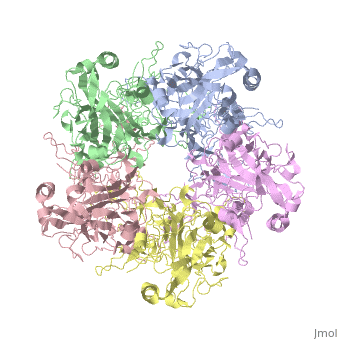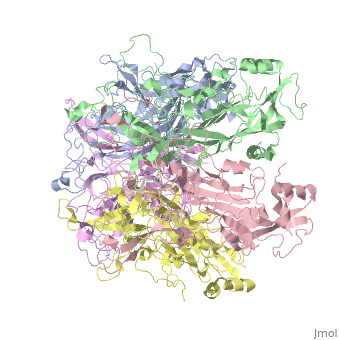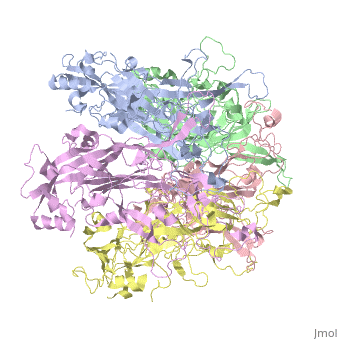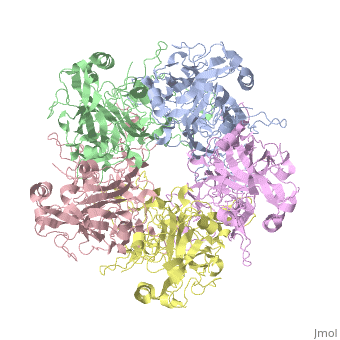Major capsid protein L1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
== Structural Highlights== | == Structural Highlights== | ||
| - | The main ingredient in Gardasil 9 is L1 Major Capsid Protein<ref name="L1"/>. L1 Major Capsid Protein has 72 pentamers of major capsid proteins that are linked together by <scene name='74/746002/L1_disulfide_bonds/2'>disulfide bonds </scene> ,shown in red on the monomer, that creates an icosahedral capsid with a T=7 symmetry, which is a spherical protein <ref>DOI: 10.1128/JVI.77.8.4818-4826.2003</ref>. The disulfide bonds are formed to increase the stability of the pentamers. The disulfide bonds in HPV16 is between <scene name='74/746002/L1_cys_175new/1'>Cys175</scene> and Cys428<ref>http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.virol.2013.05.038</ref>. L1 Major Capsid Protein is associated with L2 Minor Capsid Protein. The L1 Major Capsid Protein is built of mainly <scene name='74/746002/L1_beta_sheets/1'>Beta sheets</scene> <ref> http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P03101 </ref> shown in orange. Other inactive ingredients in Gardasil 9 are amorphous aluminum hydroxyphosphate sulfate, yeast protein, sodium chloride, L-histidine, polysorbate 80, sodium borate, and water <ref>https://www.merck.com/product/usa/pi_circulars/g/gardasil/gardasil_ppi.pdf</ref>. Amorphous aluminum hydroxyphosphate sulfate is used to increase the antibody response in the body by increasing the ability of the antigen to have a response to the virus <ref> DOI: 10.4161/hv.3.4.4309 </ref>. Yeast is used to express the specific protein from each HPV virus type in order to create numerous copies of those proteins <ref>http://www.fda.gov/BiologicsBloodVaccines/Vaccines/QuestionsaboutVaccines/ucm096052.htm</ref>. | + | The main ingredient in Gardasil 9 is L1 Major Capsid Protein<ref name="L1"/>. L1 Major Capsid Protein has 72 pentamers of major capsid proteins that are linked together by <scene name='74/746002/L1_disulfide_bonds/2'>disulfide bonds </scene> ,shown in red on the monomer, that creates an icosahedral capsid with a T=7 symmetry, which is a spherical protein <ref>DOI: 10.1128/JVI.77.8.4818-4826.2003</ref>. The disulfide bonds are formed to increase the stability of the pentamers. The disulfide bonds in HPV16 is between <scene name='74/746002/L1_cys_175new/1'>Cys175</scene> and Cys428<ref>http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.virol.2013.05.038</ref>. L1 Major Capsid Protein is associated with L2 Minor Capsid Protein. The L1 Major Capsid Protein is built of mainly <scene name='74/746002/L1_beta_sheets/1'>Beta sheets</scene> <ref> http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P03101 </ref> shown in orange. Other inactive ingredients in Gardasil 9 are amorphous aluminum hydroxyphosphate sulfate, yeast protein, sodium chloride, L-histidine, polysorbate 80, sodium borate, and water <ref>https://www.merck.com/product/usa/pi_circulars/g/gardasil/gardasil_ppi.pdf</ref>. Amorphous aluminum hydroxyphosphate sulfate is used to increase the antibody response in the body by increasing the ability of the antigen to have a response to the virus <ref> DOI: 10.4161/hv.3.4.4309 </ref>. Yeast is used to express the specific protein from each HPV virus type in order to create numerous copies of those proteins <ref>http://www.fda.gov/BiologicsBloodVaccines/Vaccines/QuestionsaboutVaccines/ucm096052.htm</ref>. L-histidine is an enzymes used to create histamines that creates an immuno-response against a pathogen <ref> http://www.news-medical.net/health/Histamine-Storage-and-Release.aspx </ref>. Polysorbate 80 is used is vaccines in order to create an even blend of all the ingredients in the vaccine <ref> www.westonaprice.org/health-topics/vaccination/adjuvants-in-vaccines/ </ref>. Sodium borate and water are used as a buffer and a solvent, respectively, for the other ingredients ingredients in Gardasil <ref> http://www.immune.org.nz/sites/default/files/resources/ConcernVaccineIngredients20140522V01Final.pdf </ref>. |
== Relevance to Human Health and Disease == | == Relevance to Human Health and Disease == | ||
Revision as of 22:23, 4 December 2016
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Zhai L, Tumban E. Gardasil-9: A global survey of projected efficacy. Antiviral Res. 2016 Jun;130:101-9. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2016.03.016. Epub, 2016 Apr 1. PMID:27040313 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.antiviral.2016.03.016
- ↑ https://www.gardasil9.com
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 http://www.hpvvaccine.org.au/the-hpv-vaccine/how-does-it-work.aspx
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/medicine/19016
- ↑ Harper DM, Vierthaler SL, Santee JA. Review of Gardasil. J Vaccines Vaccin. 2010 Nov 23;1(107). pii: 1000107. PMID:23805398 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.4172/2157-7560.1000107
- ↑ http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Scientific_Discussion/human/000703/WC500021140.pdf
- ↑ doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.1128/JVI.77.8.4818-4826.2003
- ↑ http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.virol.2013.05.038
- ↑ http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P03101
- ↑ https://www.merck.com/product/usa/pi_circulars/g/gardasil/gardasil_ppi.pdf
- ↑ doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.4161/hv.3.4.4309
- ↑ http://www.fda.gov/BiologicsBloodVaccines/Vaccines/QuestionsaboutVaccines/ucm096052.htm
- ↑ http://www.news-medical.net/health/Histamine-Storage-and-Release.aspx
- ↑ www.westonaprice.org/health-topics/vaccination/adjuvants-in-vaccines/
- ↑ http://www.immune.org.nz/sites/default/files/resources/ConcernVaccineIngredients20140522V01Final.pdf
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 16.2 Murray, Patrick R., Ken S. Rosenthal, and Michael A. Pfaller. "Papillomavirus and Polyomavirus." Medical Microbiology. Philadelphia: Elsevier/Saunders, 2013. 445-450.
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Morgan Smith, Michal Harel, Jessica Troutman., Maximillia Jackson., Jaime Prilusky