This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Zepatier
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
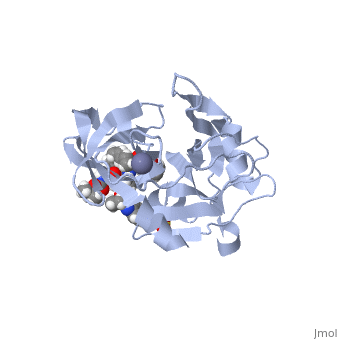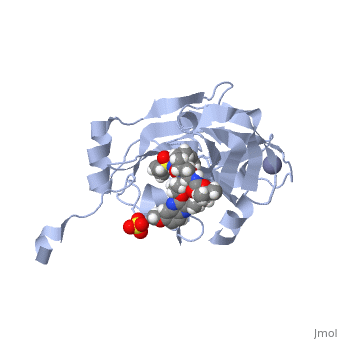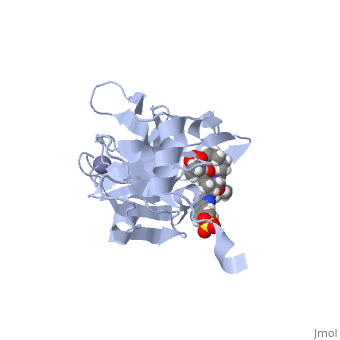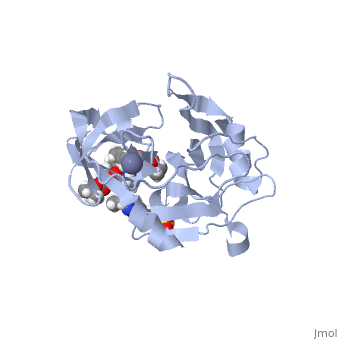
| - | Zepatier is a combination drug combating genotypes 1 and 4 of chronic hepatitis C viral (HCV) infections in adults. It is designed for the treatment of individuals with end stage renal disease on dialysis, typically genotype 1 infected patients. The drug is also utilized to treat genotype 4 patients when other methods of treatment prove ineffective <ref>Petrescu, I. O.; Biciusca, V.; Taisescu, C. I.; Alexandru, D. O.; Taisescu, O.; Comanescu, M. V.; Petrescu, F.; Popescu, I. A.; Trasca, D. M.; ForTofoiu, M. C.; Silosi, C. A.; ForTofoiu, M. Histological factors that predict the liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2016, 57, 759-765.</ref>.<scene name='74/746120/Elbasvir_structure3/1'>Elbasvir</scene> inhibits NS5A, a non-enzymatic protein essential for viral replication and assembly of hepatitis C whose exact mechanism of action is unknown. Elbasvir restricts viral production at the early stage of assembly, in turn preventing spread of the virus<ref name="elbasvir">DOI: 10.1002/cmdc.201300343</ref>. | + | Zepatier is a combination drug combating genotypes 1 and 4 of chronic hepatitis C viral (HCV) infections in adults. It is designed for the treatment of individuals with end stage renal disease on dialysis, typically genotype 1 infected patients. The drug is also utilized to treat genotype 4 patients when other methods of treatment prove ineffective <ref>Petrescu, I. O.; Biciusca, V.; Taisescu, C. I.; Alexandru, D. O.; Taisescu, O.; Comanescu, M. V.; Petrescu, F.; Popescu, I. A.; Trasca, D. M.; ForTofoiu, M. C.; Silosi, C. A.; ForTofoiu, M. Histological factors that predict the liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2016, 57, 759-765.</ref>. For an example of the HCV genome, click here [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1630/figure/ch1.f2/?report=objectonly]. <scene name='74/746120/Elbasvir_structure3/1'>Elbasvir</scene> inhibits NS5A, a non-enzymatic protein essential for viral replication and assembly of hepatitis C whose exact mechanism of action is unknown. Elbasvir restricts viral production at the early stage of assembly, in turn preventing spread of the virus<ref name="elbasvir">DOI: 10.1002/cmdc.201300343</ref>. |
<scene name='74/746120/Grazoprevir_meg/1'>Grazoprevir</scene> is a macrocyclic compound that is able to reversibly bind to the protease, NS3/4A, essential for viral replication. It is responsible for cleavage and processing of the HCV polyprotein. It is hypothesized that the protease is utilized to circumvent immune response at the primary stages of infection <ref>DOI: 10.1021/acschembio.5b00647</ref>. | <scene name='74/746120/Grazoprevir_meg/1'>Grazoprevir</scene> is a macrocyclic compound that is able to reversibly bind to the protease, NS3/4A, essential for viral replication. It is responsible for cleavage and processing of the HCV polyprotein. It is hypothesized that the protease is utilized to circumvent immune response at the primary stages of infection <ref>DOI: 10.1021/acschembio.5b00647</ref>. | ||
Revision as of 20:41, 4 December 2016
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Tan, S.-L. Hepatitis C viruses: genomes and molecular biology; Horizon bioscience: Wymondham, 2006.
- ↑ Chevaliez, S.; Pawlotsky, J. M. Virology of hepatitis C virus infection. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol.2012, 26, 381-389.
- ↑ Tan, S.-L. Hepatitis C viruses: genomes and molecular biology; Horizon bioscience: Wymondham, 2006.
- ↑ Tan, S.-L. Hepatitis C viruses: genomes and molecular biology; Horizon bioscience: Wymondham, 2006.
- ↑ Petrescu, I. O.; Biciusca, V.; Taisescu, C. I.; Alexandru, D. O.; Taisescu, O.; Comanescu, M. V.; Petrescu, F.; Popescu, I. A.; Trasca, D. M.; ForTofoiu, M. C.; Silosi, C. A.; ForTofoiu, M. Histological factors that predict the liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2016, 57, 759-765.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Coburn CA, Meinke PT, Chang W, Fandozzi CM, Graham DJ, Hu B, Huang Q, Kargman S, Kozlowski J, Liu R, McCauley JA, Nomeir AA, Soll RM, Vacca JP, Wang D, Wu H, Zhong B, Olsen DB, Ludmerer SW. Discovery of MK-8742: an HCV NS5A inhibitor with broad genotype activity. ChemMedChem. 2013 Dec;8(12):1930-40. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.201300343. Epub 2013 Oct, 14. PMID:24127258 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/cmdc.201300343
- ↑ Soumana DI, Kurt Yilmaz N, Prachanronarong KL, Aydin C, Ali A, Schiffer CA. Structural and Thermodynamic Effects of Macrocyclization in HCV NS3/4A Inhibitor MK-5172. ACS Chem Biol. 2015 Dec 18. PMID:26682473 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acschembio.5b00647
- ↑ National Center for Biotechnology Inforamtion. PubChem Compound Database; CID=71661251, https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/71661251#section=Chemical-and-Physical-Properties
- ↑ http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2013.03.030
- ↑ Fridell RA, Qiu D, Valera L, Wang C, Rose RE, Gao M. Distinct functions of NS5A in hepatitis C virus RNA replication uncovered by studies with the NS5A inhibitor BMS-790052. J Virol. 2011 Jul;85(14):7312-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00253-11. Epub 2011 May 18. PMID:21593143 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/JVI.00253-11
- ↑ National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Compound Database; CID=44603531, https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/44603531.
- ↑ Soumana DI, Kurt Yilmaz N, Prachanronarong KL, Aydin C, Ali A, Schiffer CA. Structural and Thermodynamic Effects of Macrocyclization in HCV NS3/4A Inhibitor MK-5172. ACS Chem Biol. 2015 Dec 18. PMID:26682473 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acschembio.5b00647
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] [9] [10]