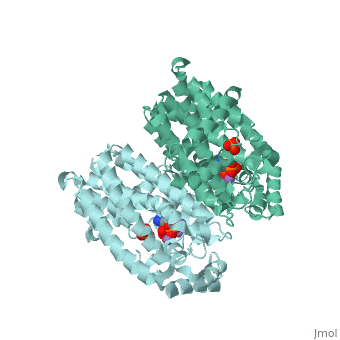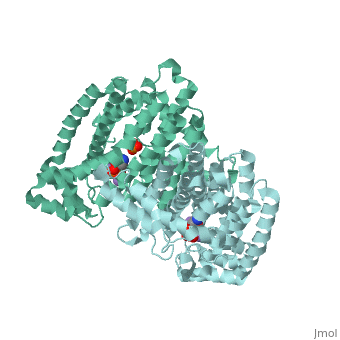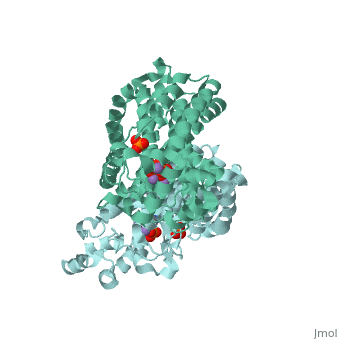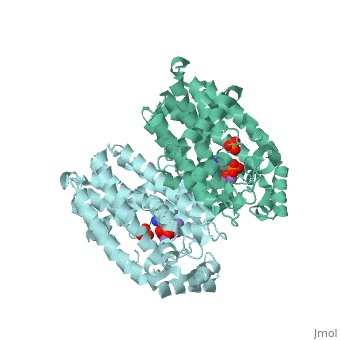
== Structural Highlights <ref>http://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbe/entry/pdb/2F89</ref> == | == Structural Highlights <ref>http://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbe/entry/pdb/2F89</ref> == | ||
Revision as of 15:50, 15 November 2016
| FOSAMAX | |
| image | |
| President: | president |
| Address: | address |
| Phone: | phone |
| Hours Open: | hours open |
Fosamax (Alendronate Sodium or Alendronic Acid) is a pharmaceutical drug administered to prevent and treat osteodegenerative diseases such as Osteoporosis. Functioning as a nitrogen-containing, second generation bisphosphonate, Fosamax binds to hydroxyapatite in bone and promotes apoptosis in osteoclasts (cells specialized in skeletal breakdown), thereby delaying the degradation of bone tissue. While incorporated in bone matrix, alendronate is not pharmacologically active, thus, it must be continuously administered to suppress osteoclasts on newly formed resorption surfaces [1]. Image:Http://baddrugrecall.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/01/fosamax.jpg
Contents |
Structural Highlights [2]
| |||||||||||
Function
Functioning as a nitrogen-containing, second generation bisphosphonate, Fosamax binds to hydroxyapatite in bone and promotes apoptosis in osteoclasts (cells specialized in skeletal breakdown), thereby slowing the degradation of bone tissue. Furthermore, alendronic acid binds to and inhibits the activity of farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase, an enzyme catalyzes a step in a biochemical pathway essential for homeostatic regulation of osteoclastic activity.
Mechanism
Fosamax inhibits farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase (FPS or FPPS), one of the enzymes in the mevalonic acid pathway involved in producing isoprenoid compounds that are essential for post-translational modification of small guanosine triphosphate (GTP)-binding proteins, such as Rho, Ras, and Rab. Inhibition of this process interferes with osteoclast function and survival [3]. The net negative charge of alendronic acid forms electrostatic interactions with Magnesium cofactors at a ligand site of FPS, binding in competition with small molecules of similar chemical structure such as pamidronate and risedronate.
Side Effects [4]
• Common side effects of Fosamax include gas, constipation, heartburn, diarrhea, bloating, nausea, vomiting, stomach pain, joint pain or swelling, swelling in your hands or feet, dizziness, headache, eye pain, back pain, or weakness.
• Serious side effects of Fosamax include severe pain (joints, bone, muscle, jaw, back or heartburn), chest pain, difficulty swallowing, bloody stools, eye pain, skin blisters, and swelling of the face, tongue, or throat.
References
- ↑ https://www.drugs.com/fosamax.html
- ↑ http://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbe/entry/pdb/2F89
- ↑ http://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00630#bond-15126
- ↑ http://www.rxlist.com/fosamax-side-effects-drug-center.htm
Contributors and Editors
Alyssa Jewel D. Floro Kidd, Justin M.