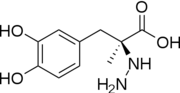
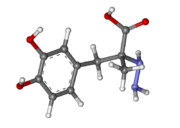
Carbidopa
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| - | <StructureSection load='1js3'=size='340' side='right' caption='Crystal structure of DOPA Decarboxylase in complex with the inhibitor carbidopa PDB:[[1js3]]' scene=''><scene name='pdbligand=142:CARBIDOPA'>Carbidopa</scene> (Lodosyn) is a drug given, in conjunction with Levadopa, to those with Parkinson's Disease in order to inhibit the extracranial metabolism of Levadopa to dopamine, allowing a greater portion of the drug to cross the blood-brain barrier and produce the desired anti-parkinsonian effects. It works by inhibiting the enzymatic activity of aromatic-L-amino-acid decarboxylase ([[DOPA Decarboxylase]] or DDC)<ref name="one">PMID:11106255</ref> | + | <StructureSection load='1js3'=size='340' side='right' caption='Crystal structure of DOPA Decarboxylase in complex with the inhibitor carbidopa PDB:[[1js3]]' scene=''><scene name='pdbligand=142:CARBIDOPA'>Carbidopa</scene> (Lodosyn) is a drug given, in conjunction with Levadopa, to those with Parkinson's Disease in order to inhibit the extracranial metabolism of Levadopa to dopamine, allowing a greater portion of the drug to cross the blood-brain barrier and produce the desired anti-parkinsonian effects in the nerve cell. It works by inhibiting the enzymatic activity of aromatic-L-amino-acid decarboxylase ([[DOPA Decarboxylase]] or DDC)<ref name="one">PMID:11106255</ref>. |
== Structure == | == Structure == | ||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
== Molecular Mechanism == | == Molecular Mechanism == | ||
| - | The conversion of L-DOPA into dopamine is catalyzed by the vitamin B6 (<scene name='pdbligand=PLP:PYRIDOXAL-5-PHOSPHATE'>PLP</scene>)-dependent enzyme DDC, an enzyme abundant in the nervous system as well as kidneys of humans<ref name="three">PMID: 7651438</ref> The catalytically active form of DDC is a homodimer, a feature typical of this class of enzymes<ref name= "four">PMID: 10673430</ref>. DDCs active site is located between the two monomers but is | + | The conversion of L-DOPA into dopamine is catalyzed by the vitamin B6 (<scene name='pdbligand=PLP:PYRIDOXAL-5-PHOSPHATE'>PLP</scene>)-dependent enzyme DDC, an enzyme abundant in the nervous system as well as kidneys of humans<ref name="three">PMID: 7651438</ref> The catalytically active form of DDC is a homodimer, a feature typical of this class of enzymes<ref name= "four">PMID: 10673430</ref>. DDCs active site is located between the two monomers but is mainly composed of residues from only one of the monomers. The cofactor PLP binds to Lys 303 through a Schiff base linkage and a salt bridge between the carboxylate group of Asp 271 and the protonated pyridine nitrogen of PLP, which acts as a strong electron sink capable of stabilizing the carbanionic intermediates produced by active DDC. the cofactor is further stabilized in the enzyme through a network of hydrogen bonds. Carbidopa works by forming a hydrazone linkage with the PLP cofactor through its hydrazine moiety and blocking the DDC <scene name='74/746001/Active_site_dopa/4'>active site</scene> residues Ile 101' and Phe 103' in the substrate binding pocket with its catechol ring<ref name="five">doi:10.1038/nsb1101-963</ref>. Due to the fact that Carbidopa cannot cross the blood-brain barrier, its inhibiting effects only are displayed in the periphery. |
== Disease in Humans == | == Disease in Humans == | ||
Revision as of 17:43, 16 November 2016
Function
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Gilbert JA, Frederick LM, Ames MM. The aromatic-L-amino acid decarboxylase inhibitor carbidopa is selectively cytotoxic to human pulmonary carcinoid and small cell lung carcinoma cells. Clin Cancer Res. 2000 Nov;6(11):4365-72. PMID:11106255
- ↑ https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/carbidopa#section=Top
- ↑ Opacka-Juffry J, Brooks DJ. L-dihydroxyphenylalanine and its decarboxylase: new ideas on their neuroregulatory roles. Mov Disord. 1995 May;10(3):241-9. PMID:7651438 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/mds.870100302
- ↑ Schneider G, Kack H, Lindqvist Y. The manifold of vitamin B6 dependent enzymes. Structure. 2000 Jan 15;8(1):R1-6. PMID:10673430
- ↑ Burkhard P, Dominici P, Borri-Voltattorni C, Jansonius JN, Malashkevich VN. Structural insight into Parkinson's disease treatment from drug-inhibited DOPA decarboxylase. Nat Struct Biol. 2001 Nov;8(11):963-7. PMID:11685243 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nsb1101-963
- ↑ Feany MB, Bender WW. A Drosophila model of Parkinson's disease. Nature. 2000 Mar 23;404(6776):394-8. PMID:10746727 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/35006074