Riboswitch
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
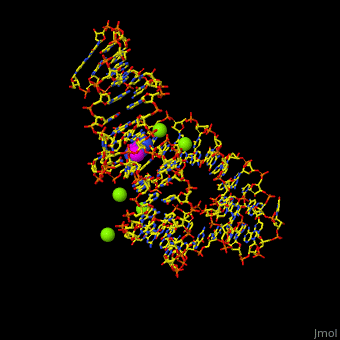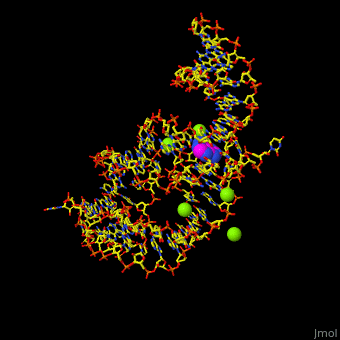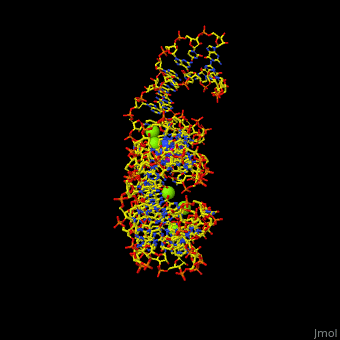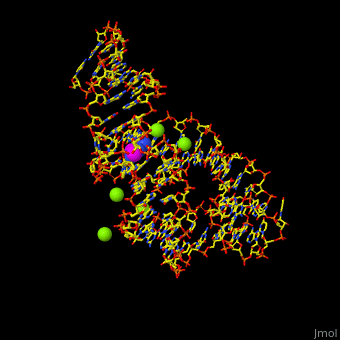
| - | <StructureSection load='1y26' size=' | + | <StructureSection load='1y26' size='350' side='right' scene='47/479252/Cv/1' caption='Adenine riboswitch complex with adenine and Mg+2 ions, [[1y26]]'> |
== Function == | == Function == | ||
Normally, a variety of proteins and protein cofactors control gene expression in an organism by binding to different sites on messenger RNA (mRNA). '''Riboswitches''' are genetic regulatory elements that are built directly into the RNA. They are a type of noncoding RNA that regulate gene expression in the absence of proteins by switching from one structural conformation (shape) to another in response to ligand binding. Most contain a single binding site that recognizes a specific ligand. The ability of a riboswitch to discriminate against molecules that are similar or closely related to its ligand is essential to prevent metabolic misregulation<ref name=scimag>Breaker, Ronald R. (28 March, 2008). Complex Riboswitches. ''Science'', 319(5871), 1795-1797. doi:[http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.1152621 10.1126/science.1152621]</ref>. | Normally, a variety of proteins and protein cofactors control gene expression in an organism by binding to different sites on messenger RNA (mRNA). '''Riboswitches''' are genetic regulatory elements that are built directly into the RNA. They are a type of noncoding RNA that regulate gene expression in the absence of proteins by switching from one structural conformation (shape) to another in response to ligand binding. Most contain a single binding site that recognizes a specific ligand. The ability of a riboswitch to discriminate against molecules that are similar or closely related to its ligand is essential to prevent metabolic misregulation<ref name=scimag>Breaker, Ronald R. (28 March, 2008). Complex Riboswitches. ''Science'', 319(5871), 1795-1797. doi:[http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.1152621 10.1126/science.1152621]</ref>. | ||
| Line 110: | Line 110: | ||
**[[3suh]], [[3sux]] – EsTHFR + THF derivative – ''Eubacterium siraeum''<br /> | **[[3suh]], [[3sux]] – EsTHFR + THF derivative – ''Eubacterium siraeum''<br /> | ||
**[[3suy]] - EsTHFR + cytidine cyclic phosphate<br /> | **[[3suy]] - EsTHFR + cytidine cyclic phosphate<br /> | ||
| - | ** | + | **[[4lvv]], [[4lvx]], [[4lvw]], [[4lvy]], [[4lvz]], [[4lw0]] – THFR + purine derivative – synthetic<br /> |
**[[3sd3]] – THFR (mutant) + pteridine derivative – synthetic<br /> | **[[3sd3]] – THFR (mutant) + pteridine derivative – synthetic<br /> | ||
Revision as of 10:35, 24 November 2016
| |||||||||||
3D structures of riboswitch
Updated on 24-November-2016
References
- ↑ Breaker, Ronald R. (28 March, 2008). Complex Riboswitches. Science, 319(5871), 1795-1797. doi:10.1126/science.1152621
- ↑ Serganov A, Yuan YR, Pikovskaya O, Polonskaia A, Malinina L, Phan AT, Hobartner C, Micura R, Breaker RR, Patel DJ. Structural basis for discriminative regulation of gene expression by adenine- and guanine-sensing mRNAs. Chem Biol. 2004 Dec;11(12):1729-41. PMID:15610857 doi:S1074-5521(04)00343-6
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, Karsten Theis, Joel L. Sussman