We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
User:Cody J Cubbage
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
==Function== | ==Function== | ||
| - | |||
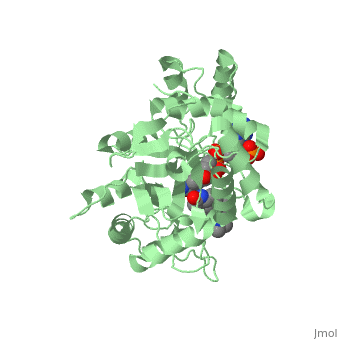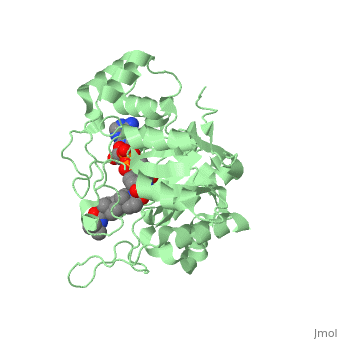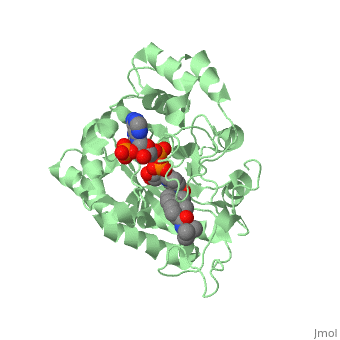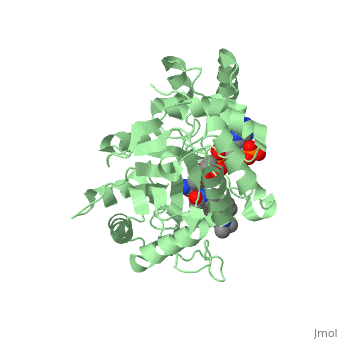
Finasteride is a synthetic 4-azasteroid compound that acts as a 5α-reductase inhibitor. The 5α-reductase enzyme is very important in the metabolism of many of the steroids produced by the body, in particular the conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT). For this reason, Finasteride is used as a treatment for benign prostate hyperplasia (BPH), which is caused by an overproduction of DHT in the male prostate. Pattern hair loss, another condition in men, caused by the build up of DHT, can also be treated with Finasteride. To see what Finasteride looks like unbound, click this link: <scene name='74/745970/Finasteride_unbound/1'>FIT</scene>. | Finasteride is a synthetic 4-azasteroid compound that acts as a 5α-reductase inhibitor. The 5α-reductase enzyme is very important in the metabolism of many of the steroids produced by the body, in particular the conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT). For this reason, Finasteride is used as a treatment for benign prostate hyperplasia (BPH), which is caused by an overproduction of DHT in the male prostate. Pattern hair loss, another condition in men, caused by the build up of DHT, can also be treated with Finasteride. To see what Finasteride looks like unbound, click this link: <scene name='74/745970/Finasteride_unbound/1'>FIT</scene>. | ||
| Line 19: | Line 18: | ||
Finasteride is a 5-alpha reductase inhibitor. There are two isoforms of the 5alpha-reductase enzyme, type I and II, and while the drug has a higher affinity for the type II enzyme, it also inhibits the function of the type I. (.....) | Finasteride is a 5-alpha reductase inhibitor. There are two isoforms of the 5alpha-reductase enzyme, type I and II, and while the drug has a higher affinity for the type II enzyme, it also inhibits the function of the type I. (.....) | ||
Typically 5 alpha-redcutase turns testosterone into Dihydrotestosterone(DHT), but the enzyme will accept Finasteride as an alternate substrate; turning it into dihydrofinasteride through an enzyme bound, NADP-dihydrofinasteride adduct. Finasteride is similar in structure to testosterone and 5alpha-reductase has almost the same affinity for both molecules. However, Finasteride , having a high affinity for 5 alpha-reductase, covalently binds to the enzyme as a Michael acceptor, through a functionally irreversible reaction. However, the NADP-dihydrofinasteride complex breaks down with a half life of about 1 month at 37˚C., which is why patients must continue taking the drug.(.....) | Typically 5 alpha-redcutase turns testosterone into Dihydrotestosterone(DHT), but the enzyme will accept Finasteride as an alternate substrate; turning it into dihydrofinasteride through an enzyme bound, NADP-dihydrofinasteride adduct. Finasteride is similar in structure to testosterone and 5alpha-reductase has almost the same affinity for both molecules. However, Finasteride , having a high affinity for 5 alpha-reductase, covalently binds to the enzyme as a Michael acceptor, through a functionally irreversible reaction. However, the NADP-dihydrofinasteride complex breaks down with a half life of about 1 month at 37˚C., which is why patients must continue taking the drug.(.....) | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Finasteride mechanism.png|left|430px]] | ||
==Medical Uses== | ==Medical Uses== | ||
Revision as of 00:49, 17 November 2016
N-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-3-oxo-(5α,17β)-4-azaandrost-1-ene-17-carboxamide
| |||||||||||
References
</references>