We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Ribavirin
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
== Disease == | == Disease == | ||
===Hepatitis C=== | ===Hepatitis C=== | ||
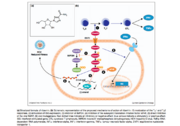
| - | Hepatitis C is an infectious disease that affects the liver due to the Hepatitis C virus (HCV). This disease can be acute or chronic and can even lead to death. By binding to the gC1qR receptor, HCV proteins are able to effectively inhibit the differentiation of helper T cells. In addition, HCV core proteins work by preventing the synthesis of the antiviral interferon IFN-γ. Thus, weakening the body’s immunity and making it susceptible to infection. Ribavirin is used in combination with peginterferon to treat Hepatitis C.<ref>doi: 10.1002/hep.22070</ref> By adding pegylated interferon-alpha to ribavirin, the drug had a longer half life, which required only single weekly dosing for Hepatitis C treatment. <ref name="paesh">doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2011.10.030</ref> | + | Hepatitis C is an infectious disease that affects the liver due to the Hepatitis C virus (HCV). This disease can be acute or chronic and can even lead to death. By binding to the gC1qR receptor, HCV proteins are able to effectively inhibit the differentiation of helper T cells. In addition, HCV core proteins work by preventing the synthesis of the antiviral interferon IFN-γ. Thus, weakening the body’s immunity and making it susceptible to infection. Ribavirin is used in combination with peginterferon to treat Hepatitis C.<ref>doi: 10.1002/hep.22070</ref> By adding pegylated interferon-alpha to ribavirin, the drug had a longer half-life, which required only single weekly dosing for Hepatitis C treatment. <ref name="paesh">doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2011.10.030</ref> There are two types of polyethylene glycol (PEG):1. P-INFa-2b and 2. P-INFa-2a. While P-INFa-2b is linear, covalently attached to histidine, and subject to hydrolysis upon injection, P-INFa-2a is branched, attached to lysine through amide bonds, and circulates as a whole molecule upon injection. The limited distribution of P-INFa-2a results in a longer half-life. <ref>doi:10.2165/11531990-000000000-00000</ref> |
===Pneumonia=== | ===Pneumonia=== | ||
Respiratory syncytial virus is responsible for viral pneumonia. This infection causes the air sacs in one or both of the lungs to become inflamed and potentially filled with fluid or pus. In infants, children, and adults over the age of 65, pneumonia can be deadly. It has been shown that Ribavirin can treat viral pneumonia by preventing transcription of respiratory syncytial virus. <ref> National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute. (2016, September 26). Pneumonia. Retrieved from https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/health-topics/topics/pnu </ref> | Respiratory syncytial virus is responsible for viral pneumonia. This infection causes the air sacs in one or both of the lungs to become inflamed and potentially filled with fluid or pus. In infants, children, and adults over the age of 65, pneumonia can be deadly. It has been shown that Ribavirin can treat viral pneumonia by preventing transcription of respiratory syncytial virus. <ref> National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute. (2016, September 26). Pneumonia. Retrieved from https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/health-topics/topics/pnu </ref> | ||
Revision as of 18:05, 5 December 2016
1-β-D-ribofuranosyl-1H-1,2,4-triazole-3-carboxamide [1]
| |||||||||||
References
- Gish, R. G. Treating HCV with ribavirin analogue and ribavirin-like molecules. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy. 2005, November 17;1-6. doi:10.1093/jac/dki405
- Thomas, E., Ghany, M., Liang, J., The application and mechanism of action of ribavirin in therapy of hepatitis C. Antiviral Chemistry & Chemotherapy 23:1-12 (2012)doi: 10.3851/IMP2125
- Chung, R.T., Gale, M.J., Polyak, S.J., Lemon, S.M., Liang, T.J., & Hoofnagle, J.H. Mechanisms of action of interferon and ribavirin in chronic hepatitis C: Summary of a workshop. Hepatology. 2008;47 (1), 306-320. doi: 10.1002/hep.22070
- Paeshuyse, J, Dallmeier, K, Neyts, J. Ribavirin for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C virus infection: a review of the proposed mechanisms of action. Current Opinion in Virology. 2011;1(6) 590-598. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2011.10.030
- National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute. Pneumonia. 2016, September 26; Retrieved from https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/health-topics/topics/pnu
- Foster, G. Pegylated interferons for the treatment of chronic Hepatitis C. Drugs. 2010;70(2):147-165. doi:10.2165/11531990-000000000-00000
- Hofmann WP, Herrmann E, Sarrazin C, Zeuzem S. Ribavirin mode of action in chronic hepatitis C: from clinical use back to molecular mechanisms. Liver Int. 2008, 28:1332-1343. doi: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2008.01896.x
- Fujimoto T, Tomimatsu M, Iga D, Endo H, Otsuka K. Changes in the Th1/Th2 ratio during a 24-week course of an interferon alpha-2b plus ribavirin combination therapy for patients with chronic hepatitis C. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 23:E432- E437. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2008.05320.x
- Feld, JJ, Nanda, S, Huang, Y, Chen, W, Cam, M, Pusek, SN, Schwigler, LM, Theodore, D, Zacks, SL, Liang, TJ, Fried, MW. Hepatic gene expression during treatment with peginterferon and ribavirin: Identifying molecule pathways for treatment response. Hepatol. 2007, 46(5): 1548-1563. doi: 10.1002/hep.21853
- Thomas E, Feld JJ, Li QS, Hu ZY, Fried MW, Liang TJ. Ribavirin potentiates interferon action by augmenting interferon stimulated gene induction in hepatitis C virus cell culture models. Hepatology 2011, 53:32-41. doi: 10.1002/hep.23985
- Shu QN, Nair V. Inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase (IMPDH) as a target in drug discovery. Med. Res. Rev. 2008, 28:219-232. doi: 10.1002/chin.200823265
- Streeter, DG, Witkowski, JT, Khare, GP, Sidwell, RW, Bauer, RJ, Robins, RK, Simon, LN. Mechanisms of action of 1-β-D-ribofuranosyl-1,2,4-triazole-3-carboxamide (virazole) a new broad spectrum antiviral agent. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 1973, 70:1174-1178. PMID: 4197928
- Kentsis, A, Topisirovic, I, Culjkovic, B, Shao, L, Borden, KLB. Ribavirin suppresses eIF4E-mediated oncogenic transformation by physical mimicry of the guanosine mRNA cap. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2004, 101:18105-18110. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0406927102
- Graci, JD, Cameron, CE. Mechanisms of action of ribavirin against distinct viruses. Rev. Med. Virol. 2006, 16: 37-48. doi: 10.1002/rmv.483
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Jamie Costa, Edmond R Atalla, Katherine Reynolds, Taylor H. Derby, Shannon Shaughnessy, Alexander Berchansky