Ribavirin
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
== Protein Interaction == | == Protein Interaction == | ||
| - | === Ribavirin with 3SFU=== | + | ===Ribavirin with 3SFU=== |
Ribavirin interacts with 3SFU by attaching the binding pocket, which is comprised of tyrosine at position 344 and aspartic acid at positions 250, 346, and 347. | Ribavirin interacts with 3SFU by attaching the binding pocket, which is comprised of tyrosine at position 344 and aspartic acid at positions 250, 346, and 347. | ||
=== Ribavirin with 4PB1=== | === Ribavirin with 4PB1=== | ||
Revision as of 02:23, 6 December 2016
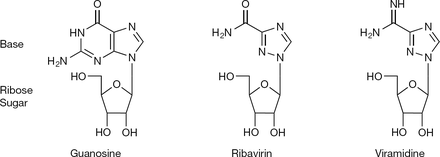
1-β-D-ribofuranosyl-1H-1,2,4-triazole-3-carboxamide [1]
| |||||||||||
References
- Gish, R. G. Treating HCV with ribavirin analogue and ribavirin-like molecules. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy. 2005, November 17;1-6. doi:10.1093/jac/dki405
- Thomas, E., Ghany, M., Liang, J., The application and mechanism of action of ribavirin in therapy of hepatitis C. Antiviral Chemistry & Chemotherapy 23:1-12 (2012)doi: 10.3851/IMP2125
- Chung, R.T., Gale, M.J., Polyak, S.J., Lemon, S.M., Liang, T.J., & Hoofnagle, J.H. Mechanisms of action of interferon and ribavirin in chronic hepatitis C: Summary of a workshop. Hepatology. 2008;47 (1), 306-320. doi: 10.1002/hep.22070
- Paeshuyse, J, Dallmeier, K, Neyts, J. Ribavirin for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C virus infection: a review of the proposed mechanisms of action. Current Opinion in Virology. 2011;1(6) 590-598. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2011.10.030
- National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute. Pneumonia. 2016, September 26; Retrieved from https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/health-topics/topics/pnu
- Foster, G. Pegylated interferons for the treatment of chronic Hepatitis C. Drugs. 2010;70(2):147-165. doi:10.2165/11531990-000000000-00000
- Hofmann WP, Herrmann E, Sarrazin C, Zeuzem S. Ribavirin mode of action in chronic hepatitis C: from clinical use back to molecular mechanisms. Liver Int. 2008, 28:1332-1343. doi: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2008.01896.x
- Fujimoto T, Tomimatsu M, Iga D, Endo H, Otsuka K. Changes in the Th1/Th2 ratio during a 24-week course of an interferon alpha-2b plus ribavirin combination therapy for patients with chronic hepatitis C. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 23:E432- E437. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2008.05320.x
- Feld, JJ, Nanda, S, Huang, Y, Chen, W, Cam, M, Pusek, SN, Schwigler, LM, Theodore, D, Zacks, SL, Liang, TJ, Fried, MW. Hepatic gene expression during treatment with peginterferon and ribavirin: Identifying molecule pathways for treatment response. Hepatol. 2007, 46(5): 1548-1563. doi: 10.1002/hep.21853
- Thomas E, Feld JJ, Li QS, Hu ZY, Fried MW, Liang TJ. Ribavirin potentiates interferon action by augmenting interferon stimulated gene induction in hepatitis C virus cell culture models. Hepatology 2011, 53:32-41. doi: 10.1002/hep.23985
- Shu QN, Nair V. Inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase (IMPDH) as a target in drug discovery. Med. Res. Rev. 2008, 28:219-232. doi: 10.1002/chin.200823265
- Streeter, DG, Witkowski, JT, Khare, GP, Sidwell, RW, Bauer, RJ, Robins, RK, Simon, LN. Mechanisms of action of 1-β-D-ribofuranosyl-1,2,4-triazole-3-carboxamide (virazole) a new broad spectrum antiviral agent. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 1973, 70:1174-1178. PMID: 4197928
- Kentsis, A, Topisirovic, I, Culjkovic, B, Shao, L, Borden, KLB. Ribavirin suppresses eIF4E-mediated oncogenic transformation by physical mimicry of the guanosine mRNA cap. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2004, 101:18105-18110. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0406927102
- Graci, JD, Cameron, CE. Mechanisms of action of ribavirin against distinct viruses. Rev. Med. Virol. 2006, 16: 37-48. doi: 10.1002/rmv.483
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Jamie Costa, Edmond R Atalla, Katherine Reynolds, Taylor H. Derby, Shannon Shaughnessy, Alexander Berchansky