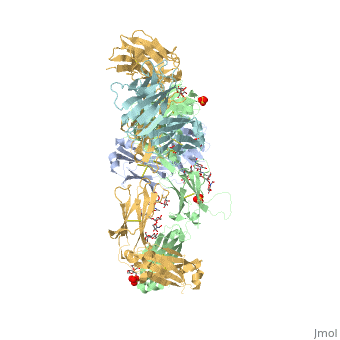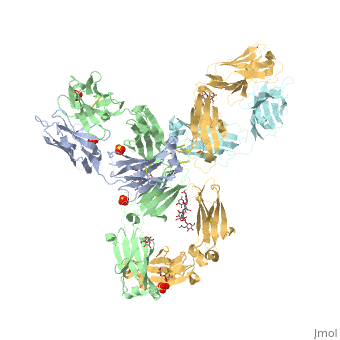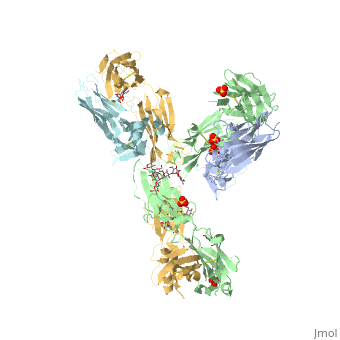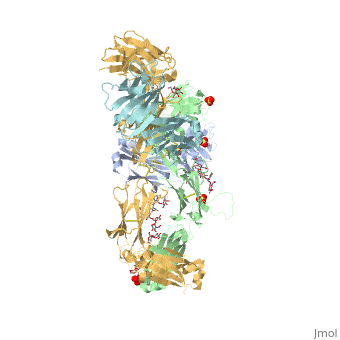We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Keytruda
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
(New page: ==Pembrolizumab antibody against PD-1 receptor== <StructureSection load='5dk3' size='350' side='right' caption='Full-Length Crystal Structure of Pembrolizumab (PDB code 5dk3)'> == Stru...) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | ==Pembrolizumab | + | ==Pembrolizumab/Keytruda== |
<StructureSection load='5dk3' size='350' side='right' caption='Full-Length Crystal Structure of Pembrolizumab (PDB code [[5dk3]])'> | <StructureSection load='5dk3' size='350' side='right' caption='Full-Length Crystal Structure of Pembrolizumab (PDB code [[5dk3]])'> | ||
| + | Click above on '''edit this page''' to modify. Be careful with the < and > signs. | ||
| + | You may include any references to papers as in: the use of JSmol in Proteopedia <ref>DOI 10.1002/ijch.201300024</ref> or to the article describing Jmol <ref>PMID:21638687</ref> to the rescue. | ||
| + | |||
== Structure and Function == | == Structure and Function == | ||
| - | Pembrolizumab, | + | Pembrolizumab, or Keytruda, is an immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4)-kappa humanized monoclonal antibody against the programmed cell death-1 (PD-1) receptor. It contains an Fv fragment (PemFv) that is the variable region of the molecule where binding orccurs, as well as a Fab fragment (PemFab) that constitutes the entire molecule. Pembrolizumab is a very compact molecule with an asymmetrical Y-shape. The short compact hinge region inflicts constraints on the molecule that creates the abnormal crystallizable heavy chain/tail region (Fc domain) compared to other immunoglobulin G (IgG) proteins. The heavy chain is <scene name='74/745945/Glycosylation/1'>glycosylated</scene> at both CH<sub>2</sub> domains on each chain and one of them is distinctively rotated 120° compared to other similar structures, making the glycan chain more solvent accessible. IgG4s have a unique function where they form dynamic bispecific antibodies by exchanging half-molecules (one heavy chain/light chain pair) among themselves, called Fab-arm exchange. This makes the molecule particularly unstable and unpredictable as a treatment, but is conquered by introducing the serine-to-proline mutation at <scene name='74/745945/Pro228/1'>amino acid 228</scene>, which prevents Fab-arm exchange and stabilizes the molecule <ref name="log">DOI:10.1080/17425255.2016.1216976</ref>. |
== Mechanism == | == Mechanism == | ||
| Line 15: | Line 18: | ||
T-cells are a major component of the immune response in the human body. They have the ability to recognize cancer-related antigens as non-self and eliminate those cells <ref>doi 10.2147/DDDT.S78036</ref>. PD-L1 and PD-L2 are ligands expressed by some tumors and inhibit T-cell function when bound to PD-1, which is located on the surface of antigen-specific T-cells <ref>doi 10.1007/s40265-016-0543-x</ref>. When PD-L1 is ligated to PD-1 an adaptive immune response occurs, and this allows cancer cells to bypass immune surveillance and grow uncontrollably. Pembrolizumab is an FDA-approved treatment that works as a PD-1 pathway inhibitor to fight numerous forms of cancer, such as metastatic melanoma and non-small cell lung cancer. As an inhibitor, Pembrolizumab targets the cell death of PD-1 and blocks the immune checkpoint pathway. Pembrolizumab has a very high affinity to PD-1, allowing it to block the interaction between PD-1 with PD-L1 and PD-L2 very efficiently. It antagonizes the interaction between PD-1 and its known ligands, and re-activates anti-tumor immunity <ref name="log" />. The PD-1/PD-L1 interaction inhibits T-lymphocyte proliferation, releases cytokines and cytotoxicity, and exhausts tumor-specific T-cells. The inhibition of this pathway reverses the exhausted t-cell phenotype and normalizes the anti-tumor response. One downside of Pembrolizumab is that it may cause inflammatory side effects <ref name="horita" />. | T-cells are a major component of the immune response in the human body. They have the ability to recognize cancer-related antigens as non-self and eliminate those cells <ref>doi 10.2147/DDDT.S78036</ref>. PD-L1 and PD-L2 are ligands expressed by some tumors and inhibit T-cell function when bound to PD-1, which is located on the surface of antigen-specific T-cells <ref>doi 10.1007/s40265-016-0543-x</ref>. When PD-L1 is ligated to PD-1 an adaptive immune response occurs, and this allows cancer cells to bypass immune surveillance and grow uncontrollably. Pembrolizumab is an FDA-approved treatment that works as a PD-1 pathway inhibitor to fight numerous forms of cancer, such as metastatic melanoma and non-small cell lung cancer. As an inhibitor, Pembrolizumab targets the cell death of PD-1 and blocks the immune checkpoint pathway. Pembrolizumab has a very high affinity to PD-1, allowing it to block the interaction between PD-1 with PD-L1 and PD-L2 very efficiently. It antagonizes the interaction between PD-1 and its known ligands, and re-activates anti-tumor immunity <ref name="log" />. The PD-1/PD-L1 interaction inhibits T-lymphocyte proliferation, releases cytokines and cytotoxicity, and exhausts tumor-specific T-cells. The inhibition of this pathway reverses the exhausted t-cell phenotype and normalizes the anti-tumor response. One downside of Pembrolizumab is that it may cause inflammatory side effects <ref name="horita" />. | ||
| + | |||
| + | This is a sample scene created with SAT to <scene name="/12/3456/Sample/1">color</scene> by Group, and another to make <scene name="/12/3456/Sample/2">a transparent representation</scene> of the protein. | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
Revision as of 23:20, 5 December 2016
Pembrolizumab/Keytruda
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Hanson, R. M., Prilusky, J., Renjian, Z., Nakane, T. and Sussman, J. L. (2013), JSmol and the Next-Generation Web-Based Representation of 3D Molecular Structure as Applied to Proteopedia. Isr. J. Chem., 53:207-216. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijch.201300024
- ↑ Herraez A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2006 Jul;34(4):255-61. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644. PMID:21638687 doi:10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Longoria TC, Tewari KS. Evaluation of the pharmacokinetics and metabolism of pembrolizumab in the treatment of melanoma. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2016 Oct;12(10):1247-53. doi:, 10.1080/17425255.2016.1216976. Epub 2016 Aug 16. PMID:27485741 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/17425255.2016.1216976
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 Horita S, Nomura Y, Sato Y, Shimamura T, Iwata S, Nomura N. High-resolution crystal structure of the therapeutic antibody pembrolizumab bound to the human PD-1. Sci Rep. 2016 Oct 13;6:35297. doi: 10.1038/srep35297. PMID:27734966 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/srep35297
- ↑ Rajakulendran T, Adam DN. Spotlight on pembrolizumab in the treatment of advanced melanoma. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015 Jun 4;9:2883-6. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S78036. eCollection, 2015. PMID:26082618 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S78036
- ↑ Deeks ED. Pembrolizumab: A Review in Advanced Melanoma. Drugs. 2016 Mar;76(3):375-86. doi: 10.1007/s40265-016-0543-x. PMID:26846323 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s40265-016-0543-x